Chapter 26: Biotechnology
... DNA and the source DNA at a specific sequence, leaving “sticky” ends, that allow a portion of source DNA to be inserted into the vector DNA. DNA ligase then seals the openings and recombinant DNA is formed. Bacterial cells take up recombinant plasmids and clone the new DNA. ...
... DNA and the source DNA at a specific sequence, leaving “sticky” ends, that allow a portion of source DNA to be inserted into the vector DNA. DNA ligase then seals the openings and recombinant DNA is formed. Bacterial cells take up recombinant plasmids and clone the new DNA. ...
HSA HW Packet #4
... D. UGC – GCA - CUC – CUC 6. During cell replication, an error may result in a base pair substitution. Which of these terms describes the changes in the base pair sequence? A. Cloning B. Meiosis C. Mutation D. Translation 7. Which type of RNA is responsible for performing transcription? A. tRNA B. mR ...
... D. UGC – GCA - CUC – CUC 6. During cell replication, an error may result in a base pair substitution. Which of these terms describes the changes in the base pair sequence? A. Cloning B. Meiosis C. Mutation D. Translation 7. Which type of RNA is responsible for performing transcription? A. tRNA B. mR ...
Bacteria and Viruses Bacterial Cells Bacterial Genome Bacterial
... • Bacteria change and evolve by… – Mutations: occur often due to high replication rate; if one mutation occurs, all future offspring will have it – Transformation: cell absorbs DNA from its environment that may have originated from another ruptured cell – Transduction: insertion of DNA by a virus – ...
... • Bacteria change and evolve by… – Mutations: occur often due to high replication rate; if one mutation occurs, all future offspring will have it – Transformation: cell absorbs DNA from its environment that may have originated from another ruptured cell – Transduction: insertion of DNA by a virus – ...
Phanerzoic Eon, Paleozoic Era
... DNA and proteins do not have all 3 functions Chemical selection Chemical within a mixture of different chemicals has special properties or advantages that cause it to increase in number compared to other chemicals in the mixture Hypothetical scenario with 2 steps One of the RNA molecules mut ...
... DNA and proteins do not have all 3 functions Chemical selection Chemical within a mixture of different chemicals has special properties or advantages that cause it to increase in number compared to other chemicals in the mixture Hypothetical scenario with 2 steps One of the RNA molecules mut ...
LAB 7
... A protein is formed by the chemical bonding of many amino acid molecules. Proteins may contain as few as 50 or as many as 5000 or more amino acids. The chemical combinations of two amino acids are called a dipeptide. The amino group of one amino acid molecule combines with the acid group of another ...
... A protein is formed by the chemical bonding of many amino acid molecules. Proteins may contain as few as 50 or as many as 5000 or more amino acids. The chemical combinations of two amino acids are called a dipeptide. The amino group of one amino acid molecule combines with the acid group of another ...
PRE-AP Stage 3 – Learning Plan
... on the family and their traits given to you. Assessment and Closing: Exit ticket will be the final product of the pedigree chart that was created. Opening: Warm-up to review Pedigrees and Karyotypes Guided Practice: Karyotype Lab-Which disorder do you have based on the karyotype. New Material: DNA f ...
... on the family and their traits given to you. Assessment and Closing: Exit ticket will be the final product of the pedigree chart that was created. Opening: Warm-up to review Pedigrees and Karyotypes Guided Practice: Karyotype Lab-Which disorder do you have based on the karyotype. New Material: DNA f ...
What is the difference between basal and activated transcription?
... phosphate backbone contacts ...
... phosphate backbone contacts ...
Lecture 35 - University of Virginia, Department of Computer Science
... • There are 4 nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T) (replaced with uracil (U) in RNA) • There are 20 different amino acids, and a stop marker (to separate proteins) • How many nucleotides are needed to ...
... • There are 4 nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T) (replaced with uracil (U) in RNA) • There are 20 different amino acids, and a stop marker (to separate proteins) • How many nucleotides are needed to ...
