Ecology - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... • The occupation of an organism is called its niche. This includes how it gets food, reproduces, avoids predators, etc. • The niche of an organism determines its habitat. • The way an organism has evolved to survive determines where it can live. ...
... • The occupation of an organism is called its niche. This includes how it gets food, reproduces, avoids predators, etc. • The niche of an organism determines its habitat. • The way an organism has evolved to survive determines where it can live. ...
File - Pedersen Science
... What is exponential population growth? Explain why the logistical population growth model can accurately model populations in the environment. Look at the graph below, what does it tell you and why? How does “K” fit in to all of this? According to the graph to the right, which has the greatest popul ...
... What is exponential population growth? Explain why the logistical population growth model can accurately model populations in the environment. Look at the graph below, what does it tell you and why? How does “K” fit in to all of this? According to the graph to the right, which has the greatest popul ...
ECOLOGY Study Guide
... What is exponential population growth? Explain why the logistical population growth model can accurately model populations in the environment. Look at the graph below, what does it tell you and why? How does “K” fit in to all of this? Accoriding to the graph to the right, which has the greatest popu ...
... What is exponential population growth? Explain why the logistical population growth model can accurately model populations in the environment. Look at the graph below, what does it tell you and why? How does “K” fit in to all of this? Accoriding to the graph to the right, which has the greatest popu ...
04populations2 3564KB Nov 01 2012 07:59:58 AM
... • Two types of factors can also limit population sizes. 1. density-dependent factors: a factor that gets worse as the population size increases * overcrowding *parasites/disease *aggression amongst members * neglect of offspring ...
... • Two types of factors can also limit population sizes. 1. density-dependent factors: a factor that gets worse as the population size increases * overcrowding *parasites/disease *aggression amongst members * neglect of offspring ...
tracking form
... in the food web or chain (Be able to relate biotic factors and terms such as carnivore, herbivore, etc.) Describe what a niche is. Discriminate and explain the difference between a realized niche and a fundamental niche (Glossary, eorarth.org). Explain how limiting factors and range of tolerance aff ...
... in the food web or chain (Be able to relate biotic factors and terms such as carnivore, herbivore, etc.) Describe what a niche is. Discriminate and explain the difference between a realized niche and a fundamental niche (Glossary, eorarth.org). Explain how limiting factors and range of tolerance aff ...
File
... a a population can contain more than one species b. an ecosystem includes both biotic and abiotic features c. a community refers to a single species d. a habitat describes the role of an organism in its ecosystem 3. Which of the following represents a producer-consumer relationship? a. Hawks eating ...
... a a population can contain more than one species b. an ecosystem includes both biotic and abiotic features c. a community refers to a single species d. a habitat describes the role of an organism in its ecosystem 3. Which of the following represents a producer-consumer relationship? a. Hawks eating ...
EOC Benchmark Review #3 Ecology and Evolution
... EOC Benchmark Review #3 Ecology and Evolution There are 20 multiple-choice questions and 3 open- ended problems on this Assessment. In order to do well, you should review the following concepts. Ecology o The flow of energy through an ecosystem Food webs Food chains Food pyramids Trophic lev ...
... EOC Benchmark Review #3 Ecology and Evolution There are 20 multiple-choice questions and 3 open- ended problems on this Assessment. In order to do well, you should review the following concepts. Ecology o The flow of energy through an ecosystem Food webs Food chains Food pyramids Trophic lev ...
Population Size Factors
... • Population sizes change based on resources • Increase – Immigration – Births ...
... • Population sizes change based on resources • Increase – Immigration – Births ...
Final exam
... What are examples of adaptations selected for by abiotic forces? B. Biotic (living) factors: What are some examples? What are examples of adaptations selected for by biotic forces? V. Aquatic ecosystems and terrestrial biomes (We didn’t go through these systematically, but you still need to know abo ...
... What are examples of adaptations selected for by abiotic forces? B. Biotic (living) factors: What are some examples? What are examples of adaptations selected for by biotic forces? V. Aquatic ecosystems and terrestrial biomes (We didn’t go through these systematically, but you still need to know abo ...
03_EcologyPP
... environment that may effect the organism. • Examples- sunlight, heat, precipitation, humidity, wind, soil conditions, or water currents ...
... environment that may effect the organism. • Examples- sunlight, heat, precipitation, humidity, wind, soil conditions, or water currents ...
Populations
... • Population increases to certain size and levels off. • Occurs when predators or other factors limit growth • K=Carrying Capacity - Maximum population size environment can support indefinitely. K ...
... • Population increases to certain size and levels off. • Occurs when predators or other factors limit growth • K=Carrying Capacity - Maximum population size environment can support indefinitely. K ...
Sheet
... 29. Compare and contrast primary and secondary succession. Give an example of each. 30. What is evolution? What would describe evolutionary success? 31. What is predation? Mutualism? Commensalism? Parasitism? 32. What is the ultimate source of energy in a land ecosystem? 33. What do age structure di ...
... 29. Compare and contrast primary and secondary succession. Give an example of each. 30. What is evolution? What would describe evolutionary success? 31. What is predation? Mutualism? Commensalism? Parasitism? 32. What is the ultimate source of energy in a land ecosystem? 33. What do age structure di ...
File
... Detritivores- non living ( get energy from) Decomposers – nonliving and their wastes. Tropic levels Food chains ...
... Detritivores- non living ( get energy from) Decomposers – nonliving and their wastes. Tropic levels Food chains ...
Unit 2 * Ecology
... the same species, which interbreed and live in the same area at the same time ...
... the same species, which interbreed and live in the same area at the same time ...
AP BiologyEcology Unit Study QuestionsMs. Dolce CHAPTER 53
... 2. What are some possible difficulties in counting populations? 3. Describe three patterns of dispersal. 4. Compare the survival strategies of species and give an example of each type. a. Type I b. Type II c. Type III 5. Write the formula for population growth without limits. Define the terms. 6. De ...
... 2. What are some possible difficulties in counting populations? 3. Describe three patterns of dispersal. 4. Compare the survival strategies of species and give an example of each type. a. Type I b. Type II c. Type III 5. Write the formula for population growth without limits. Define the terms. 6. De ...
Ecology - Pitt County Schools
... All _______________ organisms _________________ factors have effects on ______________ things and often determine which ___________ survive in a particular ______________ . For ex., lack of _____________ can cause drought in a _____________, so the animals that depend on ______________ for food woul ...
... All _______________ organisms _________________ factors have effects on ______________ things and often determine which ___________ survive in a particular ______________ . For ex., lack of _____________ can cause drought in a _____________, so the animals that depend on ______________ for food woul ...
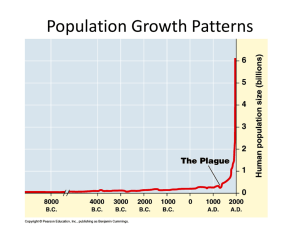
How Populations Grow - Brookwood High School
... B. Population growth: increase in size of population with time. ...
... B. Population growth: increase in size of population with time. ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.