8.L.2.1 Biotechnology Homework for Website
... 3. Which is a career that would use microorganisms to remove pollutants from water? A. Medical specialist B. DNA fingerprint specialist C. Environmental Protection Agency specialist 4. In what area would biotechnology have the greatest effect on agriculture? A. Development of biological weapons B. D ...
... 3. Which is a career that would use microorganisms to remove pollutants from water? A. Medical specialist B. DNA fingerprint specialist C. Environmental Protection Agency specialist 4. In what area would biotechnology have the greatest effect on agriculture? A. Development of biological weapons B. D ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... Any fatty acids that humans can not make from other fatty acids are called essential fatty acids. Why are they important in human diets? Without these fatty acids, ...
... Any fatty acids that humans can not make from other fatty acids are called essential fatty acids. Why are they important in human diets? Without these fatty acids, ...
RNA Viruses
... RNA Viruses • All synthesize through a double stranded intermediate - RI replication intermediate • RNA dependent RNA polymerase of viral origin but may need host factors • Termini contain recognition signals for replicase ...
... RNA Viruses • All synthesize through a double stranded intermediate - RI replication intermediate • RNA dependent RNA polymerase of viral origin but may need host factors • Termini contain recognition signals for replicase ...
Highly Sensitive and Robust Automated DNA Extraction from
... coworkers, and different instruments, to maximize potential causes for intra-assay variations. For protein concentrations of up to 25 mg/ml, both the QIAcube and MagNA Pure LC System showed comparable results, when the additional manual steps were done prior to DNA extraction with the QIAcube. Howev ...
... coworkers, and different instruments, to maximize potential causes for intra-assay variations. For protein concentrations of up to 25 mg/ml, both the QIAcube and MagNA Pure LC System showed comparable results, when the additional manual steps were done prior to DNA extraction with the QIAcube. Howev ...
Translation
... 1. The 5' leader of the message attaches to the small subunit of a ribosome (in prokaryotes, base pairing between the 5' mRNA leader and an exposed section of the 16s rRNA is asssted by IF1). 2. In eukaryotes, one of the initiation factors binds the "CAP" at the beginning of mRNA to get it located o ...
... 1. The 5' leader of the message attaches to the small subunit of a ribosome (in prokaryotes, base pairing between the 5' mRNA leader and an exposed section of the 16s rRNA is asssted by IF1). 2. In eukaryotes, one of the initiation factors binds the "CAP" at the beginning of mRNA to get it located o ...
Project 1 Concepts in Biology Project 1 Development of a PCR
... lifting in your body: digestion, circulation, immunity, communication between cells, motion-all are made possible by one or more of the estimated 100,000 different proteins that your body makes. But the genes in your DNA don't make protein directly. Instead, special proteins called enzymes read and ...
... lifting in your body: digestion, circulation, immunity, communication between cells, motion-all are made possible by one or more of the estimated 100,000 different proteins that your body makes. But the genes in your DNA don't make protein directly. Instead, special proteins called enzymes read and ...
yes - Learnblock
... For a cellular reaction to reach equilibrium the product must be continually used by the cell elsewhere opposite. if used then equilibrium never attained ...
... For a cellular reaction to reach equilibrium the product must be continually used by the cell elsewhere opposite. if used then equilibrium never attained ...
Chapter 18~Regulaton of Gene Expression
... – usually functions in catabolic pathways, • digesting nutrients to simpler molecules ...
... – usually functions in catabolic pathways, • digesting nutrients to simpler molecules ...
File
... DNA is found in all living cells – It controls all functions inside a cell – It stores all the genetic information for an entire living organism – Single cell like an amoeba – Multi cell like a human ...
... DNA is found in all living cells – It controls all functions inside a cell – It stores all the genetic information for an entire living organism – Single cell like an amoeba – Multi cell like a human ...
E. coli - JonesHonorsBioBlue
... DNA. Plasmids are a wonderful ally for biologists who want to utilize bacteria to produce very specific proteins. The plasmids can be cut, fused with other DNA, and then reabsorbed by bacteria. The bacteria can easily incorporate the new DNA information into their metabolism. This “recombining” of D ...
... DNA. Plasmids are a wonderful ally for biologists who want to utilize bacteria to produce very specific proteins. The plasmids can be cut, fused with other DNA, and then reabsorbed by bacteria. The bacteria can easily incorporate the new DNA information into their metabolism. This “recombining” of D ...
