The Genetic Code Is One in a Million
... genetic code have found evidence of nonrandom patterns in the distribution of codon assignments. It has, for example, been shown that the code minimizes the effects of point mutation or mistranslation: erroneous codons are either synonymous or code for an amino acid with chemical properties very sim ...
... genetic code have found evidence of nonrandom patterns in the distribution of codon assignments. It has, for example, been shown that the code minimizes the effects of point mutation or mistranslation: erroneous codons are either synonymous or code for an amino acid with chemical properties very sim ...
PBL SEMINAR Biochemistry Division
... Hydrogen atom on one H2O molecule is attracted to the negatively charged Oxygen atom on another water molecule Forming a weak bond (called Hydrogen bond) between the two water molecules The interaction results in the Tetrahedral structure of H2O molecules Five H2O molecules form the tetrahedra ...
... Hydrogen atom on one H2O molecule is attracted to the negatively charged Oxygen atom on another water molecule Forming a weak bond (called Hydrogen bond) between the two water molecules The interaction results in the Tetrahedral structure of H2O molecules Five H2O molecules form the tetrahedra ...
2.2.56. amino acid analysis
... by a rinse with HPLC grade methanol, dried overnight in an oven, and stored covered until use. Alternatively, pyrolysis of clean glassware at 500 °C for 4 h may also be used to eliminate contamination from hydrolysis tubes. Adequate disposable laboratory material can also be used. Acid hydrolysis is ...
... by a rinse with HPLC grade methanol, dried overnight in an oven, and stored covered until use. Alternatively, pyrolysis of clean glassware at 500 °C for 4 h may also be used to eliminate contamination from hydrolysis tubes. Adequate disposable laboratory material can also be used. Acid hydrolysis is ...
Extending the Implications of Myriad to Ambry â•fiThe New
... transcription. DNA naturally consists of both introns and exons. Molecular bonds separate into individual strands of DNA. These then stand alone as single strand DNA templates for forming the other strand, according to base-pairing principles. A complementary RNA strand, known as pre-RNA is formed. ...
... transcription. DNA naturally consists of both introns and exons. Molecular bonds separate into individual strands of DNA. These then stand alone as single strand DNA templates for forming the other strand, according to base-pairing principles. A complementary RNA strand, known as pre-RNA is formed. ...
BLUEPRINT OF THE CORE TOPICS IN BIOCHEMISTRY
... _B__57. This DNA form is seen in physiologic conditions where the cell is well hydrated: A. A form B. B form C. Z form D. D form _C__58. Regions of the DNA strand that are easily denatured are rich in this base pair: A. GC B. AT C. AU D. CT _D__59. This is the primary function of nucleic acids: A. s ...
... _B__57. This DNA form is seen in physiologic conditions where the cell is well hydrated: A. A form B. B form C. Z form D. D form _C__58. Regions of the DNA strand that are easily denatured are rich in this base pair: A. GC B. AT C. AU D. CT _D__59. This is the primary function of nucleic acids: A. s ...
Inheritance of very high oleic acid content and its relationship with
... (Heaton and Knowles, 1980). CL2 is also characterized by late flowering, presence of spines, and white corolla. Twenty-four half seeds of CL2 and CR-9 were analysed for seed oil fatty acid profile. The seeds were germinated and, after fifteen days in a growth chamber, the plants were transplanted to ...
... (Heaton and Knowles, 1980). CL2 is also characterized by late flowering, presence of spines, and white corolla. Twenty-four half seeds of CL2 and CR-9 were analysed for seed oil fatty acid profile. The seeds were germinated and, after fifteen days in a growth chamber, the plants were transplanted to ...
Variations in amino acid composition in bacterial single stranded
... in their Ct domain (Table 2) and also show some additional specific structural variations which contribute to structural stability of respective SSBs (18, 23). Based on this, we proposed that all reported variations may be of significance for SSB functioning in a high GC content bacteria (18). In th ...
... in their Ct domain (Table 2) and also show some additional specific structural variations which contribute to structural stability of respective SSBs (18, 23). Based on this, we proposed that all reported variations may be of significance for SSB functioning in a high GC content bacteria (18). In th ...
Improving Virus C type 4 Interferon using Bioinformatics Techniques
... the anticodon of tRNA carrying methionine. A large ribosomal subunit binds to the complex, and the reactions of protein synthesis itself can begin. The aminoacyl-tRNA to be called for next is determined by the next codon (the next three bases) on the mRNA as shown in figure [3]. Each amino acid is c ...