P5: 5` AAT GAT ACG GCG ACC ACC GA 3` P7: 5` CAA GCA GAA
... Libraries which begin with a linker, barcode, or other “non-random” sequence will not perform well unless they are basebalanced. This is particularly important on the MiSeq which has only 1 lane. If your sample has the same sequence in the first 6 positions, then we must add a balancer DNA, e.g. Phi ...
... Libraries which begin with a linker, barcode, or other “non-random” sequence will not perform well unless they are basebalanced. This is particularly important on the MiSeq which has only 1 lane. If your sample has the same sequence in the first 6 positions, then we must add a balancer DNA, e.g. Phi ...
Exam II Answer Key
... Codon for Met: AUG Codon for Thr: ACG (C converted from U in the Met codon and A converted from the G in the Ala codon. After the first mutagenic treatment, a Valine is converted to either an Alanine or a Methionine. All three amino acids are hydrophobic so it’s possible that neither mutation will h ...
... Codon for Met: AUG Codon for Thr: ACG (C converted from U in the Met codon and A converted from the G in the Ala codon. After the first mutagenic treatment, a Valine is converted to either an Alanine or a Methionine. All three amino acids are hydrophobic so it’s possible that neither mutation will h ...
CHNOPS Document
... Simulating Protein Synthesis to create a CHNOPS! Read the following to help you complete a successful CHNOPS organism. Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics such as hair color as blood type. Genes consist of DNA molecules that code for the proteins our cells make. The sequen ...
... Simulating Protein Synthesis to create a CHNOPS! Read the following to help you complete a successful CHNOPS organism. Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics such as hair color as blood type. Genes consist of DNA molecules that code for the proteins our cells make. The sequen ...
A Flexible Approach to Implement Genomic
... The implementation of the Genomics Education Partnership at Longwood University was successful. At Longwood University a total of five annotation and four finishing projects were completed and submitted during my two-semester involvement with this project. The finishing of D. mojavensis and annotati ...
... The implementation of the Genomics Education Partnership at Longwood University was successful. At Longwood University a total of five annotation and four finishing projects were completed and submitted during my two-semester involvement with this project. The finishing of D. mojavensis and annotati ...
EMS-treated culture
... • Untreated culture Do a serial dilution of the untreated wildtype E. coli culture: Fill 7 tubes with 4.5 ml of sterile saline. Transfer 0.5 ml of the undiluted culture to one of the tubes. This is a 10-1 dilution. Next make serial dilutions of 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5, 10-6 and 10-7. Always change pi ...
... • Untreated culture Do a serial dilution of the untreated wildtype E. coli culture: Fill 7 tubes with 4.5 ml of sterile saline. Transfer 0.5 ml of the undiluted culture to one of the tubes. This is a 10-1 dilution. Next make serial dilutions of 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5, 10-6 and 10-7. Always change pi ...
Nature vs. Nurture
... • Male with reduced masculine characteristics, enlarged breasts, obesity, and excessive height • Turner’s Syndrome– the 23rd pair is ______ an ___ for females • Female who is very short, infertile, and sexually underdeveloped ...
... • Male with reduced masculine characteristics, enlarged breasts, obesity, and excessive height • Turner’s Syndrome– the 23rd pair is ______ an ___ for females • Female who is very short, infertile, and sexually underdeveloped ...
3.3.1: How is DNA Passed Through the Generations?
... o DNA replicates so that there are two copies. o DNA condenses into a compact form called chromosomes. Each chromosome contains two identical copies of DNA called sister chromatids. ...
... o DNA replicates so that there are two copies. o DNA condenses into a compact form called chromosomes. Each chromosome contains two identical copies of DNA called sister chromatids. ...
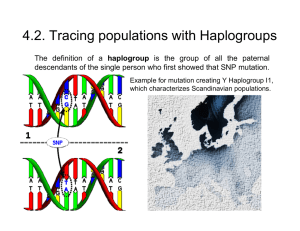
4.2. Tracing populations with Haplogroups
... with Cro-Magnon in Europe) J => 45,000 years ago (in the Near East) X => over 30,000 years ago (in Caucasus) (Neanderthal???) I => 30,000 years ago (origin unknown - probably in Europe) W => 25,000 years ago (in north-east Europe or north-west Asia) K => 15,000 years ago (in the Near East) (Oetzi) T ...