An overview of biochemistry for bioCHEM480
... Living organisms are remarkably similar at the molecular level** despite the observed biological diversity. In nature, there exists a biochemical unity of diverse living organisms in that there is a wide range of adaptations around a common chemical framework (Can you name some common compounds foun ...
... Living organisms are remarkably similar at the molecular level** despite the observed biological diversity. In nature, there exists a biochemical unity of diverse living organisms in that there is a wide range of adaptations around a common chemical framework (Can you name some common compounds foun ...
Gene Regulation
... Lactose operon-2 • When lactose does appear, E. coli wants to use it. Lactose binds to repressor, causing shape change; repressor falls off DNA, allows unhindered transcription by RNA polymerase. Translation of mRNA results in enzymes needed to use lactose. ...
... Lactose operon-2 • When lactose does appear, E. coli wants to use it. Lactose binds to repressor, causing shape change; repressor falls off DNA, allows unhindered transcription by RNA polymerase. Translation of mRNA results in enzymes needed to use lactose. ...
Ch11_Lecture no writing
... The structure of the DNA double helix was described by Watson and Crick in 1953. Explain the structure of the DNA double helix, including its subunits and the way in which they are bonded together. (Total 8 marks) ...
... The structure of the DNA double helix was described by Watson and Crick in 1953. Explain the structure of the DNA double helix, including its subunits and the way in which they are bonded together. (Total 8 marks) ...
Carbohydrates & Begin Lipids
... • Isomers are molecules that have the same formula, but a different physical structure. • Glucose (C6H12O6) and galactose (C6H12O6) and fructose (C6H12O6) are examples of isomers. ...
... • Isomers are molecules that have the same formula, but a different physical structure. • Glucose (C6H12O6) and galactose (C6H12O6) and fructose (C6H12O6) are examples of isomers. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Nerve activates contraction
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Repressor protein - Edwin C. Foreman High School
... – usually functions in catabolic pathways, • digesting nutrients to simpler molecules ...
... – usually functions in catabolic pathways, • digesting nutrients to simpler molecules ...
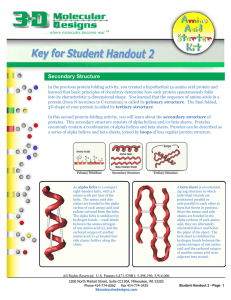
Secondary Structure - 3D Molecular Designs
... attracting RNA polymerase. A zinc finger protein contains two cysteine amino acids and two histidine amino acids which simultaneously bind to a single zinc atom. These four amino acids are contained within a 30 amino acid sequence that folds into a two-stranded beta sheet and short alpha helix. Many ...
... attracting RNA polymerase. A zinc finger protein contains two cysteine amino acids and two histidine amino acids which simultaneously bind to a single zinc atom. These four amino acids are contained within a 30 amino acid sequence that folds into a two-stranded beta sheet and short alpha helix. Many ...
Cellular respiration
... Pyruvic acid is reduced to: a reduced organic acid (for example, lactic acid or mixed acids) or an alcohol (for example, ethanol or butanediol) ...
... Pyruvic acid is reduced to: a reduced organic acid (for example, lactic acid or mixed acids) or an alcohol (for example, ethanol or butanediol) ...
462a Reading and Homework Assignment 3
... Most of the residues with “unfavorable” , angles probably involve glycine residues. c. Which of the two Ramachandran diagrams corresponds to which of the two proteins shown below? Explain. Protein 1 (Ramachandran plot A) is T4 lysozyme, which is almost all -helical. Protein 2 (Ramachandran plot ...
... Most of the residues with “unfavorable” , angles probably involve glycine residues. c. Which of the two Ramachandran diagrams corresponds to which of the two proteins shown below? Explain. Protein 1 (Ramachandran plot A) is T4 lysozyme, which is almost all -helical. Protein 2 (Ramachandran plot ...
Lecture 35: Basics of DNA Cloning-I
... cohesive ends are generated. These single stranded sticky ends can form hydrogen bond with the complementary DNA sequence from different source. For example, two DNA sequences of different origin both containing EcoR1 restriction site can be ligated if they are digested with the EcoR1 restriction en ...
... cohesive ends are generated. These single stranded sticky ends can form hydrogen bond with the complementary DNA sequence from different source. For example, two DNA sequences of different origin both containing EcoR1 restriction site can be ligated if they are digested with the EcoR1 restriction en ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.