Regents Review 2.0 Living Environment PowerPoint Presentation
... can live in very cold water. The fish produces an “antifreeze” protein that prevents ice crystals from forming in its blood. The DNA for this protein has been identified. An enzyme is used to cut and remove this section of flounder DNA that is then spliced into the DNA of a strawberry plant. As a re ...
... can live in very cold water. The fish produces an “antifreeze” protein that prevents ice crystals from forming in its blood. The DNA for this protein has been identified. An enzyme is used to cut and remove this section of flounder DNA that is then spliced into the DNA of a strawberry plant. As a re ...
DNA: Contamination Control - Sacramento County District Attorney
... To minimize the potential for carry-over contamination, the DNA Laboratory is organized so that the area in which amplified DNA is handled is physically isolated from the extraction and set up areas. See DNA laboratory work areas ...
... To minimize the potential for carry-over contamination, the DNA Laboratory is organized so that the area in which amplified DNA is handled is physically isolated from the extraction and set up areas. See DNA laboratory work areas ...
6.1 Mutation
... do some people have lighter skin and other have darker skin? Why would a cuckoo bird lay her eggs in another birds’ nest? Why did white moths become less common and gray moths become more common near a factory? ...
... do some people have lighter skin and other have darker skin? Why would a cuckoo bird lay her eggs in another birds’ nest? Why did white moths become less common and gray moths become more common near a factory? ...
Slide 1
... Gregor Mendel (a friar and scientist) discovered that units (called genes) were passed from parents to offspring. The combination and interaction of genes from the mother and father decided how the offspring would look and function. -it was later discovered that these units or genes were segments of ...
... Gregor Mendel (a friar and scientist) discovered that units (called genes) were passed from parents to offspring. The combination and interaction of genes from the mother and father decided how the offspring would look and function. -it was later discovered that these units or genes were segments of ...
Living Environment Review NYS (power point)
... can live in very cold water. The fish produces an “antifreeze” protein that prevents ice crystals from forming in its blood. The DNA for this protein has been identified. An enzyme is used to cut and remove this section of flounder DNA that is then spliced into the DNA of a strawberry plant. As a re ...
... can live in very cold water. The fish produces an “antifreeze” protein that prevents ice crystals from forming in its blood. The DNA for this protein has been identified. An enzyme is used to cut and remove this section of flounder DNA that is then spliced into the DNA of a strawberry plant. As a re ...
What is the hierarchy of Life? In order of increasing complexity
... Animal cells have exclusive structures like centrioles, flagella and lysosomes A hypothesis is a possible answer to some question. It is phrased as a statement and should be testable and falsifiable. ...
... Animal cells have exclusive structures like centrioles, flagella and lysosomes A hypothesis is a possible answer to some question. It is phrased as a statement and should be testable and falsifiable. ...
Final Review Guide
... 5) Create a chart comparing the two major phases of photosynthesis: the light reactions and the Calvin cycle (light independent reactions). In your chart include: the location (be specific!), the main function, and the inputs/outputs of each. 6) Distinguish between C3, C4 and CAM plants with respect ...
... 5) Create a chart comparing the two major phases of photosynthesis: the light reactions and the Calvin cycle (light independent reactions). In your chart include: the location (be specific!), the main function, and the inputs/outputs of each. 6) Distinguish between C3, C4 and CAM plants with respect ...
The Tools of Molecular Biology How do scientists make changes to
... The Tools of Molecular Biology How do scientists make changes to DNA? ...
... The Tools of Molecular Biology How do scientists make changes to DNA? ...
video slide - Saginaw Valley State University
... A A G Anticodon (a) Two-dimensional structure. The four base-paired regions and three loops are characteristic of all tRNAs, as is the base sequence of the amino acid attachment site at the 3 end. The anticodon triplet is unique to each tRNA type. (The asterisks mark bases that have been chemically ...
... A A G Anticodon (a) Two-dimensional structure. The four base-paired regions and three loops are characteristic of all tRNAs, as is the base sequence of the amino acid attachment site at the 3 end. The anticodon triplet is unique to each tRNA type. (The asterisks mark bases that have been chemically ...
sample exam 2010
... c. serve as starting points for DNA strand elongation by DNA polymerase III in prokaryotes d. prevent new-separated strands of DNA from rejoining e. serve as a binding site for DNA ligase ...
... c. serve as starting points for DNA strand elongation by DNA polymerase III in prokaryotes d. prevent new-separated strands of DNA from rejoining e. serve as a binding site for DNA ligase ...
3 - Copley-Fairlawn City Schools
... Rationale: The definition of Lewis acids is commonly taught in a first-year high school chemistry course and is therefore considered prior knowledge. Note: The formation of complex ions and the qualitative impact on solubility are both part of the AP Chemistry course. ...
... Rationale: The definition of Lewis acids is commonly taught in a first-year high school chemistry course and is therefore considered prior knowledge. Note: The formation of complex ions and the qualitative impact on solubility are both part of the AP Chemistry course. ...
