studying the ecological impacts of light pollution on wildlife
... Amphibians, including frogs and salamanders (very little is known about the basic light-relevant ecology of caecilians), are good models for examining the impact of light pollution on wildlife for several reasons. First, many species are nocturnally active, such that reproduction and activity primar ...
... Amphibians, including frogs and salamanders (very little is known about the basic light-relevant ecology of caecilians), are good models for examining the impact of light pollution on wildlife for several reasons. First, many species are nocturnally active, such that reproduction and activity primar ...
Guppies and the Empirical Study of Adaptation
... of the change could be seen in retrospect in the dated collections of thousands of moths accumulated by moth fanciers. You might wonder that such a person as a moth fancier could ever exist, but there were ample numbers of them in Victorian England. They were among Charles Darwin’s audience. This ch ...
... of the change could be seen in retrospect in the dated collections of thousands of moths accumulated by moth fanciers. You might wonder that such a person as a moth fancier could ever exist, but there were ample numbers of them in Victorian England. They were among Charles Darwin’s audience. This ch ...
The Role of Infectious Diseases in Marine Communities M
... parasites, and they differ in trophic strategy from predators in that they attack just one resource during a particular parasitic life stage. They differ in trophic strategy from decomposers by attacking living resources. Parasites have a diversity of trophic strategies, and we use these strategies ...
... parasites, and they differ in trophic strategy from predators in that they attack just one resource during a particular parasitic life stage. They differ in trophic strategy from decomposers by attacking living resources. Parasites have a diversity of trophic strategies, and we use these strategies ...
Reef Fishes at All Trophic Levels Respond Positively to
... Department of Environment, Costa Rica Sistema Nacional de Areas de Conservacion, Galapagos National Parks Service, NSW Department of Primary Industries, New Zealand Department of Conservation, Panama Autoridad Nacional del Ambiente, Parks Victoria, Parques Nacionales Naturales de Colombia, Rottnest ...
... Department of Environment, Costa Rica Sistema Nacional de Areas de Conservacion, Galapagos National Parks Service, NSW Department of Primary Industries, New Zealand Department of Conservation, Panama Autoridad Nacional del Ambiente, Parks Victoria, Parques Nacionales Naturales de Colombia, Rottnest ...
Inertia: the discrepancy between individual and common good in
... performance. Individuals can be selected to have traits that diminish a common good and make population persistence difficult. At the extreme, the discrepancy between levels of selection is predicted to make traits evolve towards values at which a population can no longer persist (evolutionary suici ...
... performance. Individuals can be selected to have traits that diminish a common good and make population persistence difficult. At the extreme, the discrepancy between levels of selection is predicted to make traits evolve towards values at which a population can no longer persist (evolutionary suici ...
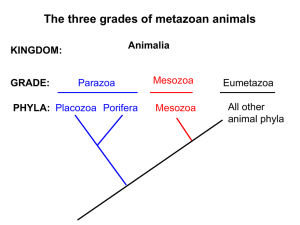
Porifera_1-18
... (predation and competition) are important : •Competition plays a more important role in determining sponge diversity in mangrove habitats. •Predation plays a more important role in determining sponge diversity in coral reef habitats. ...
... (predation and competition) are important : •Competition plays a more important role in determining sponge diversity in mangrove habitats. •Predation plays a more important role in determining sponge diversity in coral reef habitats. ...
Foliar elemental composition of European forest tree species
... among the foliar elemental composition of the species studied and therefore to determine the extent to which foliar N, P, K, Ca and Mg concentrations, N : P, N : K, P : K, N : Ca, P : Ca, K : Ca, N : Mg, P : Mg, K : Mg and Ca : Mg ratios and principal component analysis (PCA) component scores had ph ...
... among the foliar elemental composition of the species studied and therefore to determine the extent to which foliar N, P, K, Ca and Mg concentrations, N : P, N : K, P : K, N : Ca, P : Ca, K : Ca, N : Mg, P : Mg, K : Mg and Ca : Mg ratios and principal component analysis (PCA) component scores had ph ...
- New Zealand Ecological Society
... clearance, and predation and competition from introduced European mammals. Some forest bird species have continued to decline since 1986, while others have increased, usually after intensive species-specific research and management programmes. In this paper, we review what is known about major cause ...
... clearance, and predation and competition from introduced European mammals. Some forest bird species have continued to decline since 1986, while others have increased, usually after intensive species-specific research and management programmes. In this paper, we review what is known about major cause ...
Food choice by the introduced crayfish Procambarus clarkii
... herbivorous, whereas juveniles tended to be predatory. Trophic selection of macroinvertebrates appeared related to their availability. Food choice by different life stages indicates that alterations in the demography or abundance of P. clarkii may change its structural and functional trophic role in ...
... herbivorous, whereas juveniles tended to be predatory. Trophic selection of macroinvertebrates appeared related to their availability. Food choice by different life stages indicates that alterations in the demography or abundance of P. clarkii may change its structural and functional trophic role in ...
