* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review for Ecology Test
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
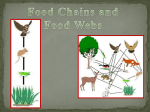
Name: ____________________________ Hr:_____ Ecology Study Guide MUST BE 100% done to take the Test!!!!! PAGE NUMBERS TO READ AND STUDY Chapter 3: p. 64-78 Chapter 4: p. 99-104 Chapter 5: 130-141 Extra Credit Opportunity Do Flash Cards! 1. A biotic factor is any __________ component of the environment. Give 2 examples of a biotic factor: 2. An abiotic factor is any _____________ component of the environement. Give 2 examples of an abiotic factor: 3. Match the following: a. Species b. Population c. Community d. Ecosystem e. Biome f. Biosphere ________ _________ _________ _________ _________ __________ 1. All zebra that live in a certain grassland. 2. Zebra 3. Zebra, lion, anteaters, grass and trees in a certain area 4. All the zebras, lions, anteaters, grass and trees in an area as well as the amount of sunlight and water available. 5. All the living and non living things on our planet 6. All the grassland area in the world, including all living and non living components 4. The ________________ is the largest population that can be supported in a certain environment. 5. What is the definition that I gave to you for a niche? 6. Describe one predator/prey relationship. 7. What is symbiosis? Name: ____________________________ Hr:_____ 8. Match the following symbiotic relationships. a. Commensalism_________ b. Mutualism _________ c. Parasitism _________ 1. Both organisms benefit,such as e.coli living in you intestines to help break down food 2. One organism benefits and one organism is harmed ,such as a tick feeding on human blood 3. One organism benefits and one is unaffected, such as bacteria feeding on human skin cells on the hand but not causing disease to the human 9. ____________ will result when 2 organisms obtain the same niche, meaning they are using the exact same food resource and shelter in the exact same habitat. 10. What is the definition of ecology? 11. The number of individuals of a population in a specific area is called population __________. 12. Match the following: a. Omnivore b. Herbivore c. Carnivore d. Scavenger e. Decomposer _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ 1. An owl eats a mouse. 2. A mouse eats grain. 3. A raccoon eats both berries and mice. 4. Bacteria break down decaying matter 5. A vulture eats dead animals 13. How are a food chain and a food web related? 14. A __________ pyramid shows how energy moves through a food chain. Only _____ of the stored energy gets transferred from one trophic level to the next highest trophic level. The most energy would be found in the _________ trophic level. Name: ____________________________ Hr:_____ 15. Plants are able to make their own food so they are called ____________ or ___________. The animals that feed on plants are called ___________ consumers and those that feed on the herbivores are called ______________ consumers. 16. What would happen to the populations of a specific roducers in a certain area if the primary consumer that feeds on that producer suddenly became extinct? 17. Density ____________ factors limit population growth when populations are very large. a. Give one example: 18. Density ____________ factors limit population growth regardless of population size. a. Give one example: There has been a lot of vocabulary with this unit. Be sure that you not only understand the terms, but you also know how to apply them to various situations. The list below should help you determine which terms you know and which you need to study more. abiotic autotrophs biodiversity biome biosphere biotic birth rate carnivore carrying capacity carrying capacity climax community commensalism community competitive exclusion principle death rate decomposers detritivores detritus ecological energy pyramid ecology ecosystem ecosystem emigration energy flow exponential growth food chains food webs habitat herbivore herbivory heterotrophs immigration lichens logistic growth mutualism niche omnivore parasitism pioneer species population population growth predation primary consumer primary producers primary succession producer scavengers secondary consumer secondary succession species succession symbiosis tertiary consumer trophic levels