DNA TEST, PART 2: DNA MESSAGE DECODING You will be given
... FIRST: Put your name, seat number, date, and period at top of page. SECOND: copy the number of your message and the DNA message itself in the spaces so designated. THIRD: decode the message, showing each step completely, just as it happens in your cells; be sure to label each step with the type of m ...
... FIRST: Put your name, seat number, date, and period at top of page. SECOND: copy the number of your message and the DNA message itself in the spaces so designated. THIRD: decode the message, showing each step completely, just as it happens in your cells; be sure to label each step with the type of m ...
Gene Technologies
... violent immune system reaction and died. The study was halted until a safe dose could be established. ...
... violent immune system reaction and died. The study was halted until a safe dose could be established. ...
DETERMINATIVE DEGREE AND NUCLEOTIDE CONTENT OF DNA
... amino acids. For latter the analogous, but passive characteristics “predeterminativity” is also proposed, and it is shown that it correlates with the interaction energy of nitrous bases in corresponding DNA triplets. Purine-pyrimidine content of DNA sequences is considered in terms of the determinat ...
... amino acids. For latter the analogous, but passive characteristics “predeterminativity” is also proposed, and it is shown that it correlates with the interaction energy of nitrous bases in corresponding DNA triplets. Purine-pyrimidine content of DNA sequences is considered in terms of the determinat ...
Chirality in Chemistry
... anniversary of the publication of the structure of DNA by Francis Watson and James Crick – definitely something worth looking into if you are interested in big moments which have changed science), and as this is a spiral just like spiral staircases it is chiral. In human cells we have B-DNA and not ...
... anniversary of the publication of the structure of DNA by Francis Watson and James Crick – definitely something worth looking into if you are interested in big moments which have changed science), and as this is a spiral just like spiral staircases it is chiral. In human cells we have B-DNA and not ...
How an Organism`s Genotype Determines Its Phenotype How an
... the usual growth medium, – determined that these strains lacked an enzyme in a metabolic pathway that synthesized arginine, – showed that each mutant was defective in a single gene, and – hypothesized that the function of an individual gene is to dictate the production of a specific enzyme. ...
... the usual growth medium, – determined that these strains lacked an enzyme in a metabolic pathway that synthesized arginine, – showed that each mutant was defective in a single gene, and – hypothesized that the function of an individual gene is to dictate the production of a specific enzyme. ...
Buffer Solutions in Ocular Irrigation
... Why does MorTan recommend irrigation with lactated Ringer's? Lactated Ringer's (LR) Irrigation solution (very similar to Hartmann's solution and also called Ringer's lactate) is a buffering solution with a pH similar to that of the eye. Human tears have a pH of 6.5 to 7.6 (and an average of 7.1) whi ...
... Why does MorTan recommend irrigation with lactated Ringer's? Lactated Ringer's (LR) Irrigation solution (very similar to Hartmann's solution and also called Ringer's lactate) is a buffering solution with a pH similar to that of the eye. Human tears have a pH of 6.5 to 7.6 (and an average of 7.1) whi ...
Activity 10
... Note: If creating your own DNA strands for this activity seems too tedious, there are some activities on the web which provide downloadable DNA strands that might be adapted to this activity or allow for more efficient creation of the strands through use of cut and paste functions. Examples include ...
... Note: If creating your own DNA strands for this activity seems too tedious, there are some activities on the web which provide downloadable DNA strands that might be adapted to this activity or allow for more efficient creation of the strands through use of cut and paste functions. Examples include ...
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of
... The two daughter DNA molecules produced by DNA replication during interphase of the cell-division cycle are separately folded to produce two sister chromosomes, or sister chromatids, held together at their centromeres. ...
... The two daughter DNA molecules produced by DNA replication during interphase of the cell-division cycle are separately folded to produce two sister chromosomes, or sister chromatids, held together at their centromeres. ...
lect 8- Transformation
... • After the heat shock step intact plasmid DNA molecules replicate in bacterial host cells • To help the bacterial cells recover from the heat shock cells are briefly incubated with non-selective growth ...
... • After the heat shock step intact plasmid DNA molecules replicate in bacterial host cells • To help the bacterial cells recover from the heat shock cells are briefly incubated with non-selective growth ...
My Genetic Profile Worksheet
... • Each DNA cluster will be strongly attracted to any cDNA made from complimentary mRNA strands. For example: DNA strands with the base sequence TTCAGGCAG will be attracted to any cDNA strands with the sequence AAGTCCGTC. In other words each DNA cluster will be attracted to cDNA that were made using ...
... • Each DNA cluster will be strongly attracted to any cDNA made from complimentary mRNA strands. For example: DNA strands with the base sequence TTCAGGCAG will be attracted to any cDNA strands with the sequence AAGTCCGTC. In other words each DNA cluster will be attracted to cDNA that were made using ...
Acids and bases
... much larger than the size of the molecules themselves. 2. Particles in a gas move in straight line paths and random directions. 3. Particles in a gas collide frequently with the sides of the container and less frequently with each other. All collisions are elastic (no energy is gained or lost as a r ...
... much larger than the size of the molecules themselves. 2. Particles in a gas move in straight line paths and random directions. 3. Particles in a gas collide frequently with the sides of the container and less frequently with each other. All collisions are elastic (no energy is gained or lost as a r ...
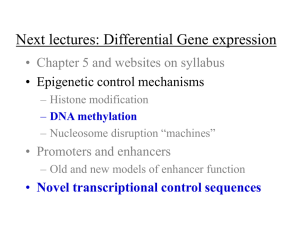
Next lectures: Differential Gene expression
... • Timing and activation: LCR, enhancer • Facilitating factor access: MAR, LCR • Insulation: boundary, LCR • RNA pol II activity: promoter, enhancer • Needs chromatin: LCR, MAR, boundary** ...