The Mechanisms and Consequences of Interspecific Competition
... traits that improve resource capture and competitive effect and responses (Chesson 2000). In other words, plants good at acquiring resources are also good all-around competitors. But other theoretical models predict that tolerance and suppression will be negatively correlated: Traits that improve to ...
... traits that improve resource capture and competitive effect and responses (Chesson 2000). In other words, plants good at acquiring resources are also good all-around competitors. But other theoretical models predict that tolerance and suppression will be negatively correlated: Traits that improve to ...
Peter A. Abrams 1 1 Publications of Peter A. Abrams April 2012 I
... Abrams, P. A. 2002. Will declining population sizes warn us of impending extinctions? American Naturalist. 160:293-305. Abrams, P. A. and X. Chen. 2002. The evolution of traits affecting resource acquisition and predator vulnerability; character displacement under real and apparent competition. Amer ...
... Abrams, P. A. 2002. Will declining population sizes warn us of impending extinctions? American Naturalist. 160:293-305. Abrams, P. A. and X. Chen. 2002. The evolution of traits affecting resource acquisition and predator vulnerability; character displacement under real and apparent competition. Amer ...
Mediterranean-climate oak savannas: the interplay between abiotic
... Africa, Protea nitida in south Africa and Eucalyptus sp. in Australia. Interactions between the two contrasting life-forms, trees and herbs, in savannas may be synergistic or antago- ...
... Africa, Protea nitida in south Africa and Eucalyptus sp. in Australia. Interactions between the two contrasting life-forms, trees and herbs, in savannas may be synergistic or antago- ...
pdf
... fan size were calculated for all colonies sampled (Table 5). In no species did the porosity values vary with the size of the colony. However, this parameter showed a high degree of variation in all species, ranging from 1.9 to 6.8 in E. singularis, from 2.2 to 8.5 in E. cavolini and from 1.9 to 4.4 ...
... fan size were calculated for all colonies sampled (Table 5). In no species did the porosity values vary with the size of the colony. However, this parameter showed a high degree of variation in all species, ranging from 1.9 to 6.8 in E. singularis, from 2.2 to 8.5 in E. cavolini and from 1.9 to 4.4 ...
the maintenance of species diversity by disturbance
... It originated in the early theoretical work of Volterra (1928), who concluded that species utilizing resources in an identical fashion are unlikely to stably coexist. The experimental studies of Gause (1934) reinforced this idea, showing that two species do not coexist, at least not in a simple syst ...
... It originated in the early theoretical work of Volterra (1928), who concluded that species utilizing resources in an identical fashion are unlikely to stably coexist. The experimental studies of Gause (1934) reinforced this idea, showing that two species do not coexist, at least not in a simple syst ...
The Role of Whales in Marine Ecosystems
... The Big Unanswered Questions • Which is more important: top-down or bottom-up forcing – *Both* are important – As whales recover, top-down forcing deserves more attention ...
... The Big Unanswered Questions • Which is more important: top-down or bottom-up forcing – *Both* are important – As whales recover, top-down forcing deserves more attention ...
Great Basin Fact Sheet No. 1: Putting Resilience and Resistance
... among alternative states) to describe the range in composition and function of plant communities within ESDs (Briske et al. 2008). STMs illustrate changes or transitions among states that are characterized by thresholds that may persist over time without active intervention. They also show restorati ...
... among alternative states) to describe the range in composition and function of plant communities within ESDs (Briske et al. 2008). STMs illustrate changes or transitions among states that are characterized by thresholds that may persist over time without active intervention. They also show restorati ...
population
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
original version of Chapter 5
... Fundamental and realised niche ......................................................................................... 8 ...
... Fundamental and realised niche ......................................................................................... 8 ...
the biology, ecology and conservation of euphorbia
... provided better predictions of population density) and a more comprehensive survey and data analysis in this study, and a failure to implement the conservation management plan proposed by Raal (1986). It is estimated that the total number of individuals in all the populations comprise approximately ...
... provided better predictions of population density) and a more comprehensive survey and data analysis in this study, and a failure to implement the conservation management plan proposed by Raal (1986). It is estimated that the total number of individuals in all the populations comprise approximately ...
effects on plant abundance, distribution and population growth
... based on how strongly various herbivores influence single components of plant performance, such as reproduction or biomass. Whether these results extrapolate to the plant population level is uncertain, and clouds generalizations about the relative importance of particular consumers in influencing pl ...
... based on how strongly various herbivores influence single components of plant performance, such as reproduction or biomass. Whether these results extrapolate to the plant population level is uncertain, and clouds generalizations about the relative importance of particular consumers in influencing pl ...
Models of Extinction
... than a realistic theory. At the other end of the scale, an increasing number of biologists and ecologists are supporting the idea that extinction has biotic causes—that extinction is a natural part of the dynamics of ecosystems and would take place regardless of any stresses arising from the environ ...
... than a realistic theory. At the other end of the scale, an increasing number of biologists and ecologists are supporting the idea that extinction has biotic causes—that extinction is a natural part of the dynamics of ecosystems and would take place regardless of any stresses arising from the environ ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.