... with Cro-Magnon in Europe) J => 45,000 years ago (in the Near East) X => over 30,000 years ago (in Caucasus) (Neanderthal???) I => 30,000 years ago (origin unknown - probably in Europe) W => 25,000 years ago (in north-east Europe or north-west Asia) K => 15,000 years ago (in the Near East) (Oetzi) T ...
- faculty lounge: non
... The particular amino acid sequence of a protein determines how it folds into a particular shape. ...
... The particular amino acid sequence of a protein determines how it folds into a particular shape. ...
Epigenet-web
... CpGs are vastly underrepresented genome-wide compared to what would be expected by chance (0.23 in the human genome and 0.19 in the mouse genome, respectively) This is because deamination of cytosine gives rise to uracil, which is easily recognized as foreign within the DNA strand and replaced, wher ...
... CpGs are vastly underrepresented genome-wide compared to what would be expected by chance (0.23 in the human genome and 0.19 in the mouse genome, respectively) This is because deamination of cytosine gives rise to uracil, which is easily recognized as foreign within the DNA strand and replaced, wher ...
Biotechnology
... mRNA- RNA molecules that carry information that specifies amino acid sequence of a protein molecule during translation rRNA- RNA molecules that form the ribosomal subunits; Mediate the translation of mRNA into proteins tRNA- molecules that decode sequence information in and mRNA snRNA- very short RN ...
... mRNA- RNA molecules that carry information that specifies amino acid sequence of a protein molecule during translation rRNA- RNA molecules that form the ribosomal subunits; Mediate the translation of mRNA into proteins tRNA- molecules that decode sequence information in and mRNA snRNA- very short RN ...
Document
... 40 Vk x 5 Jk = 200combinations 30 Vl x 4 Jl = 120 combinations = 320 different light chains If H and L chains pair randomly as H2L2 i.e. 10,530x 320 = 3,369,600 possibilities Due only to COMBINATORIAL diversity In practice, some H + L combinations do not occur as they are unstable Certain V and J ge ...
... 40 Vk x 5 Jk = 200combinations 30 Vl x 4 Jl = 120 combinations = 320 different light chains If H and L chains pair randomly as H2L2 i.e. 10,530x 320 = 3,369,600 possibilities Due only to COMBINATORIAL diversity In practice, some H + L combinations do not occur as they are unstable Certain V and J ge ...
3.1 Genetics
... • During translation, the written code (codons) on mRNA is ‘TRANSLATED’ into a specific amino acid sequence by TRANSFER RIBONUCLUEIC ACID (tRNA) in the cytoplasm. • A tRNA molecule is a small piece of RNA that has an AMINO ACID attached to it. • The tRNA also has a special sequence of 3 bases known ...
... • During translation, the written code (codons) on mRNA is ‘TRANSLATED’ into a specific amino acid sequence by TRANSFER RIBONUCLUEIC ACID (tRNA) in the cytoplasm. • A tRNA molecule is a small piece of RNA that has an AMINO ACID attached to it. • The tRNA also has a special sequence of 3 bases known ...
Chapter 11 Radiation Damage to Biomolecules — From water
... completely free the g-value would have been 2.0023 (the socalled Lamb shift results in this deviation from 2). The cage itself has an influence on the broadness of the line. Thus, in a cage of heavy water (D2O) the line is more narrow. If Na is dissolved in liquid ammonia, electrons are formed and t ...
... completely free the g-value would have been 2.0023 (the socalled Lamb shift results in this deviation from 2). The cage itself has an influence on the broadness of the line. Thus, in a cage of heavy water (D2O) the line is more narrow. If Na is dissolved in liquid ammonia, electrons are formed and t ...
Document
... • Tertiary structure – Interaction among the R groups of amino acids – Interactions include ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and covalent bonds – What type of amino acids involved in each? ...
... • Tertiary structure – Interaction among the R groups of amino acids – Interactions include ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and covalent bonds – What type of amino acids involved in each? ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.