Topic 1: Cells - Gimnasio del Norte
... Skeletal muscle and some fungal hyphae are not divided into cells but have a multinucleate cytoplasm. Some biologists consider unicellular organisms to be acellular. 1.1.2 State that a virus is a non-cellular structure consisting of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. 1.1.3 State that all cells ...
... Skeletal muscle and some fungal hyphae are not divided into cells but have a multinucleate cytoplasm. Some biologists consider unicellular organisms to be acellular. 1.1.2 State that a virus is a non-cellular structure consisting of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. 1.1.3 State that all cells ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... of these amino acids are Hydroxyproline, γ-Carboxyglutamate, o-Phosphoserine o-Phosphotyrosine which are not common amino acids. Here the Hydroxiproline is formed when the Pralines is attached with a specific –OH group which is one other amino acid not among the common amino acids. It can be observe ...
... of these amino acids are Hydroxyproline, γ-Carboxyglutamate, o-Phosphoserine o-Phosphotyrosine which are not common amino acids. Here the Hydroxiproline is formed when the Pralines is attached with a specific –OH group which is one other amino acid not among the common amino acids. It can be observe ...
Topic 1: Cells - Cardinal Newman High School
... Skeletal muscle and some fungal hyphae are not divided into cells but have a multinucleate cytoplasm. Some biologists consider unicellular organisms to be acellular. 1.1.2 State that a virus is a non-cellular structure consisting of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. 1.1.3 State that all cells ...
... Skeletal muscle and some fungal hyphae are not divided into cells but have a multinucleate cytoplasm. Some biologists consider unicellular organisms to be acellular. 1.1.2 State that a virus is a non-cellular structure consisting of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. 1.1.3 State that all cells ...
Chemistry/Biology 302 – Biochemistry: Exam 1 Practice Problems
... these questions come from several years of past Biochem tests. Over those years, we've used several different textbooks, and some of them use different approximate pKa values for buffers and amino acids. I've tried to update these questions so that they all use consistent pKa values, but if I've mis ...
... these questions come from several years of past Biochem tests. Over those years, we've used several different textbooks, and some of them use different approximate pKa values for buffers and amino acids. I've tried to update these questions so that they all use consistent pKa values, but if I've mis ...
amino acid, peptides, proteins, enzymes, and nucleic acids
... he chemistry of life is largely the chemistry of polyfunctional organic compounds. The functional groups usually are of types that interact rather strongly as, for example, the hydroxyl and carbonyl functions of carbohydrates (Chapter 20). The interaction between amino and carboxyl functions of amin ...
... he chemistry of life is largely the chemistry of polyfunctional organic compounds. The functional groups usually are of types that interact rather strongly as, for example, the hydroxyl and carbonyl functions of carbohydrates (Chapter 20). The interaction between amino and carboxyl functions of amin ...
Database homology searching
... frames) against a protein database. • tblastn: searches a protein sequence against a DNA database (translated in all six reading frames) – essential for searching EST databases. and in the interests of completeness there is: • tblastx: searches a DNA sequence (translated in all six reading frames) a ...
... frames) against a protein database. • tblastn: searches a protein sequence against a DNA database (translated in all six reading frames) – essential for searching EST databases. and in the interests of completeness there is: • tblastx: searches a DNA sequence (translated in all six reading frames) a ...
Building and Animating Amino Acids and DNA Nucleotides in 1
... We explain how to export using the amino acid Arginine created in Section 4.2 above. We assume you have the 3ds max file open and have created the Arginine amino acid as shown in Figure 4-2.2. Make sure your active viewport is Perspective and not any other viewport (e.g. front), otherwise your amino ...
... We explain how to export using the amino acid Arginine created in Section 4.2 above. We assume you have the 3ds max file open and have created the Arginine amino acid as shown in Figure 4-2.2. Make sure your active viewport is Perspective and not any other viewport (e.g. front), otherwise your amino ...
midyear outline BioAP
... I can define matter, and provide examples I can explain the different between an element and a compound, and provide an example of each. I know the difference between an atom and an ion I know how to draw Bohr models for BOTH atoms and ions I can explain why a certain atom would become an anion or a ...
