A GRAPHICAL MODEL FORMULATION OF THE DNA BASE
... from this general model. We will follow this exposition, to first account for the available possibilities, and, then identify the one that we think has more merit and will be pursued further. For example; if we reduce the ancestral subset to just the last event (Z M(i) = {zi−1 }), we get a first-ord ...
... from this general model. We will follow this exposition, to first account for the available possibilities, and, then identify the one that we think has more merit and will be pursued further. For example; if we reduce the ancestral subset to just the last event (Z M(i) = {zi−1 }), we get a first-ord ...
Voiumon Numberi7i983 NucleicAcids Research
... alogy of Tn1721 [2,20] and the near identity of the tet determinants of RP1 and Tn1721. In subsequent discussions results pertaining to the tet genes of RP1 and Tn1721 will be taken to be equally applicable to either determinant. Open reading frames Bennett and Shales [21] used insertional inactivat ...
... alogy of Tn1721 [2,20] and the near identity of the tet determinants of RP1 and Tn1721. In subsequent discussions results pertaining to the tet genes of RP1 and Tn1721 will be taken to be equally applicable to either determinant. Open reading frames Bennett and Shales [21] used insertional inactivat ...
DNA, Technology, and Florida Strawberries 1 - EDIS
... not been a GMO strawberry commercialized anywhere in the world. All commercial strawberry varieties have been developed by conventional breeding methods. While foods derived from genetically engineered crops have shown no evidence of health risks, there are still major social barriers to the accepta ...
... not been a GMO strawberry commercialized anywhere in the world. All commercial strawberry varieties have been developed by conventional breeding methods. While foods derived from genetically engineered crops have shown no evidence of health risks, there are still major social barriers to the accepta ...
Modulation of base excision repair of 8
... frequency of at least several hundred lesions per human cell per day by reaction of intracellularly produced reactive oxygen species with DNA (1); this rate is further increased under oxidative stress conditions (2,3). Failure of repair mechanisms to properly deal with such a damage load has several ...
... frequency of at least several hundred lesions per human cell per day by reaction of intracellularly produced reactive oxygen species with DNA (1); this rate is further increased under oxidative stress conditions (2,3). Failure of repair mechanisms to properly deal with such a damage load has several ...
A new drug inactivates the helicase enzyme by binding to its active
... (D) The variation is due to differences in how the two organisms undergo cell division, because bacterial cells from Earth replicate their DNA before dividing, while the microorganisms from the moon do not undergo DNA replication before dividing. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the studen ...
... (D) The variation is due to differences in how the two organisms undergo cell division, because bacterial cells from Earth replicate their DNA before dividing, while the microorganisms from the moon do not undergo DNA replication before dividing. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the studen ...
Part 1: DNA Replication
... How to recognize the 5’ and 3’ ends of a DNA strand. The structural differences between free nucleotides (nucleoside triphosphates), and nucleotides in a nucleic acid. Why replication is necessary for cells, where it happens, its inputs and its outputs. The specific details of the process of replica ...
... How to recognize the 5’ and 3’ ends of a DNA strand. The structural differences between free nucleotides (nucleoside triphosphates), and nucleotides in a nucleic acid. Why replication is necessary for cells, where it happens, its inputs and its outputs. The specific details of the process of replica ...
Abundance of an mRNA is the average number of molecules per cell
... Condensation reaction is one in which a covalent bond is formed with loss of a water molecule, as in the addition of an amino acid to a polypeptide chain. Conditional lethal mlutations kill a cell or virus under certain (nonpermissive) conditions, but allow it to survive under other (permissive) con ...
... Condensation reaction is one in which a covalent bond is formed with loss of a water molecule, as in the addition of an amino acid to a polypeptide chain. Conditional lethal mlutations kill a cell or virus under certain (nonpermissive) conditions, but allow it to survive under other (permissive) con ...
Hybrid tryptophan aporepressor containing ligand binding sites
... ferred conformations of the DNA-binding domains of an aporepressor to a subset of conformations that bind ...
... ferred conformations of the DNA-binding domains of an aporepressor to a subset of conformations that bind ...
MCQ Sample I- Blue
... MCQ Sample I- Blue 4. Which of the following is NOT TRUE about bacterial chromosomes? a) the bacterial chromosome is a circular loop of DNA b) the bacterial chromosome is in the cytoplasm of the cell c) the bacterial chromosome is wrapped around histone proteins d) bacteria have the haploid number, ...
... MCQ Sample I- Blue 4. Which of the following is NOT TRUE about bacterial chromosomes? a) the bacterial chromosome is a circular loop of DNA b) the bacterial chromosome is in the cytoplasm of the cell c) the bacterial chromosome is wrapped around histone proteins d) bacteria have the haploid number, ...
Sensitive and Sequence-Specific DNA Assays
... between the capture probe and its complementary target (plateau of curve d) decreased by more than 50% when the target has only one base mismatching the capture probe (curve c). This suggests that, when surface modification and DNA hybridization conditions are optimized, the SPR technique can provid ...