... the anticodon of tRNA carrying methionine. A large ribosomal subunit binds to the complex, and the reactions of protein synthesis itself can begin. The aminoacyl-tRNA to be called for next is determined by the next codon (the next three bases) on the mRNA as shown in figure [3]. Each amino acid is c ...
Document
... Mendel’s Law of Segregation A. Law of Segregation states that a pair of factors (alleles) is segregated, or separated, during the formation of gametes (reproductive cells) (1) When two gametes combine during fertilization, the offspring have two factors controlling a specific trait (Gg) ...
... Mendel’s Law of Segregation A. Law of Segregation states that a pair of factors (alleles) is segregated, or separated, during the formation of gametes (reproductive cells) (1) When two gametes combine during fertilization, the offspring have two factors controlling a specific trait (Gg) ...
Isolation and characterization of (S)
... obtained (Kutchan, 1995). Alkaloids are a group of naturally occurring low-molecular weight nitrogenous compounds found in about 20% of plant species. The majority of alkaloids in plants are derived from the amino acids tyrosine, tryptophan and phenylalanine. They are often basic and contain nitroge ...
... obtained (Kutchan, 1995). Alkaloids are a group of naturally occurring low-molecular weight nitrogenous compounds found in about 20% of plant species. The majority of alkaloids in plants are derived from the amino acids tyrosine, tryptophan and phenylalanine. They are often basic and contain nitroge ...
NMSU IBC rDNA Worksheet for PI - Office of Research Compliance
... Caution - Special care should be used in the evaluation of containment conditions for some experiments with transgenic animals. For example, such experiments might lead to the creation of novel mechanisms or increased transmission of a recombinant pathogen or production of undesirable traits in the ...
... Caution - Special care should be used in the evaluation of containment conditions for some experiments with transgenic animals. For example, such experiments might lead to the creation of novel mechanisms or increased transmission of a recombinant pathogen or production of undesirable traits in the ...
NUCLEIC ACID ECONOMY IN BACTERIA INFECTED WITH
... 0.1 gin. gelatin, and HC1 to adjust to pH 7.4. Analytical Methods.--Most of the experiments required periodic measures of DNAP~ and mature phage P~. DNA-P 3~ was determined (Schmidt and Thannhauser, 1945) by precipitating a chilled 1 ml. sample of the culture in a conical tube with 9 ml. 0.3 M trich ...
... 0.1 gin. gelatin, and HC1 to adjust to pH 7.4. Analytical Methods.--Most of the experiments required periodic measures of DNAP~ and mature phage P~. DNA-P 3~ was determined (Schmidt and Thannhauser, 1945) by precipitating a chilled 1 ml. sample of the culture in a conical tube with 9 ml. 0.3 M trich ...
Amino Acid Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships
... biologists have found that such biochemical evidence compares favorably with other lines of evidence for evolutionary relationships. An interesting additional line of evidence supporting evolution involves sequences of DNA known as "pseudogenes." Pseudogenes are remnants of genes that no longer func ...
... biologists have found that such biochemical evidence compares favorably with other lines of evidence for evolutionary relationships. An interesting additional line of evidence supporting evolution involves sequences of DNA known as "pseudogenes." Pseudogenes are remnants of genes that no longer func ...
Table S2
... Table S2, continued Pds1: Inhibits the onset of anaphase by binding and sequestering the Esp1 protease that cleaves the cohesin complexes that hold sister chromatids together. Binding of Pds1 to Esp1 was reported to depend in Cdc28 phosphorylation[53] Sic1: Inhibitor of Clb-Cdc28. Phosphorylation o ...
... Table S2, continued Pds1: Inhibits the onset of anaphase by binding and sequestering the Esp1 protease that cleaves the cohesin complexes that hold sister chromatids together. Binding of Pds1 to Esp1 was reported to depend in Cdc28 phosphorylation[53] Sic1: Inhibitor of Clb-Cdc28. Phosphorylation o ...
Ch. 03 The Molecules of Life
... • In aqueous solutions, monosaccharides form rings • Monosaccharides are the main fuel that cells use for cellular work (rapid conversion to cellular energy): This is why an aqueous solution of glucose is injected into bloodstream of sick patients. ...