... I can define matter, and provide examples I can explain the different between an element and a compound, and provide an example of each. I know the difference between an atom and an ion I know how to draw Bohr models for BOTH atoms and ions I can explain why a certain atom would become an anion or a ...
Worked solutions to textbook questions 1 Chapter 14 From organic
... molecular structure that is common to all three drugs. How does the structure of these molecules differ? ...
... molecular structure that is common to all three drugs. How does the structure of these molecules differ? ...
Applications of Genomics
... a disease than other people or respond differently to medications is that their DNA variants affect the function of genes. There are rare variants that have a large effect on the function of a gene by either significantly increasing or decreasing the activity of the gene; these are the kind of varia ...
... a disease than other people or respond differently to medications is that their DNA variants affect the function of genes. There are rare variants that have a large effect on the function of a gene by either significantly increasing or decreasing the activity of the gene; these are the kind of varia ...
BBF RFC 39: The USER cloning standard
... removal of the uracil base (see Figure 1). The vector with a USER cassette is digested with the restriction enzyme PacI and the nicking enzyme Nt.BbvCI as illustrated in Figure 1. This leaves a single stranded DNA overhang complementary to the overhang on the USERTM treated PCR products, hereby allo ...
... removal of the uracil base (see Figure 1). The vector with a USER cassette is digested with the restriction enzyme PacI and the nicking enzyme Nt.BbvCI as illustrated in Figure 1. This leaves a single stranded DNA overhang complementary to the overhang on the USERTM treated PCR products, hereby allo ...
Standard Mutation Nomenclature in Molecular Diagnostics
... nomenclature based on not only a genomic DNA reference sequence but also a coding DNA reference sequence. This is because a genomic reference sequence cannot describe the relation to an adjacent exon as can nomenclature based on a coding DNA reference sequence in the form of “c.###⫹#G⬎T” or “c.###⫺# ...
... nomenclature based on not only a genomic DNA reference sequence but also a coding DNA reference sequence. This is because a genomic reference sequence cannot describe the relation to an adjacent exon as can nomenclature based on a coding DNA reference sequence in the form of “c.###⫹#G⬎T” or “c.###⫺# ...
Acid-base balance
... ● Acidemia- pH< normal range(7.35-7.45). i.e. H+ in the blood above normal range ● Alkalemia-pH>normal (7.35-7.45). i.e. H+ in the blood less than normal range ● An acidosis & alkalossis is a pathologic process that causes an increase or decrease in the hydrogen ion ...
... ● Acidemia- pH< normal range(7.35-7.45). i.e. H+ in the blood above normal range ● Alkalemia-pH>normal (7.35-7.45). i.e. H+ in the blood less than normal range ● An acidosis & alkalossis is a pathologic process that causes an increase or decrease in the hydrogen ion ...
e Study of RNA Polymerase Pausing by Optical Traps
... the DNA templates have eight concatenated pauses, and gel electrophoresis assays indicated the expected template lengths of 6.8 kilobases for the his pause template and 6.7 kilobases for the ops pause template. The DNA sequence has been modified with the appropriate digoxigenin labels for the hinder ...
... the DNA templates have eight concatenated pauses, and gel electrophoresis assays indicated the expected template lengths of 6.8 kilobases for the his pause template and 6.7 kilobases for the ops pause template. The DNA sequence has been modified with the appropriate digoxigenin labels for the hinder ...
sample - Test Bank Team
... Answer: base pairing of A with T, and G with C Section: 1.3 33) Reference is often made to adapter molecules when describing protein synthesis in that they allow amino acids to associate with nucleic acids. To what class of molecules does this term refer? Answer: tRNA Section: 1.3 34) Given that DNA ...
... Answer: base pairing of A with T, and G with C Section: 1.3 33) Reference is often made to adapter molecules when describing protein synthesis in that they allow amino acids to associate with nucleic acids. To what class of molecules does this term refer? Answer: tRNA Section: 1.3 34) Given that DNA ...
