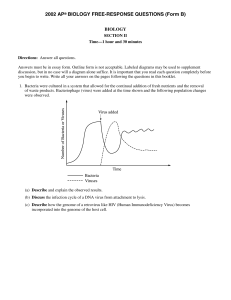
2002 AP Biology Free-Response Questions Form B
... Answers must be in essay form. Outline form is not acceptable. Labeled diagrams may be used to supplement discussion, but in no case will a diagram alone suffice. It is important that you read each question completely before you begin to write. Write all your answers on the pages following the quest ...
... Answers must be in essay form. Outline form is not acceptable. Labeled diagrams may be used to supplement discussion, but in no case will a diagram alone suffice. It is important that you read each question completely before you begin to write. Write all your answers on the pages following the quest ...
Microbial Genetics - University of Montana
... – Bacterial chromosomal DNA packaged into phage heads – After lysis, phage particles inject this DNA into new host – Homologous recombination: donor DNA incorporated into recipient genome • DNA replacement ...
... – Bacterial chromosomal DNA packaged into phage heads – After lysis, phage particles inject this DNA into new host – Homologous recombination: donor DNA incorporated into recipient genome • DNA replacement ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... Chemotactic bacteria are known to collectively migrate towards sources of attractants. In confined convectionless geometries, concentration “waves” of swimming Escherichia coli can form and propagate through a self-organized process involving hundreds of thousands of these microorganisms. These waves ...
... Chemotactic bacteria are known to collectively migrate towards sources of attractants. In confined convectionless geometries, concentration “waves” of swimming Escherichia coli can form and propagate through a self-organized process involving hundreds of thousands of these microorganisms. These waves ...
STATION 1: Nucleic acids
... transductants were selected. Which of the following best describes the predicted genotypes of these transductants? (A) Mostly a− b+ c− (B) Mostly a− b+ c+ (C) Mostly a+ b+ c+ (D) Mostly a+ b+ c− (E) a+ b+ c+ and a− b+ c− in equal frequencies 8) Explain your reasoning for your answer to question 7. 9 ...
... transductants were selected. Which of the following best describes the predicted genotypes of these transductants? (A) Mostly a− b+ c− (B) Mostly a− b+ c+ (C) Mostly a+ b+ c+ (D) Mostly a+ b+ c− (E) a+ b+ c+ and a− b+ c− in equal frequencies 8) Explain your reasoning for your answer to question 7. 9 ...
Chapters 1, 2, and 3
... A nucleotide contains phosphate, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases in DNA are adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. In RNA, uracil replaces thymine. Polynucleotide Structure DNA is a double helix—if unwound its structure resembles a stepladder. Phosphate and the pentose s ...
... A nucleotide contains phosphate, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases in DNA are adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. In RNA, uracil replaces thymine. Polynucleotide Structure DNA is a double helix—if unwound its structure resembles a stepladder. Phosphate and the pentose s ...
Test Review PowerPoint
... 5. How does the sun enhance or diminish the moon’s gravitational pull? The sun enhances the moon’s gravitational pull when it is in a line with the earth and moon. The sun diminishes the moon’s gravitational pull when it makes a right angle with moon and ...
... 5. How does the sun enhance or diminish the moon’s gravitational pull? The sun enhances the moon’s gravitational pull when it is in a line with the earth and moon. The sun diminishes the moon’s gravitational pull when it makes a right angle with moon and ...
Document
... – These contain 12 codons for glutamic acid – Glutamic acid can be coded by either GAA or GAG • They both mean the same thing • All other things being equal, there’s no reason why to choose either over the other ...
... – These contain 12 codons for glutamic acid – Glutamic acid can be coded by either GAA or GAG • They both mean the same thing • All other things being equal, there’s no reason why to choose either over the other ...
ch2
... Most proteins probably go through several intermediate stages before achieving its active conformation. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in cells. ...
... Most proteins probably go through several intermediate stages before achieving its active conformation. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in cells. ...
Chapter 17 Presentation Transcription Translation and Gene
... Wobble enables tRNA to bind differently in one of its base pairs. This is why codons for some aa’s differ in their 3rd base. ...
... Wobble enables tRNA to bind differently in one of its base pairs. This is why codons for some aa’s differ in their 3rd base. ...
ExamView - Final Exam.tst
... D. Ser—Tyr—Arg—Gly 6. DNA is copied during a process called A. replication. B. translation. C. transformation. D. transcription. 7. Unlike DNA, RNA contains A. uracil. B. adenine. C. thymine. D. phosphate groups. 8. What kind of cell (or cells) are used to make animal clones? A. egg cell and sperm c ...
... D. Ser—Tyr—Arg—Gly 6. DNA is copied during a process called A. replication. B. translation. C. transformation. D. transcription. 7. Unlike DNA, RNA contains A. uracil. B. adenine. C. thymine. D. phosphate groups. 8. What kind of cell (or cells) are used to make animal clones? A. egg cell and sperm c ...
