* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.3 Populations
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
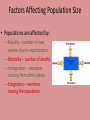
5.3 Populations Factors Affecting Population Size • Populations are affected by: – Natality – number of new species due to reproduction – Mortality – number of deaths – Immigration – members arriving from other places – Emigration – members leaving the population Population Growth Curve Exponential Growth Phase a) The number of individuals is increasing at a fast rate due to higher natality compared to mortality, abundant resources (little/no limiting factors), little/no disease and predators, more immigration than emigration Transitional Phase b) a slowing but still high growth rate because limiting factors are starting to take effect which increases competition, natality falls and/or mortality rises, increases in number of predator/diseases Plateau Phase c) population remains constant over time because natality + immigration = mortality + emigration, the limited resources and predators/diseases keeps population at carrying capacity Limiting Factors 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Shortage of food or prey Disease/Parasites Accumulation of waste Predation Availability of resources like water, food, sunlight, shelter The Human Population Graph What part of the Population Growth Curve are human populations currently under? What will be the limiting factors that affect the human population?