* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Populations
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Human population planning wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
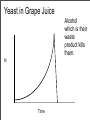
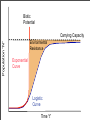
Populations Environmental Science NSC 22304 Ecosystem • All living and non-living components in a particular area Biotic •Plants •Animals •Microbes Abiotic •Soil •Water •Air •Detritus Ecosystem Subgroups Community-All living organisms in an ecosystem (i.e. biotic protion) Population-All organisms of the same species in an ecosystem Example: All the pickeral frogs in one wetland Population All organisms of the same species in an ecosystem Pickeral frogs in two different wetlands are 2 different populations though same species. Population Size • • Number of individuals in a population Symbolized by letter “N” N=12 N=8 Change in Population Size Activity • • • • Beetles in corn field Start (Week 0) - 10 beetles Doubles every week How many in week 10? Striped Corn Beetle Population Growth 12000 10240 10000 N 8000 6000 5120 4000 2000 0 2560 10 20 40 80 160 1280 640 320 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Weeks Exponential “J” Growth Curve • Population size increases proportional to current size. N t • Occurs when new species placed in environment with lots of food and no predators. Alaskan Island 128 sq miles Yeast in Grape Juice N What do you think causes crash? Time Yeast in Grape Juice N Lack of food is good hypothesis but incorrect. Time Yeast in Grape Juice N Lack of space is good hypothesis but incorrect. Time Yeast in Grape Juice Alcohol which is their waste product kills them. N Time Invasive Species • • • • Species put in an area by humans. Much food. Few if any predators Grow exponentially. Purple Loosestrife • Plant brought to US from Europe for gardens • Escaped to wild • Invades wetlands • Outcompeting native species. Zebra Mussel • Accidentally introduced to Great Lakes in ship ballast water. • Has spread throughout Mississippi River and tributaries as well as other river systems. • Gets on boats, piers • Clogs industrial pipes Can you think of other invasive species? Logistic “S” Growth Curve • Population increases to certain size and levels off. • Occurs when predators or other factors limit growth • K=Carrying Capacity - Maximum population size environment can support indefinitely. K ( ) dN = rN K-N dt K N t Biotic Potential Population “N” Carrying Capacity Environmental Resistance Exponential Curve Logistic Curve Time “t” Environmental Resistance • Factors that inhibit population growth • Includes: • • • • Predators Disease or Parasites Competitors Adverse Weather - flood, drought, fire, etc. • Amount of resources - food, space, water, etc. Biotic Potential • Biological ability of population to grow. • Factors affecting potential: • • • • • • Life span Age of first reproduction Number of offspring per reproduction Number of times individuals reproduce Ability to spread Ability to withstand adverse conditions Population Balance N Biotic Potential Environmental Resistance