- human genetics
... The process of DNA fingerprinting is based on the fact that a. the most important genes are different among most people. b. no two people, except identical twins, have exactly the same DNA. c. most genes are dominant. d. most people have DNA that contains repeats. What conclusion CANNOT be made h m ...
... The process of DNA fingerprinting is based on the fact that a. the most important genes are different among most people. b. no two people, except identical twins, have exactly the same DNA. c. most genes are dominant. d. most people have DNA that contains repeats. What conclusion CANNOT be made h m ...
Nucleic Acids
... patterns revealed that, even though the base composition of DNA isolated from different organisms varies, DNA molecules themselves are remarkably uniform in thickness. They are long and fairly straight, with an outside diameter of approximately 20 Å, and not more than a dozen atoms thick. Furthermor ...
... patterns revealed that, even though the base composition of DNA isolated from different organisms varies, DNA molecules themselves are remarkably uniform in thickness. They are long and fairly straight, with an outside diameter of approximately 20 Å, and not more than a dozen atoms thick. Furthermor ...
Unit One
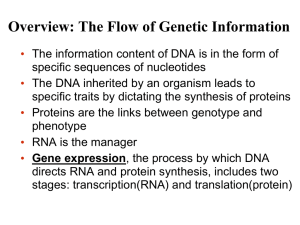
... with hundreds or thousands of genes • Genes encode information for building proteins • DNA is inherited by offspring from their parents • DNA controls the development (Meiosis) and maintenance of organisms (Mitosis) ...
... with hundreds or thousands of genes • Genes encode information for building proteins • DNA is inherited by offspring from their parents • DNA controls the development (Meiosis) and maintenance of organisms (Mitosis) ...
P10
... • Give examples of some exceptions to this rule, and describe how the alteration in the amino acid sequence are generated. – exceptions to this rule can arise, for example, from splice site mutations that lead to missplicing of an exon. The exon may be excluded from the mRNA, generating either an in ...
... • Give examples of some exceptions to this rule, and describe how the alteration in the amino acid sequence are generated. – exceptions to this rule can arise, for example, from splice site mutations that lead to missplicing of an exon. The exon may be excluded from the mRNA, generating either an in ...
Final exam review 4
... 4. Explain the significance of these ratios: 3:1 and 9:3:3:1 5. Know all bold terms page 167 to 169. 6. Know how to do a punnet square and describe the outcomes. Example: What are the probably genotype and phenotype ratios for a homozygous blue eyed parent that mates with a parent that is heterozygo ...
... 4. Explain the significance of these ratios: 3:1 and 9:3:3:1 5. Know all bold terms page 167 to 169. 6. Know how to do a punnet square and describe the outcomes. Example: What are the probably genotype and phenotype ratios for a homozygous blue eyed parent that mates with a parent that is heterozygo ...
Introduction to Proteins
... Proteins play key roles in living systems • Examples of protein functions Alcohol dehydrogenase oxidizes alcohols to aldehydes or ketones ...
... Proteins play key roles in living systems • Examples of protein functions Alcohol dehydrogenase oxidizes alcohols to aldehydes or ketones ...
Document
... The assembly of a messenger RNA strand that normally begins with UAC has been changed so that the newly assembled messenger RNA strand begins with UAG. Which of the following will most likely occur? A The protein will be missing the first amino acid. B The amino acids that make up the protein will a ...
... The assembly of a messenger RNA strand that normally begins with UAC has been changed so that the newly assembled messenger RNA strand begins with UAG. Which of the following will most likely occur? A The protein will be missing the first amino acid. B The amino acids that make up the protein will a ...
A1982NK48200001
... the same as later found in all waters, even in the Sargasso Sea. Finally, the timing of the paper was right as liquid scintillation had just replaced planchette counters, proportional counters, and ion ‘chambers for measuring ‘~Cand nothing better has come along. Today, a number of ecologists have h ...
... the same as later found in all waters, even in the Sargasso Sea. Finally, the timing of the paper was right as liquid scintillation had just replaced planchette counters, proportional counters, and ion ‘chambers for measuring ‘~Cand nothing better has come along. Today, a number of ecologists have h ...
Leukaemia Section t(1;9)(p34;q34) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... recombination. The SFPQ/NONO heterodimer enhances DNA strand break rejoining. SFPQ has homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining activities. SFPQ is associated with the RAD51 protein complex. Role in transcriptional regulation: SFPQ and PTK6 (protein tyrosine kinase 6, also called BRK) ...
... recombination. The SFPQ/NONO heterodimer enhances DNA strand break rejoining. SFPQ has homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining activities. SFPQ is associated with the RAD51 protein complex. Role in transcriptional regulation: SFPQ and PTK6 (protein tyrosine kinase 6, also called BRK) ...
20DNAtech - Mid
... Infiltrating Lymphocytes have the ability to find and slow the growth of tumors ...
... Infiltrating Lymphocytes have the ability to find and slow the growth of tumors ...
