Biology EOC Class 5 - Steilacoom School District
... decrease over time Even throughout = the population will remain constant over time ...
... decrease over time Even throughout = the population will remain constant over time ...
I. What is Ecology? A. Definition: The study of the interactions of
... 1. Humans are as dependent as other organisms on "the environment" - nutrient cycling (decomposition/ release of 'fertilizers') - atmospheric and climatic regulation (maintaining climate and oxygen levels fit for human existence) - water and air waste treatment - food, shelter, and energy (coal, tim ...
... 1. Humans are as dependent as other organisms on "the environment" - nutrient cycling (decomposition/ release of 'fertilizers') - atmospheric and climatic regulation (maintaining climate and oxygen levels fit for human existence) - water and air waste treatment - food, shelter, and energy (coal, tim ...
Marine Ecology
... – Doubling occurs rapidly – Occurs with no limits to growth – e.g fig. 10.2b (dinoflagellates…much like these bacteria) ...
... – Doubling occurs rapidly – Occurs with no limits to growth – e.g fig. 10.2b (dinoflagellates…much like these bacteria) ...
Common language
... •Sheep in Santa Catalina Mountains (Arizona) are likely to be next to go extinct •management of herd and local habitat not enough •settlement, roads, agriculture have made intermountain travel nearly impossible (Krausman 1997) ...
... •Sheep in Santa Catalina Mountains (Arizona) are likely to be next to go extinct •management of herd and local habitat not enough •settlement, roads, agriculture have made intermountain travel nearly impossible (Krausman 1997) ...
14.4 Interactions within Communities
... a given ecosystem. • Some organisms within communities cannot exist independently of one another and work together for survival. ...
... a given ecosystem. • Some organisms within communities cannot exist independently of one another and work together for survival. ...
Parasitism - Nutley Public Schools
... Example: a snake (predator) eating a praying mantis (prey). ...
... Example: a snake (predator) eating a praying mantis (prey). ...
1.1 Safety in the Science Classroom
... Although they are sometimes overlooked, the abiotic components are what allow the biotic components to survive in an ecosystem. Abiotic factors include oxygen, water, nutrients, light and soil. Oxygen is produced by the green plants and certain micro-organisms, and is used by animals and most ot ...
... Although they are sometimes overlooked, the abiotic components are what allow the biotic components to survive in an ecosystem. Abiotic factors include oxygen, water, nutrients, light and soil. Oxygen is produced by the green plants and certain micro-organisms, and is used by animals and most ot ...
Ecosystems
... Although they are sometimes overlooked, the abiotic components are what allow the biotic components to survive in an ecosystem. Abiotic factors include oxygen, water, nutrients, light and soil. Oxygen is produced by the green plants and certain micro-organisms, and is used by animals and most ot ...
... Although they are sometimes overlooked, the abiotic components are what allow the biotic components to survive in an ecosystem. Abiotic factors include oxygen, water, nutrients, light and soil. Oxygen is produced by the green plants and certain micro-organisms, and is used by animals and most ot ...
File
... –Temperature, light, water, wind (together = climate, prevailing weather conditions at a certain location) ...
... –Temperature, light, water, wind (together = climate, prevailing weather conditions at a certain location) ...
I can classify organisms as producers, consumers, or decomposers
... 8. I can identify factors in an ecosystem that determine and affect population size (birth rate, death rate, immigration, emigration, limiting factors). ...
... 8. I can identify factors in an ecosystem that determine and affect population size (birth rate, death rate, immigration, emigration, limiting factors). ...
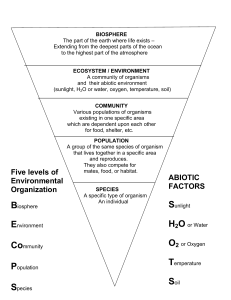
Five levels of Environmental Organization ABIOTIC FACTORS
... BIOSPHERE The part of the earth where life exists – Extending from the deepest parts of the ocean to the highest part of the atmosphere ...
... BIOSPHERE The part of the earth where life exists – Extending from the deepest parts of the ocean to the highest part of the atmosphere ...
Populations, Communities, Ecosystems
... 12. Exponential Growth Model – It continues to grow very fast at maximum reproduction rate (r) even beyond carrying capacity. Soon population faces population crash when the resources are exhausted. It is J- shaped. It is called Boom and Bust population. It is found in Opportunistic Populations. For ...
... 12. Exponential Growth Model – It continues to grow very fast at maximum reproduction rate (r) even beyond carrying capacity. Soon population faces population crash when the resources are exhausted. It is J- shaped. It is called Boom and Bust population. It is found in Opportunistic Populations. For ...
Population
... individuals per unit of area 3. Growth Rate: Increase, Decrease, or Stay the Same ...
... individuals per unit of area 3. Growth Rate: Increase, Decrease, or Stay the Same ...
Ecology Review from 7th Grade PowerPoint
... • At any step along the way, an organism might die and be consumed by other scavengers or break down through the work of decomposers, such as insects and bacteria. ...
... • At any step along the way, an organism might die and be consumed by other scavengers or break down through the work of decomposers, such as insects and bacteria. ...
Matcuk-Grischow Biology 2014-09-01
... • Describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e., organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere). • Describe characteristic biotic and abiotic components of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems • Describe how energy flows through an ecosystem (e.g., food chains, food webs, ene ...
... • Describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e., organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere). • Describe characteristic biotic and abiotic components of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems • Describe how energy flows through an ecosystem (e.g., food chains, food webs, ene ...
Vocabulary for the Adaptation and Variation: Colorado Animals and
... organism becomes better suited to its habitat. Plants with smooth-edged leaves are better adapted to warmer climates. Biology – A science that deals with living beings and life processes. Kyle planned to study biology in college to work at the zoo. Characteristics - Features that can be used to iden ...
... organism becomes better suited to its habitat. Plants with smooth-edged leaves are better adapted to warmer climates. Biology – A science that deals with living beings and life processes. Kyle planned to study biology in college to work at the zoo. Characteristics - Features that can be used to iden ...
Species Competition
... When they compete, these niches overlap The more they overlap the more they compete Humans are competing with species for food, space and other resources ...
... When they compete, these niches overlap The more they overlap the more they compete Humans are competing with species for food, space and other resources ...
ap ecology review sheet
... number of species found on an island, and explain how such concepts are important in conservation biology and restoration ecology. 8. You should be able to discuss and calculate biodiversity, and discuss the how prehuman and contemporary processes or actions affect biodiversity. 9. You should be abl ...
... number of species found on an island, and explain how such concepts are important in conservation biology and restoration ecology. 8. You should be able to discuss and calculate biodiversity, and discuss the how prehuman and contemporary processes or actions affect biodiversity. 9. You should be abl ...
Biomes and Ecological Succession Test Review Students all need
... 17. How does biodiversity contribute to sustainability? ...
... 17. How does biodiversity contribute to sustainability? ...
Biomes Study Guide: Bio Lab H
... Chapter 3 Ch 3 vocab: ammonia, biogeochemical cycle, nitrogen fixation, denitrification, limiting nutrient, ecosystems, keystone species, food chain, ...
... Chapter 3 Ch 3 vocab: ammonia, biogeochemical cycle, nitrogen fixation, denitrification, limiting nutrient, ecosystems, keystone species, food chain, ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.