... • In aqueous solutions, monosaccharides form rings • Monosaccharides are the main fuel that cells use for cellular work (rapid conversion to cellular energy): This is why an aqueous solution of glucose is injected into bloodstream of sick patients. ...
Absorption Spectroscopy
... Like phosphate buffer, the phosphate groups do not contribute to the extinction. Within experimental error, ATP, ADP and AMP all have the same extinction properties. Absorbance of an individual nucleoside at 260 nm is about 10,000 OD 260 nm/(mol*cm). This strong extinction allows measurement down to ...
... Like phosphate buffer, the phosphate groups do not contribute to the extinction. Within experimental error, ATP, ADP and AMP all have the same extinction properties. Absorbance of an individual nucleoside at 260 nm is about 10,000 OD 260 nm/(mol*cm). This strong extinction allows measurement down to ...
An ACP-Independent Fatty Acid Synthesis Pathway in Archaea
... of an acetyl-CoA moiety from an acyl-CoA chain or the opposite condensation reaction, so the major difference between KAS and these other enzymes is the use of substrates linked to ACP instead of CoA. Thus, our results support that the cenancestor was able to (de)acetylate acyl-CoA chains, whereas t ...
... of an acetyl-CoA moiety from an acyl-CoA chain or the opposite condensation reaction, so the major difference between KAS and these other enzymes is the use of substrates linked to ACP instead of CoA. Thus, our results support that the cenancestor was able to (de)acetylate acyl-CoA chains, whereas t ...
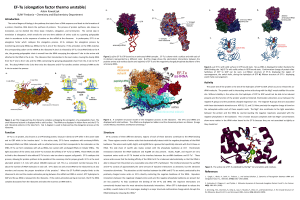
EF-Tu (elongation factor thermo unstable)
... The active site of the protein is the site of the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP, which occurs to release the aatRNA molecule. The protein and its interacting amino acids along with the Mg2+ metal stabilize this active site. Without stability in the active site the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP would not be ab ...
... The active site of the protein is the site of the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP, which occurs to release the aatRNA molecule. The protein and its interacting amino acids along with the Mg2+ metal stabilize this active site. Without stability in the active site the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP would not be ab ...
Effects of mutation on key amino acid residues in
... stabilizes p53 from degradation by MDM2 mediated pathway [3]. The central DNA binding core domain (amino acid residues 102-292), most conserved among all the domains is responsible for sequence specific binding to DNA and it is characterized by two copies of 10 bp consensus sequence 5’-PuPuPuC(A/T)- ...
... stabilizes p53 from degradation by MDM2 mediated pathway [3]. The central DNA binding core domain (amino acid residues 102-292), most conserved among all the domains is responsible for sequence specific binding to DNA and it is characterized by two copies of 10 bp consensus sequence 5’-PuPuPuC(A/T)- ...
Complementary DNA Cloning, Messenger RNA
... comprising most of the protein coding region. Both filters were washed at relatively low stringency (Ix standard saline citrate, composed of 150 HIMNaCl and 15 mivi Na citrate, pH 7.0, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, at 63°C).cDNA inserts were subcloned into pUCIS plasmid vector and transfected into E ...
... comprising most of the protein coding region. Both filters were washed at relatively low stringency (Ix standard saline citrate, composed of 150 HIMNaCl and 15 mivi Na citrate, pH 7.0, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, at 63°C).cDNA inserts were subcloned into pUCIS plasmid vector and transfected into E ...
Thesis-1965R-K29r
... composition of the nucleolus is chiefly RNA and proteins. It may also contain certain enzymes and I ipids. The synthesis of RNA in the nucleolus is generally accepted. The types are not agreed on. The transfer of RNA to the cytoplasm seems probable but the method is not apparent. Protein synthesis w ...
... composition of the nucleolus is chiefly RNA and proteins. It may also contain certain enzymes and I ipids. The synthesis of RNA in the nucleolus is generally accepted. The types are not agreed on. The transfer of RNA to the cytoplasm seems probable but the method is not apparent. Protein synthesis w ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... methylation pattern acquired in response to abiotic or biotic stress is often inherited over one to several subsequent generations. Cytosine methylation marks affect physiological functions of plants via their effect(s) on gene expression levels. They also repress transposable elements that are abun ...
... methylation pattern acquired in response to abiotic or biotic stress is often inherited over one to several subsequent generations. Cytosine methylation marks affect physiological functions of plants via their effect(s) on gene expression levels. They also repress transposable elements that are abun ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.