Unit 3 - Lesson 7 - Malthusian Catastrophe
... resources are finite. In biology, the theory asserts that the reproductive potential of most organisms or species greatly exceeds the Earth’s capacity to support all possible offspring. Consequently, species diversity is preserved through mechanisms and checks that work to keep population sizes at l ...
... resources are finite. In biology, the theory asserts that the reproductive potential of most organisms or species greatly exceeds the Earth’s capacity to support all possible offspring. Consequently, species diversity is preserved through mechanisms and checks that work to keep population sizes at l ...
Population Dynamics
... All living things need resources such as water, energy and living space. ...
... All living things need resources such as water, energy and living space. ...
Population Dynamics
... approximately 6 billion. If nothing were to slow the rate of population growth, what would the population be in the ...
... approximately 6 billion. If nothing were to slow the rate of population growth, what would the population be in the ...
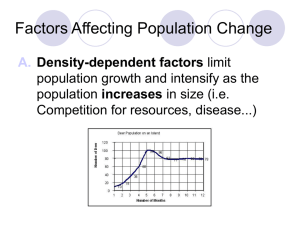
FACTORS AFFECTING POPULATION CHANGE
... the smallest number of individuals that ensures the population will persist for a certain period of time. Allows biologists to determine whether a species is endangered. ...
... the smallest number of individuals that ensures the population will persist for a certain period of time. Allows biologists to determine whether a species is endangered. ...
Review for Ecology Test
... the stored energy gets transferred from one trophic level to the next highest trophic level. The most energy would be found in the _________ trophic level. ...
... the stored energy gets transferred from one trophic level to the next highest trophic level. The most energy would be found in the _________ trophic level. ...
Human overpopulation
Human overpopulation occurs if the number of people in a group exceeds the carrying capacity of the region occupied by that group. Overpopulation can further be viewed, in a long term perspective, as existing when a population cannot be maintained given the rapid depletion of non-renewable resources or given the degradation of the capacity of the environment to give support to the population.The term human overpopulation often refers to the relationship between the entire human population and its environment: the Earth, or to smaller geographical areas such as countries. Overpopulation can result from an increase in births, a decline in mortality rates, an increase in immigration, or an unsustainable biome and depletion of resources. It is possible for very sparsely populated areas to be overpopulated if the area has a meager or non-existent capability to sustain life (e.g. a desert). Advocates of population moderation cite issues like quality of life, carrying capacity and risk of starvation as a basis to argue against continuing high human population growth and for population decline.