... between the capture probe and its complementary target (plateau of curve d) decreased by more than 50% when the target has only one base mismatching the capture probe (curve c). This suggests that, when surface modification and DNA hybridization conditions are optimized, the SPR technique can provid ...
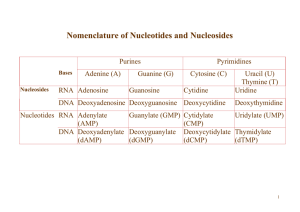
Nomenclature of Nucleotides and Nucleosides
... c. Increased synthesis of purines. Because there is little or no HGPRT activity in people affected with Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, hypoxanthine and guanine are not salvaged. Also, the intracellular levels of PRPP increase, whereas those of IMP and GMP decrease. This leads to increased de novo synthesis o ...
... c. Increased synthesis of purines. Because there is little or no HGPRT activity in people affected with Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, hypoxanthine and guanine are not salvaged. Also, the intracellular levels of PRPP increase, whereas those of IMP and GMP decrease. This leads to increased de novo synthesis o ...
Chapter 4. Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... We usually think that an oxidation necessarily involves a reaction with oxygen and/or addition of an atom of oxygen to the formula. We often think that all atoms of the same element must have the same oxidation number and that this number is uniquely related to the atom’s location in the periodic ta ...
... We usually think that an oxidation necessarily involves a reaction with oxygen and/or addition of an atom of oxygen to the formula. We often think that all atoms of the same element must have the same oxidation number and that this number is uniquely related to the atom’s location in the periodic ta ...
- Circle of Docs
... 86. The structure of vitamin D is such that it is classified as a/an A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 86. The structure of vitamin D is such that it is classified as a/an A. B. C. D. E. ...
2ndDisinfection
... – Bacteria: denaturation of proteins, inhibition of enzymes, damages on plasma membrane – Viruses and fungi: Unknown ...
... – Bacteria: denaturation of proteins, inhibition of enzymes, damages on plasma membrane – Viruses and fungi: Unknown ...
Biology Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Lab
... is the inability to taste this particular molecule. This is an SNP lab, so by definition we are not measuring a mutation, but rather a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism. Remember that an SNP is where a single base (nucleotide without its Ribose) is changed in the sequence that code for the functioning ...
... is the inability to taste this particular molecule. This is an SNP lab, so by definition we are not measuring a mutation, but rather a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism. Remember that an SNP is where a single base (nucleotide without its Ribose) is changed in the sequence that code for the functioning ...
LAB 1: Scientific Method/Tools of Scientific Inquiry
... one of four possible nitrogenous bases (“bases” for short) on the other. The phosphate group is acidic and thus negatively charged. This is why DNA has a net negative charge. Because all nucleotides in DNA contain deoxyribose they are called deoxyribonucleotides, though for simplicity we will just c ...
... one of four possible nitrogenous bases (“bases” for short) on the other. The phosphate group is acidic and thus negatively charged. This is why DNA has a net negative charge. Because all nucleotides in DNA contain deoxyribose they are called deoxyribonucleotides, though for simplicity we will just c ...
Document
... 1. site-invariant dna-based mutation model 2. site-specific amino acid level selection model ...
... 1. site-invariant dna-based mutation model 2. site-specific amino acid level selection model ...
Atomistic understanding of kinetic pathways for single base
... dynamics associated with hybridization, about which little is known. In particular, there is insufficient understanding of the mechanism underlying the fundamental event in this process, the binding兾unbinding of an individual base pair. In this work we use atomistic simulations to examine the free e ...
... dynamics associated with hybridization, about which little is known. In particular, there is insufficient understanding of the mechanism underlying the fundamental event in this process, the binding兾unbinding of an individual base pair. In this work we use atomistic simulations to examine the free e ...
Genome structure, analysis and evolufion Lecture 1
... Further poten?al for confusion comes from new uses of the term ‘genome’ recently spawned by genome sequencers. These concern the counter-‐intui?ve meaning of a ‘wholly’, ‘completely’ or ‘en?rely’ sequenced geno ...
... Further poten?al for confusion comes from new uses of the term ‘genome’ recently spawned by genome sequencers. These concern the counter-‐intui?ve meaning of a ‘wholly’, ‘completely’ or ‘en?rely’ sequenced geno ...
41. Specific terms of reference for the NCR for drug
... Each National Reference Centre (NRC) must meet both the general and the specific terms of reference. In the specific terms of reference, the NRC tasks dedicated to each selected pathogen or group of pathogens are described. It aims to guarantee the knowledge, the know-how and the epidemiological sur ...
... Each National Reference Centre (NRC) must meet both the general and the specific terms of reference. In the specific terms of reference, the NRC tasks dedicated to each selected pathogen or group of pathogens are described. It aims to guarantee the knowledge, the know-how and the epidemiological sur ...
Amino Acids
... Amino acids with nonpolar side chains. Aromatic R Groups. Amino acids with uncharged polar side chains. Positively Charged (Basic) R Groups. Amino acids with acidic side chains. ...
... Amino acids with nonpolar side chains. Aromatic R Groups. Amino acids with uncharged polar side chains. Positively Charged (Basic) R Groups. Amino acids with acidic side chains. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.