WEEK 10
... nucleoproteins. Each individual strand of a nucleic acid is a polymer of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of purine or pyrimidine, ribose or deoxyribose and Phosphoric acid. An actual molecule of DNA consists of two chains of nucleotides coiled in a double-helix structure. Within e ...
... nucleoproteins. Each individual strand of a nucleic acid is a polymer of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of purine or pyrimidine, ribose or deoxyribose and Phosphoric acid. An actual molecule of DNA consists of two chains of nucleotides coiled in a double-helix structure. Within e ...
Extension and Enrichment
... R. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a single change in the amino acid sequence. Amino acid 6 is Glutamic acid in normal hemoglobin. It is replaced with Valine in sickle cell anemia. Using the information you just learned, explain why sickle cell anemia leads to deformed blood cells. ...
... R. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a single change in the amino acid sequence. Amino acid 6 is Glutamic acid in normal hemoglobin. It is replaced with Valine in sickle cell anemia. Using the information you just learned, explain why sickle cell anemia leads to deformed blood cells. ...
n - 1
... conservation biology. Environmental change is a continuous process & genetic diversity is required for populations to evolve to adapt to such change. Loss of genetic diversity is often associated with inbreeding and reduction in reproductive ...
... conservation biology. Environmental change is a continuous process & genetic diversity is required for populations to evolve to adapt to such change. Loss of genetic diversity is often associated with inbreeding and reduction in reproductive ...
Vocabulary: Did you know?
... Genotype-‐ Your genotype is the composition of alleles you have for a particular gene or genes. Remember than many genes come in two or more different “flavors” or alleles—one version (or allele) may ...
... Genotype-‐ Your genotype is the composition of alleles you have for a particular gene or genes. Remember than many genes come in two or more different “flavors” or alleles—one version (or allele) may ...
16_Lecture_Presentation
... • They were recognized by their ability to coagulate or flocculate (come out of suspension) based on heating or the addition of acid • Frederic Sanger was the 1st to correctly sequence a protein: insulin • And won a Nobel for this in 1958 ...
... • They were recognized by their ability to coagulate or flocculate (come out of suspension) based on heating or the addition of acid • Frederic Sanger was the 1st to correctly sequence a protein: insulin • And won a Nobel for this in 1958 ...
Natural language and the genetic code: from the semiotic analogy to
... formulated their theories under models taken from biology. Computer science has become almost a bioinspired field thanks to the great development of natural computing and DNA computing. Biology and semiotics are two different sciences challenged by the same common goal of deciphering the codes of th ...
... formulated their theories under models taken from biology. Computer science has become almost a bioinspired field thanks to the great development of natural computing and DNA computing. Biology and semiotics are two different sciences challenged by the same common goal of deciphering the codes of th ...
Amino acid lecture(1) by Prof.Dr.Moaed Al
... Amino acid lecture(1) by Prof.Dr.Moaed Al-Gazally Metabolism of individual amino acids ...
... Amino acid lecture(1) by Prof.Dr.Moaed Al-Gazally Metabolism of individual amino acids ...
PROTEINS - ssag.sk
... The amino acid sequence is coded for by DNA and is unique for each kind of protein ...
... The amino acid sequence is coded for by DNA and is unique for each kind of protein ...
Hot Seat - Metabolism and Organic Molecules
... C. Interact with a specific type of substrate molecule D. React at identical rates under all conditions ...
... C. Interact with a specific type of substrate molecule D. React at identical rates under all conditions ...
Chapter 3
... For each replichore, the enzyme will produce one continuous DNA strand, which is called the leading strand. The complementary strand of each replichore can only be made with multiple starts, from multiple primers (separated every 1000 - 2000 basepairs), as it is elongated in the opposite direction o ...
... For each replichore, the enzyme will produce one continuous DNA strand, which is called the leading strand. The complementary strand of each replichore can only be made with multiple starts, from multiple primers (separated every 1000 - 2000 basepairs), as it is elongated in the opposite direction o ...
- Environmental Biosafety Research
... (1) Recombinant nucleic acid techniques involving the formation of new combinations of genetic material by the insertion of nucleic acid molecules produced by whatever means outside an organism, into any virus, bacterial plasmid or other vector system and their incorporation into a host organism in ...
... (1) Recombinant nucleic acid techniques involving the formation of new combinations of genetic material by the insertion of nucleic acid molecules produced by whatever means outside an organism, into any virus, bacterial plasmid or other vector system and their incorporation into a host organism in ...
A Basic Introduction to the Science Underlying NCBI Resources
... accumulation of mutations. Mitochondrial DNA mutations can also concentrate in the mitochondria of specific tissues. A variety of deadly diseases are attributable to a large number of accumulated mutations in mitochondria. There is even a theory, the Mitochondrial Theory of Aging, that suggests that ...
... accumulation of mutations. Mitochondrial DNA mutations can also concentrate in the mitochondria of specific tissues. A variety of deadly diseases are attributable to a large number of accumulated mutations in mitochondria. There is even a theory, the Mitochondrial Theory of Aging, that suggests that ...
im11
... components. A weak acid contains mostly molecular components with very few ions present. 46. Polyprotic acids ionize by a multi-step process in which one proton is removed from the acid at a time. This stepwise process is outlined below. H2X H+ + HXHX- H+ + X-2 47. When a reaction is in equilibr ...
