Answers to Questions 1-14 From Chapter 8 A sea otter is an
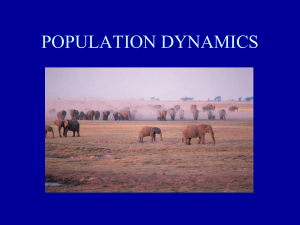
... -Random distribution is usually seen in plants although it is considered rare, it happens when the wind or water randomly carries seeds or spawn to random places and the organisms sort of grow where they land. 4. Examples would be: Uniform-Joshua Trees in the desert, clumped-elephants in the savanna ...
... -Random distribution is usually seen in plants although it is considered rare, it happens when the wind or water randomly carries seeds or spawn to random places and the organisms sort of grow where they land. 4. Examples would be: Uniform-Joshua Trees in the desert, clumped-elephants in the savanna ...
Population Biology
... DD limiting factors are more often biological rather than physical. Predation and food: Often hard to determine what effect predation has on a population. Predation as a DD factor: we will work on an activity with this. Is predation beneficial? ...
... DD limiting factors are more often biological rather than physical. Predation and food: Often hard to determine what effect predation has on a population. Predation as a DD factor: we will work on an activity with this. Is predation beneficial? ...
Human Population and the Environment
... Environment • Human population is growing rapidly and steadily. • Ultimately, there can be no long-term solutions to environmental problems unless the human population stops increasing. • Countries with a high standard of living (developed countries) have moved more quickly to a lower birth rate tha ...
... Environment • Human population is growing rapidly and steadily. • Ultimately, there can be no long-term solutions to environmental problems unless the human population stops increasing. • Countries with a high standard of living (developed countries) have moved more quickly to a lower birth rate tha ...
Slide 1 - willisworldbio
... Like the populations of many other living organisms, the size of the human population tends to ______ with time. 500 years ago the human population began to grow rapidly. 1. Agriculture and industry made life easier 2. Food supply more reliable. ...
... Like the populations of many other living organisms, the size of the human population tends to ______ with time. 500 years ago the human population began to grow rapidly. 1. Agriculture and industry made life easier 2. Food supply more reliable. ...
Population – Limiting Factors
... • Disease in a population increases with the large populations. • High densities makes it easier for parasites to find hosts and spread the disease. – A parasite is an organism that lives in or on another organism (called a host) to get nourishment. ...
... • Disease in a population increases with the large populations. • High densities makes it easier for parasites to find hosts and spread the disease. – A parasite is an organism that lives in or on another organism (called a host) to get nourishment. ...
FACTORS AFFECTING POPULATION CHANGE Density
... enough to offset the mortality rate. This occurs in populations so small or spread out that it is difficult to find mates (ex/ the decline of the passenger pigeon which only breeds in large colonies) Small populations can also lead to inbreeding and loss of genetic variation. The minimum viable popu ...
... enough to offset the mortality rate. This occurs in populations so small or spread out that it is difficult to find mates (ex/ the decline of the passenger pigeon which only breeds in large colonies) Small populations can also lead to inbreeding and loss of genetic variation. The minimum viable popu ...
Unit 5 Population Dynamics Expectations
... F1.1 analyse the effects of human population growth, personal consumption, and technological development on our ecological footprint (e.g., the deforestation resulting from expanding development and demand for wood products causes the destruction of habitats that support biological diversity; the ac ...
... F1.1 analyse the effects of human population growth, personal consumption, and technological development on our ecological footprint (e.g., the deforestation resulting from expanding development and demand for wood products causes the destruction of habitats that support biological diversity; the ac ...
Human overpopulation
Human overpopulation occurs if the number of people in a group exceeds the carrying capacity of the region occupied by that group. Overpopulation can further be viewed, in a long term perspective, as existing when a population cannot be maintained given the rapid depletion of non-renewable resources or given the degradation of the capacity of the environment to give support to the population.The term human overpopulation often refers to the relationship between the entire human population and its environment: the Earth, or to smaller geographical areas such as countries. Overpopulation can result from an increase in births, a decline in mortality rates, an increase in immigration, or an unsustainable biome and depletion of resources. It is possible for very sparsely populated areas to be overpopulated if the area has a meager or non-existent capability to sustain life (e.g. a desert). Advocates of population moderation cite issues like quality of life, carrying capacity and risk of starvation as a basis to argue against continuing high human population growth and for population decline.