RNA Structure, Function, and Synthesis RNA - Rose
... RNA differs from DNA in both structural and functional respects. RNA has two major structural differences: each of the ribose rings contains a 2´-hydroxyl, and RNA uses uracil in place of thymine. RNA molecules are capable of base pairing, but generally will not form large regions of stable RNA-RNA ...
... RNA differs from DNA in both structural and functional respects. RNA has two major structural differences: each of the ribose rings contains a 2´-hydroxyl, and RNA uses uracil in place of thymine. RNA molecules are capable of base pairing, but generally will not form large regions of stable RNA-RNA ...
2.5.2 Heredity and Gene Expression
... which can then be used to distinguish that DNA from other DNA DNA profiling is also called genetic or DNA fingerprinting. Stages involved in DNA profiling 1. DNA isolation Cells are broken down to release DNA 2. DNA is cut into fragments The DNA is cut into fragments using special restriction enzyme ...
... which can then be used to distinguish that DNA from other DNA DNA profiling is also called genetic or DNA fingerprinting. Stages involved in DNA profiling 1. DNA isolation Cells are broken down to release DNA 2. DNA is cut into fragments The DNA is cut into fragments using special restriction enzyme ...
Annex A: Highlights of the “Biotechnology Revolution”: 1953–present 1953 Nature
... In a letter to Science, Stanford biochemist Paul Berg and others called for the National Institutes of Health to enact guidelines for DNA splicing. Their letter recommended that scientists stop doing certain types of recombinant DNA experiments until questions of safety could be addressed. This lett ...
... In a letter to Science, Stanford biochemist Paul Berg and others called for the National Institutes of Health to enact guidelines for DNA splicing. Their letter recommended that scientists stop doing certain types of recombinant DNA experiments until questions of safety could be addressed. This lett ...
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
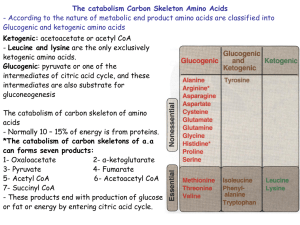
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
Document
... Which equation best describes the stoichiometry of the reaction? (a) A2 + 2 B A2B2 (b) 10 A + 5 B2 5 A2B2 (c) 2 A + B2 A2B2 (d) 5 A + 5 B2 5 A2B2 ...
... Which equation best describes the stoichiometry of the reaction? (a) A2 + 2 B A2B2 (b) 10 A + 5 B2 5 A2B2 (c) 2 A + B2 A2B2 (d) 5 A + 5 B2 5 A2B2 ...
Chapter 7: DNA and Gel Electrophoresis Extended Objective Checklist
... At the conclusion of this unit, the student should be able to do: DNA Background _____1. Write the full name of the DNA molecule _____ 2. Describe the structure of a DNA molecule as proposed by Watson Crick in 1953. _____3. List four nitrogen bases found in a DNA molecule. _____ 4. Explain complemen ...
... At the conclusion of this unit, the student should be able to do: DNA Background _____1. Write the full name of the DNA molecule _____ 2. Describe the structure of a DNA molecule as proposed by Watson Crick in 1953. _____3. List four nitrogen bases found in a DNA molecule. _____ 4. Explain complemen ...
Document
... Finding DNA motifs by positional conservation of palindromes • The approach targets sites for dimeric proteins and is particularly suited for helix-turn-helix proteins of Bacteria and Archea • HTH proteins bind as dimers usually with variable sequence spacing ...
... Finding DNA motifs by positional conservation of palindromes • The approach targets sites for dimeric proteins and is particularly suited for helix-turn-helix proteins of Bacteria and Archea • HTH proteins bind as dimers usually with variable sequence spacing ...
2.3 Carbon Compounds
... group, an R group, and a carboxyl group. An amino group has the formula –NH2, a carboxyl group is –COOH, and the R group varies from one amino acid to another. Two amino acids are joined in a chemical reaction that links them by a peptide bond. Follow the directions. Then answer the questions. ...
... group, an R group, and a carboxyl group. An amino group has the formula –NH2, a carboxyl group is –COOH, and the R group varies from one amino acid to another. Two amino acids are joined in a chemical reaction that links them by a peptide bond. Follow the directions. Then answer the questions. ...
DNA replication
... Chromosomes also must be attached to the mitotic spindle for mitosis to complete (failure to attach can result in nondisjunction). ...
... Chromosomes also must be attached to the mitotic spindle for mitosis to complete (failure to attach can result in nondisjunction). ...
File
... group of compounds called purines (double ring of carbon) * [T] & [C] – belong to a group of compounds called pyrimidines (single ring of carbon) ...
... group of compounds called purines (double ring of carbon) * [T] & [C] – belong to a group of compounds called pyrimidines (single ring of carbon) ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.