... components. A weak acid contains mostly molecular components with very few ions present. 46. Polyprotic acids ionize by a multi-step process in which one proton is removed from the acid at a time. This stepwise process is outlined below. H2X H+ + HXHX- H+ + X-2 47. When a reaction is in equilibr ...
for Genetic Testing
... • Pfu DNA polymerase is an enzyme found in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. It possesses a proofreading activity, and are being used instead of (or in combination with) Taq for high-fidelity amplification. • The primers are oriented in such a way that at the end of each cycle, the ...
... • Pfu DNA polymerase is an enzyme found in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. It possesses a proofreading activity, and are being used instead of (or in combination with) Taq for high-fidelity amplification. • The primers are oriented in such a way that at the end of each cycle, the ...
The replication of DNA
... placement of sliding camp on DNA. These enzyme couple ATP binding and hydrolysis to the placement of sliding clamp around primer template junction, every time that this junction is present in the cell. The clamp loaders also remove the slide clamp from DNA once all of the enzymes that interact with ...
... placement of sliding camp on DNA. These enzyme couple ATP binding and hydrolysis to the placement of sliding clamp around primer template junction, every time that this junction is present in the cell. The clamp loaders also remove the slide clamp from DNA once all of the enzymes that interact with ...
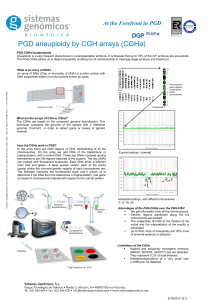
At the Forefront in PGD
... chromosomal PGD is based on CGH arrays technology. It allows to identify the altered embryos (unbalanced) in relation to the translocation/inversion and it also allows us to study aneuploidy for 24 chromosomes, simultaniously and in the same cell. The information of the non involved chromosomes in t ...
... chromosomal PGD is based on CGH arrays technology. It allows to identify the altered embryos (unbalanced) in relation to the translocation/inversion and it also allows us to study aneuploidy for 24 chromosomes, simultaniously and in the same cell. The information of the non involved chromosomes in t ...
+ O 2
... • Under normal conditions these iron-sulfur centers are reduced • When oxidized, SoxR changes configuration and is able to activate transcription of oxidative stress-related proteins (MnSOD, G6PDH, etc.) ...
... • Under normal conditions these iron-sulfur centers are reduced • When oxidized, SoxR changes configuration and is able to activate transcription of oxidative stress-related proteins (MnSOD, G6PDH, etc.) ...
Leica DNA digital levels Equipment List
... stations provide the right solution for every application. They unite reliable results with easy operation and user-friendly applications. Our total stations are designed to meet your specific requirements. Modern technology enables you to work fast and productively, thanks to the straightforward an ...
... stations provide the right solution for every application. They unite reliable results with easy operation and user-friendly applications. Our total stations are designed to meet your specific requirements. Modern technology enables you to work fast and productively, thanks to the straightforward an ...
Detection of Free Radicals
... • Under normal conditions these iron-sulfur centers are reduced • When oxidized, SoxR changes configuration and is able to activate transcription of oxidative stress-related proteins (MnSOD, G6PDH, etc.) ...
... • Under normal conditions these iron-sulfur centers are reduced • When oxidized, SoxR changes configuration and is able to activate transcription of oxidative stress-related proteins (MnSOD, G6PDH, etc.) ...
Lesson_3_liver_function
... • It contains energy so can be used for respiration. • It is broken down by hepatocytes by the enzyme ethanol dehydrogenase to ethanal. • Ethanal dehydrogenase then breaks the ethanal down into ethanoate. • Ethanoate combines with coenzyme A to form acetyl coenzyme A, and this molecule can enter the ...
... • It contains energy so can be used for respiration. • It is broken down by hepatocytes by the enzyme ethanol dehydrogenase to ethanal. • Ethanal dehydrogenase then breaks the ethanal down into ethanoate. • Ethanoate combines with coenzyme A to form acetyl coenzyme A, and this molecule can enter the ...
Preview Sample 2
... B) a carbon-hydrogen bond. C) the interaction between an amino and a carboxylate group. D) a van der Waals interaction. E) an interaction between —NH3+ and a water molecule. Answer: B Objective: 2.1 Global LO: G7 2) The most important noncovalent interaction in biochemistry is the ________ bond. Ans ...
... B) a carbon-hydrogen bond. C) the interaction between an amino and a carboxylate group. D) a van der Waals interaction. E) an interaction between —NH3+ and a water molecule. Answer: B Objective: 2.1 Global LO: G7 2) The most important noncovalent interaction in biochemistry is the ________ bond. Ans ...
34 Lambda Appendix - RIT
... When λ enters a susceptible cell, the single-stranded tails anneal to generate a circle. The site formed by the single stranded tails is called COS (cohesive site) and the left and right arms become contiguous and form a single operon, the right hand operon. The central region comprises a second ope ...
... When λ enters a susceptible cell, the single-stranded tails anneal to generate a circle. The site formed by the single stranded tails is called COS (cohesive site) and the left and right arms become contiguous and form a single operon, the right hand operon. The central region comprises a second ope ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.