... • Timing and activation: LCR, enhancer • Facilitating factor access: MAR, LCR • Insulation: boundary, LCR • RNA pol II activity: promoter, enhancer • Needs chromatin: LCR, MAR, boundary** ...
Molecular Biology BIO 250
... Know what linkage is. How is the behavior of linked genes during meiosis different from genes that Mendel studied? Which one of Mendel’s laws does not apply when two genes are linked? How is genetic distance between two genes located on the same chromosome calculated using linkage? Who discovere ...
... Know what linkage is. How is the behavior of linked genes during meiosis different from genes that Mendel studied? Which one of Mendel’s laws does not apply when two genes are linked? How is genetic distance between two genes located on the same chromosome calculated using linkage? Who discovere ...
•MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
... A template DNA strand is transcribed into a complementary RNA chain by RNA. Ribonucleoside triphosphate (rNTP) are polymerized to form a complementary RNA by RNA polymerase. Polymerization involves a nucleophilic attack by the 3’ oxygen in the growing RNA chain on the a phosphate of the next nucleot ...
... A template DNA strand is transcribed into a complementary RNA chain by RNA. Ribonucleoside triphosphate (rNTP) are polymerized to form a complementary RNA by RNA polymerase. Polymerization involves a nucleophilic attack by the 3’ oxygen in the growing RNA chain on the a phosphate of the next nucleot ...
Chromosomes and Mutations Chromosomes and
... How are genes mutated? • Genes can be mutated when the DNA is mutated or when the chromosomes are mutated • There are two types of DNA (gene) mutations: • Point Mutations: a change in a single base pair • Frameshift Mutations: a single base is added or deleted from DNA ...
... How are genes mutated? • Genes can be mutated when the DNA is mutated or when the chromosomes are mutated • There are two types of DNA (gene) mutations: • Point Mutations: a change in a single base pair • Frameshift Mutations: a single base is added or deleted from DNA ...
Molecular Evolution and Non-extensive Statistics
... RNA density in the ocean is low, this density decreases as the inverse square of the distance between the two codons, and thus α=3, or faster. We can also suppose that the proteins produced may be inactivated by some reason, as damage or digestion, so that we may expect α≥2. In this case the system ...
... RNA density in the ocean is low, this density decreases as the inverse square of the distance between the two codons, and thus α=3, or faster. We can also suppose that the proteins produced may be inactivated by some reason, as damage or digestion, so that we may expect α≥2. In this case the system ...
Stabilization of poly-L-lysine-based cancer
... Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, 2The Center for Future Chemistry, Kyushu University, 3International Research Center for Molecular Systems, Kyushu University ...
... Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, 2The Center for Future Chemistry, Kyushu University, 3International Research Center for Molecular Systems, Kyushu University ...
Purification and Characterization of a DNA Plasmid Part A
... Midiprep resin. Mix by swirling. This allows the DNA to bind to the resin in batch mode. Discard the pellet. 5. Place the column tip (labeled with your initials) into the vacuum manifold. Pour the DNAresin slurry into the column. Apply vacuum to pack the slurry into the column. Once the "flow-throug ...
... Midiprep resin. Mix by swirling. This allows the DNA to bind to the resin in batch mode. Discard the pellet. 5. Place the column tip (labeled with your initials) into the vacuum manifold. Pour the DNAresin slurry into the column. Apply vacuum to pack the slurry into the column. Once the "flow-throug ...
File - Miss Jenkins
... • Pedigree chart – a branching tree diagram that shows traits being passed through a family. • Semi-conservative – one half of the original DNA strand is kept (conserved) in a new strand after DNA replication. The new strand contains half old and half new DNA. ...
... • Pedigree chart – a branching tree diagram that shows traits being passed through a family. • Semi-conservative – one half of the original DNA strand is kept (conserved) in a new strand after DNA replication. The new strand contains half old and half new DNA. ...
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. The chemical mechanisms that cells use to mak ...
... A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. The chemical mechanisms that cells use to mak ...
Decoding the Flu
... headed out to the truck that would carry her and the samples to the airport. “This will hopefully give the lab back home a head start investigating this new strain of flu. I’ll be back in a couple of hours. The team’s condition seems to be getting better so I don’t think you will have much trouble w ...
... headed out to the truck that would carry her and the samples to the airport. “This will hopefully give the lab back home a head start investigating this new strain of flu. I’ll be back in a couple of hours. The team’s condition seems to be getting better so I don’t think you will have much trouble w ...
Decoding the Flu - National Center for Case Study Teaching in
... headed out to the truck that would carry her and the samples to the airport. “This will hopefully give the lab back home a head start investigating this new strain of flu. I’ll be back in a couple of hours. The team’s condition seems to be getting better so I don’t think you will have much trouble w ...
... headed out to the truck that would carry her and the samples to the airport. “This will hopefully give the lab back home a head start investigating this new strain of flu. I’ll be back in a couple of hours. The team’s condition seems to be getting better so I don’t think you will have much trouble w ...
II. Beta oxidation of fatty acid
... _B__57. This DNA form is seen in physiologic conditions where the cell is well hydrated: A. A form B. B form C. Z form D. D form _C__58. Regions of the DNA strand that are easily denatured are rich in this base pair: A. GC B. AT C. AU D. CT _D__59. This is the primary function of nucleic acids: A. s ...
... _B__57. This DNA form is seen in physiologic conditions where the cell is well hydrated: A. A form B. B form C. Z form D. D form _C__58. Regions of the DNA strand that are easily denatured are rich in this base pair: A. GC B. AT C. AU D. CT _D__59. This is the primary function of nucleic acids: A. s ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.