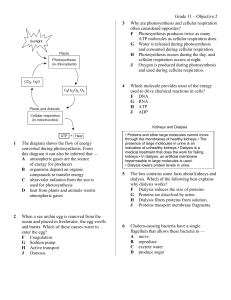
Grade 11 – Objective 2 1 The diagram shows the flow
... 21 In all plant and animal cells, the nucleus contains long molecules of DNA. Which of the following best describes the function of DNA? F DNA provides the shape and structure of the nucleus. G DNA packages materials for transport through the nucleus. H DNA carries materials into and out of the ...
... 21 In all plant and animal cells, the nucleus contains long molecules of DNA. Which of the following best describes the function of DNA? F DNA provides the shape and structure of the nucleus. G DNA packages materials for transport through the nucleus. H DNA carries materials into and out of the ...
Honors Biology Lab Manual
... proteins determine your body’s form and carry out its functions. DNA determines what all of these proteins will be. How does a cell “read” the chemical message coded in its DNA in the form of specific base sequences? Part of the answer lies with a second molecule in the nucleus of cells called ribo ...
... proteins determine your body’s form and carry out its functions. DNA determines what all of these proteins will be. How does a cell “read” the chemical message coded in its DNA in the form of specific base sequences? Part of the answer lies with a second molecule in the nucleus of cells called ribo ...
Determinants of mRNA localization University
... segmentation gene transcripts exhibit different patterns of localization in the periplasm surrounding the cortical layer nuclei [34**]. At the end of the blastodeml stage, cell membranes invaginate to subdivide the periplasm of an individual cell into apical (above nuclei) and basal (below nuclei) p ...
... segmentation gene transcripts exhibit different patterns of localization in the periplasm surrounding the cortical layer nuclei [34**]. At the end of the blastodeml stage, cell membranes invaginate to subdivide the periplasm of an individual cell into apical (above nuclei) and basal (below nuclei) p ...
PTC Genetics Lab Student Worksheet
... The sensation of taste can be categorized into five basic types: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami (the taste of monosodium glutamate). These five tastes serve to classify compounds into potentially nutritive and beneficial (sweet, salty, umami) or potentially harmful or toxic (bitter, sour). Th ...
... The sensation of taste can be categorized into five basic types: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami (the taste of monosodium glutamate). These five tastes serve to classify compounds into potentially nutritive and beneficial (sweet, salty, umami) or potentially harmful or toxic (bitter, sour). Th ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • Both of these transcription factors are required for transcription of the classical polymerase III genes • They depend on each other for their activities • TFIIIC is an assembly factor that allows TFIIIB to bind to the region just upstream of the transcription start site • TFIIIB can remain bound ...
... • Both of these transcription factors are required for transcription of the classical polymerase III genes • They depend on each other for their activities • TFIIIC is an assembly factor that allows TFIIIB to bind to the region just upstream of the transcription start site • TFIIIB can remain bound ...
Chemistry of Life
... – macromolecules created by disassembling other macromolecules into their constituent parts by adding an –OH group to form one subunit and an H to form the other subunit • this, in effect, constitutes the addition a molecule of water (H2O) for every macromolecule that is disassembled • energy is rel ...
... – macromolecules created by disassembling other macromolecules into their constituent parts by adding an –OH group to form one subunit and an H to form the other subunit • this, in effect, constitutes the addition a molecule of water (H2O) for every macromolecule that is disassembled • energy is rel ...
Phenyl Acetate Preparation ( from Phenol and
... and that this c&nprised not more than about 13.5% ester (Table 1). Water removal via acetic acid azeotroping markedly raised this, so that preparations employing this technique and using a four mole excess of acetic acid, achieved 55-60% yields of ester based on phenol (Table 2 ) . With less efficie ...
... and that this c&nprised not more than about 13.5% ester (Table 1). Water removal via acetic acid azeotroping markedly raised this, so that preparations employing this technique and using a four mole excess of acetic acid, achieved 55-60% yields of ester based on phenol (Table 2 ) . With less efficie ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.