PPT 4
... H –C–C–H + Cl2 H–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H If more chlorine is provided, the reaction will produce... H H H H H –C–C–Cl + Cl2 Cl–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H AND SO ON. ...
... H –C–C–H + Cl2 H–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H If more chlorine is provided, the reaction will produce... H H H H H –C–C–Cl + Cl2 Cl–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H AND SO ON. ...
DNA sequence representation by trianders and determinative
... Bulmer, 1987; Luo et al., 1998; Nieselt-Struwe, 1997; Fickett et al., 1992; Buldyrev et al., 1998; Azbel, 1995) and various symmetry investigations (Findley et al., 1982; Hornos and Hornos, 1993; Bashford et al., 1997; Bhry et al., 1998; Forger and Sachse, 1998; Frappat et al., 1998) is an extremely ...
... Bulmer, 1987; Luo et al., 1998; Nieselt-Struwe, 1997; Fickett et al., 1992; Buldyrev et al., 1998; Azbel, 1995) and various symmetry investigations (Findley et al., 1982; Hornos and Hornos, 1993; Bashford et al., 1997; Bhry et al., 1998; Forger and Sachse, 1998; Frappat et al., 1998) is an extremely ...
Transfer RNA and Protein Building Name_________________
... important molecules used for: building cell parts, as transport molecules, as enzymes and hormones and numerous other functions. Proteins are built of long chains of ______________________________. Each protein must be built with the correct sequence of amino acids. How does mRNA direct the ribosome ...
... important molecules used for: building cell parts, as transport molecules, as enzymes and hormones and numerous other functions. Proteins are built of long chains of ______________________________. Each protein must be built with the correct sequence of amino acids. How does mRNA direct the ribosome ...
Regulation of Transcription
... – Negative: “turns off” transcription via a repressor e.g. [tryptophan] ...
... – Negative: “turns off” transcription via a repressor e.g. [tryptophan] ...
Mutation - Liberty Union High School District
... They account for all the variation we see in human hair color, skin color, height, shape, and behavior. ...
... They account for all the variation we see in human hair color, skin color, height, shape, and behavior. ...
BIO 402/502 Advanced Cell & Developmental Biology
... other studies of purified protein. • The proteins are produced as fusion proteins of the cDNA gene coding sequence ligated to a protein expression marker or reporter protein e.g. beta-galactosidase • They can also be used as a major tool in cell biology to study the expression of proteins in cells f ...
... other studies of purified protein. • The proteins are produced as fusion proteins of the cDNA gene coding sequence ligated to a protein expression marker or reporter protein e.g. beta-galactosidase • They can also be used as a major tool in cell biology to study the expression of proteins in cells f ...
Lab Practicum #2
... 5. What happens in conjugation? Know possible conjugation results for the following matings: F+ x F-, Hfr x F-. Given locations (F-plasmid versus chromosome) and types of antibiotic resistance genes (AmpR, StrR, NalR) for different E. coli strains, be able to predict which will grow on different ant ...
... 5. What happens in conjugation? Know possible conjugation results for the following matings: F+ x F-, Hfr x F-. Given locations (F-plasmid versus chromosome) and types of antibiotic resistance genes (AmpR, StrR, NalR) for different E. coli strains, be able to predict which will grow on different ant ...
Balancing Reactions 1
... 1. Write equations for the ionization of the following acids. a. Hydrochloric acid b. Nitric acid c. Chloric acid 2. Write equations for the ionization of the following acids. Which ones ionize only slightly? a. HF b. H2SO3 c. CH3COOH d. HNO3 3. Classify each substance as either a strong or weak ele ...
... 1. Write equations for the ionization of the following acids. a. Hydrochloric acid b. Nitric acid c. Chloric acid 2. Write equations for the ionization of the following acids. Which ones ionize only slightly? a. HF b. H2SO3 c. CH3COOH d. HNO3 3. Classify each substance as either a strong or weak ele ...
Challenge:
... to classify organisms. To gain a better understanding of what they are using, define the following: a. Homology b. Conserved sequence c. Phylogenic tree When we have DNA or protein sequences from many organisms, we can compare them to one another in order to determine which organisms are more closel ...
... to classify organisms. To gain a better understanding of what they are using, define the following: a. Homology b. Conserved sequence c. Phylogenic tree When we have DNA or protein sequences from many organisms, we can compare them to one another in order to determine which organisms are more closel ...
Document
... Split Genes and RNA Splicing • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually express ...
... Split Genes and RNA Splicing • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually express ...
Nucleic acid content in different tissues of the fish, N. notopterus in
... knowledge of proximate composition of fish is of paramount importance to evaluate in regard to nutrient value and physiological condition (Gershamovich et al., 1984). Besides nucleic acid content in fish, the fish flesh also offers minerals, iodine, vitamins, fat etc. The knowledge of functional pro ...
... knowledge of proximate composition of fish is of paramount importance to evaluate in regard to nutrient value and physiological condition (Gershamovich et al., 1984). Besides nucleic acid content in fish, the fish flesh also offers minerals, iodine, vitamins, fat etc. The knowledge of functional pro ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.