Q1. Lysozyme is an enzyme consisting of a single polypeptide chain
... Name the type of mutation represented by mutation 1. ...
... Name the type of mutation represented by mutation 1. ...
AP Protein Sythesis
... suggested that genes coded for enzymes each disease (phenotype) is caused by non-functional gene product ...
... suggested that genes coded for enzymes each disease (phenotype) is caused by non-functional gene product ...
Traffic Lights Biological Cpds
... twenty types which differ by the R group. Can identify amino acid structure, given a structural formula and a suitable table showing -R groups. 26. Polymerisation occurs by condensation, to form peptide bonds giving rise to dipeptides and polypeptides. Can complete a diagram showing condensation, gi ...
... twenty types which differ by the R group. Can identify amino acid structure, given a structural formula and a suitable table showing -R groups. 26. Polymerisation occurs by condensation, to form peptide bonds giving rise to dipeptides and polypeptides. Can complete a diagram showing condensation, gi ...
Name: ____________ Pd.: ______ Date: Read Section 2.1 – Atoms
... 3. The nucleus of an atom is made up of the ____protons__________ and _______neutrons_______. 4. Because an atom has equal numbers of positively charged ___protons__________ and negatively charged _______electrons________, it is electrically neutral. 5. ______element________: One particular type of ...
... 3. The nucleus of an atom is made up of the ____protons__________ and _______neutrons_______. 4. Because an atom has equal numbers of positively charged ___protons__________ and negatively charged _______electrons________, it is electrically neutral. 5. ______element________: One particular type of ...
Restriction Digestion and Analysis of Lambda DNA
... carefully adjusted so they are randomly and infrequently incorporated into the growing DNA strand. Once a dideoxynucleotide is incorporated into a single strand, DNA synthesis is terminated since the modified nucleotide does not have a free 3’ hydroxyl group on the sugar which is the site of the add ...
... carefully adjusted so they are randomly and infrequently incorporated into the growing DNA strand. Once a dideoxynucleotide is incorporated into a single strand, DNA synthesis is terminated since the modified nucleotide does not have a free 3’ hydroxyl group on the sugar which is the site of the add ...
Bacterial Transcription Bacterial Transcription Bacterial
... • reduces affinity to non-specific sites. ...
... • reduces affinity to non-specific sites. ...
Rate of evolution
... the uptake and successful expression of foreign DNA or RNA. The foreign allele that is taken up by the cell replaces the cell’s existing allele for a particular characteristic. Many bacteria have cell-surface proteins that recognise DNA from closely related species and transport it into the cell. On ...
... the uptake and successful expression of foreign DNA or RNA. The foreign allele that is taken up by the cell replaces the cell’s existing allele for a particular characteristic. Many bacteria have cell-surface proteins that recognise DNA from closely related species and transport it into the cell. On ...
Mutations booklet MutationsAND Consequences
... Mutations are changes in the DNA. Mutations occur frequently, but these changes may or may not impact the protein that the DNA codes for. Therefore, mutations may have negative consequences, positive consequences, or may be neutral (inconsequential/no effect). In the table below, Use the single st ...
... Mutations are changes in the DNA. Mutations occur frequently, but these changes may or may not impact the protein that the DNA codes for. Therefore, mutations may have negative consequences, positive consequences, or may be neutral (inconsequential/no effect). In the table below, Use the single st ...
Intro to Biology & Biochemistry
... the activation energy but are not used up in the reaction. They are specific (think key & lock). The substrate is what the enzyme acts on. The active site is where the enzyme & substrate come into contact. Coenzymes help enzymes bind to the substrate (vitamins). Inhibitors slow or stop enzyme activi ...
... the activation energy but are not used up in the reaction. They are specific (think key & lock). The substrate is what the enzyme acts on. The active site is where the enzyme & substrate come into contact. Coenzymes help enzymes bind to the substrate (vitamins). Inhibitors slow or stop enzyme activi ...
Transcription - SCIS Teachers
... Environmental changes and regulation of genes Another type of operon control involves activators, proteins that turn operons on by • binding to DNA and • making it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter. ...
... Environmental changes and regulation of genes Another type of operon control involves activators, proteins that turn operons on by • binding to DNA and • making it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter. ...
26 DNA Transcription - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... 2)Ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) are structural and catalytic components of the ribosome, the large RNA-protein assembly where protein is synthesized in all living systems. In the ribosome, amino acids are transfered from tRNAs to a nascent (growing) polypeptide chain, with the amino acid sequence controlled ...
... 2)Ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) are structural and catalytic components of the ribosome, the large RNA-protein assembly where protein is synthesized in all living systems. In the ribosome, amino acids are transfered from tRNAs to a nascent (growing) polypeptide chain, with the amino acid sequence controlled ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.























