Chapter 7 (Human population) Study Guide
... 2. Growth rate of population, definition, calculation and its impact ( positive and negative ) to the number of population (e.g. if r is positive and constant the population decrease each year) 3. Compare the population growth rate in developing vs. developed country. 4. Factors that controls popula ...
... 2. Growth rate of population, definition, calculation and its impact ( positive and negative ) to the number of population (e.g. if r is positive and constant the population decrease each year) 3. Compare the population growth rate in developing vs. developed country. 4. Factors that controls popula ...
What is population ecology? - Mrs. Cindy Williams Biology website
... • the measure of how crowded organisms are in their environment • organisms compete for resources, keeping a balance is important If the population is too high, some organisms will __________. ...
... • the measure of how crowded organisms are in their environment • organisms compete for resources, keeping a balance is important If the population is too high, some organisms will __________. ...
Environmental Systems Scope and Sequence
... Carrying Capacity and Resources Invasive and Extinct Species Protecting Biodiversity Maintaining the Balance The Dynamic Earth Parts of the Earth and Atmosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Tectonic Events Weather Patterns 3rd Six Weeks Using Earth’s Resources Human Population Growth and Demographics Land ...
... Carrying Capacity and Resources Invasive and Extinct Species Protecting Biodiversity Maintaining the Balance The Dynamic Earth Parts of the Earth and Atmosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Tectonic Events Weather Patterns 3rd Six Weeks Using Earth’s Resources Human Population Growth and Demographics Land ...
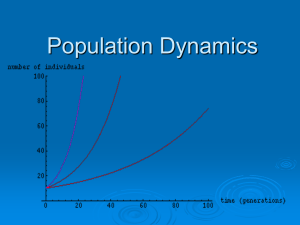
POPULATION BIOTIC POTENTIAL: REPRODUCTIVE RATE
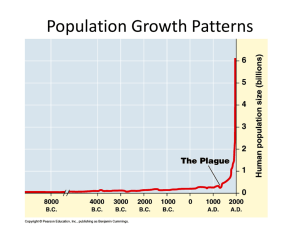
... HISTORY OF POPULATION: A) HOMINID SPECIES: MAN-LIKE APE, 3-4 MILLION YEARS AGO. B) HOMOSAPIENS: 100,000 YEARS AGO. SMALL FAMILIES AND TRIBES, SURVIVED BY HUNTING AND GATHERING, NOMADIC, MIGRATING. SINCE IT WAS DIFFICULT TO MIGRATE WITH CHILDREN, THEY HAD LOW BIRTH RATES. C) 10-12000 YEARS AGO, MAN L ...
... HISTORY OF POPULATION: A) HOMINID SPECIES: MAN-LIKE APE, 3-4 MILLION YEARS AGO. B) HOMOSAPIENS: 100,000 YEARS AGO. SMALL FAMILIES AND TRIBES, SURVIVED BY HUNTING AND GATHERING, NOMADIC, MIGRATING. SINCE IT WAS DIFFICULT TO MIGRATE WITH CHILDREN, THEY HAD LOW BIRTH RATES. C) 10-12000 YEARS AGO, MAN L ...
Human overpopulation
Human overpopulation occurs if the number of people in a group exceeds the carrying capacity of the region occupied by that group. Overpopulation can further be viewed, in a long term perspective, as existing when a population cannot be maintained given the rapid depletion of non-renewable resources or given the degradation of the capacity of the environment to give support to the population.The term human overpopulation often refers to the relationship between the entire human population and its environment: the Earth, or to smaller geographical areas such as countries. Overpopulation can result from an increase in births, a decline in mortality rates, an increase in immigration, or an unsustainable biome and depletion of resources. It is possible for very sparsely populated areas to be overpopulated if the area has a meager or non-existent capability to sustain life (e.g. a desert). Advocates of population moderation cite issues like quality of life, carrying capacity and risk of starvation as a basis to argue against continuing high human population growth and for population decline.