A primer on the structure and function of genes
... The deterministic view of the gene was not only popular, but productive; without it we could not have identified the genetic basis of many diseases. In fact, one of the motivating factors behind the huge effort and expense of the human genome project (HGP) was based on this view of the gene. It was ...
... The deterministic view of the gene was not only popular, but productive; without it we could not have identified the genetic basis of many diseases. In fact, one of the motivating factors behind the huge effort and expense of the human genome project (HGP) was based on this view of the gene. It was ...
Mechanisms of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) in bacteria DNA can
... this, commonly we use E.coli as host organism. The strain of E.coli has been cultured in the laboratory and it has been selected for characteristics that make it especially useful in the molecular biology laboratory. Plasmid is the other important element in the transformation system. Plasmid encode ...
... this, commonly we use E.coli as host organism. The strain of E.coli has been cultured in the laboratory and it has been selected for characteristics that make it especially useful in the molecular biology laboratory. Plasmid is the other important element in the transformation system. Plasmid encode ...
DNA Sequencing
... Polymerase Chain Reaction Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) • Produces many sequence copies without host cloning • Amplifies known DNA sequences for analysis • Only copies sequence of interest ...
... Polymerase Chain Reaction Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) • Produces many sequence copies without host cloning • Amplifies known DNA sequences for analysis • Only copies sequence of interest ...
DNA ------------> RNA Transcription RNA processing
... - Catalyzes the attachment of amino acids to tRNA by using ATP - 20 types of amino acyl-tRNA synthetase exits (one for each a.a) 1) Binding of Amino acid & & ATP ...
... - Catalyzes the attachment of amino acids to tRNA by using ATP - 20 types of amino acyl-tRNA synthetase exits (one for each a.a) 1) Binding of Amino acid & & ATP ...
Life on Earth
... • GCC means yet another amino acid • Some triplet sequences also mean “start” a structure and some mean “stop” the structure • So … DNA is literally a set of instructions on how to build a living creature, one protein at a time ...
... • GCC means yet another amino acid • Some triplet sequences also mean “start” a structure and some mean “stop” the structure • So … DNA is literally a set of instructions on how to build a living creature, one protein at a time ...
chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules
... ° A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ° The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ° Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. ...
... ° A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ° The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ° Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. ...
BL414 Genetics Spring 2006 page Test 2
... Primase, primosome or polymerase : creates RNA primers DNA polymerase : elongation of the DNA strand 3’-to-5’-exonuclease: corrects mismatches bases PolI or RPA: removes RNA primers 8) (10pts) The molecules below are used in an in vitro DNA sequencing reaction, one is dideoxyadenosine and one is d ...
... Primase, primosome or polymerase : creates RNA primers DNA polymerase : elongation of the DNA strand 3’-to-5’-exonuclease: corrects mismatches bases PolI or RPA: removes RNA primers 8) (10pts) The molecules below are used in an in vitro DNA sequencing reaction, one is dideoxyadenosine and one is d ...
Ch27 PowerPoint LN
... • plasmids are present • thermal denaturation resistance: provided by the presence of a high salt concentration and DNA binding proteins ...
... • plasmids are present • thermal denaturation resistance: provided by the presence of a high salt concentration and DNA binding proteins ...
Quiz 15
... D) hydrogen bonds E) peptide bonds 8. A hydrophilic R-group of an amino acid in hemoglobin would NOT be attracted to: A) the water molecules surrounding hemoglobin. B) a hydrophobic amino acid R group of hemoglobin. C) a charged amino acid R group of hemoglobin. D) a polar amino acid R group of hemo ...
... D) hydrogen bonds E) peptide bonds 8. A hydrophilic R-group of an amino acid in hemoglobin would NOT be attracted to: A) the water molecules surrounding hemoglobin. B) a hydrophobic amino acid R group of hemoglobin. C) a charged amino acid R group of hemoglobin. D) a polar amino acid R group of hemo ...
Cell Line Characterization - Sigma
... information that can be utilized for the authentication of mammalian cell lines2. The Multi-Locus Probe (MLP) 33.15 is derived from specific hypervariable mini-satellite regions in the human genome and will hybridize to repetitive DNA sequences distributed throughout the genomes of a diverse range o ...
... information that can be utilized for the authentication of mammalian cell lines2. The Multi-Locus Probe (MLP) 33.15 is derived from specific hypervariable mini-satellite regions in the human genome and will hybridize to repetitive DNA sequences distributed throughout the genomes of a diverse range o ...
central dogma of molecular biology - Rose
... The term “central dogma of molecular biology” is patterned after religious terminology. However, it refers to a process that is subject to the changes in understanding that are associated with any scientific research. The most simplified form of the central dogma is that the flow of information is f ...
... The term “central dogma of molecular biology” is patterned after religious terminology. However, it refers to a process that is subject to the changes in understanding that are associated with any scientific research. The most simplified form of the central dogma is that the flow of information is f ...
MOLECULES OF LIFE
... Large polymer made of repeating monomers called amino acids A. Functions of Proteins Enzymes: catalyze cell’s reactions ...
... Large polymer made of repeating monomers called amino acids A. Functions of Proteins Enzymes: catalyze cell’s reactions ...
Exam I will be on lectures 1 to 6 (Introduction to )
... d. the process by which cells become different from one another. e. the fate of a plant cell. The three tissue systems of vascular plants are: a. the dermal, vascular, and ground tissue systems. b. protoderm, procambium, and ground ...
... d. the process by which cells become different from one another. e. the fate of a plant cell. The three tissue systems of vascular plants are: a. the dermal, vascular, and ground tissue systems. b. protoderm, procambium, and ground ...
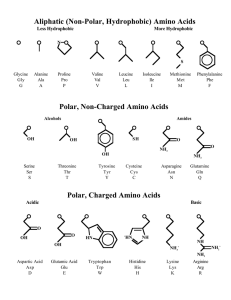
Amino Acids - Sehr Gut Web
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
Cut-and-paste DNA: fixing mutations with `genome editing`
... disease. But what if we could actually go one further and remove the mutation that causes HD from the DNA of patients? The idea seemed completely impossible until recently. Cells have mechanisms that repair DNA if it’s altered, and every cell in the body has the same DNA. So the idea is much more ra ...
... disease. But what if we could actually go one further and remove the mutation that causes HD from the DNA of patients? The idea seemed completely impossible until recently. Cells have mechanisms that repair DNA if it’s altered, and every cell in the body has the same DNA. So the idea is much more ra ...
9.3 DNA Fingerprinting
... – The probability that two people share identical numbers of repeats in several locations is ...
... – The probability that two people share identical numbers of repeats in several locations is ...
Fatty Acid Spiral
... • Two carbons at a time are cleaved from a fatty acyl-CoA as acetyl-CoA. • This cleavage continues until the entire fatty acid has been converted into acetyl-CoA. ...
... • Two carbons at a time are cleaved from a fatty acyl-CoA as acetyl-CoA. • This cleavage continues until the entire fatty acid has been converted into acetyl-CoA. ...
Golden Rice, or Frankenfood?
... consisting of base sequences from 2 or more organisms of the same or different species Cloning vector – a plasmid that has accepted foreign DNA and can be slipped into host DNA ...
... consisting of base sequences from 2 or more organisms of the same or different species Cloning vector – a plasmid that has accepted foreign DNA and can be slipped into host DNA ...
Document
... • Two carbons at a time are cleaved from a fatty acyl-CoA as acetyl-CoA. • This cleavage continues until the entire fatty acid has been converted into acetyl-CoA. ...
... • Two carbons at a time are cleaved from a fatty acyl-CoA as acetyl-CoA. • This cleavage continues until the entire fatty acid has been converted into acetyl-CoA. ...
Lecture 7
... • An enzyme that removes Uracil from DNA • Resulting abasic site is filled in by polymerase • Uracil in DNA comes mainly from deamination of cytosine • That may be why DNA uses thymine instead of uracil • If the uracil isn’t removed, it will pair with A, causing C/G --> T/A transition. ...
... • An enzyme that removes Uracil from DNA • Resulting abasic site is filled in by polymerase • Uracil in DNA comes mainly from deamination of cytosine • That may be why DNA uses thymine instead of uracil • If the uracil isn’t removed, it will pair with A, causing C/G --> T/A transition. ...
Name: Ch 6 Take Home Quiz Due: 3/22/13 Multiple
... A) a peptide. B) a gene. C) a ribosome. D) an RNA. 8) Which of the following statements is NOT true of non-essential amino acids? A) They are synthesized by the body. B) They are not necessary for protein synthesis. C) There are 11 amino acids that belong to this group. D) They can be broken down to ...
... A) a peptide. B) a gene. C) a ribosome. D) an RNA. 8) Which of the following statements is NOT true of non-essential amino acids? A) They are synthesized by the body. B) They are not necessary for protein synthesis. C) There are 11 amino acids that belong to this group. D) They can be broken down to ...
Lecture 10 Types of mutations Substitutions that occur in protein
... • An enzyme that removes Uracil from DNA • Resulting abasic site is filled in by polymerase • Uracil in DNA comes mainly from deamination of cytosine • That may be why DNA uses thymine instead of uracil • If the uracil isn’t removed, it will pair with A, causing C/G --> T/A transition. ...
... • An enzyme that removes Uracil from DNA • Resulting abasic site is filled in by polymerase • Uracil in DNA comes mainly from deamination of cytosine • That may be why DNA uses thymine instead of uracil • If the uracil isn’t removed, it will pair with A, causing C/G --> T/A transition. ...
DNA Technology Power Point
... 3.Cutting clone vector cut plasmid with same restriction enzyme 4.Ligation: donor gene is spliced into plasmid DNA, DNA ligase glues it (this forms recombinant DNA = plasmid DNA + new piece of DNA) 5.Plasmid returned to bacterium & reproduces using donor gene in it (this is transgenic organism = or ...
... 3.Cutting clone vector cut plasmid with same restriction enzyme 4.Ligation: donor gene is spliced into plasmid DNA, DNA ligase glues it (this forms recombinant DNA = plasmid DNA + new piece of DNA) 5.Plasmid returned to bacterium & reproduces using donor gene in it (this is transgenic organism = or ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.