Ecosystem Review Game
... If two species occupy the same niche, one of the species will eventually ___________. ...
... If two species occupy the same niche, one of the species will eventually ___________. ...
Homework
... Basic unit of biological classification Organisms that resemble each other, that are similar in genetic makeup, chemistry, and behavior, and that are able to interbreed and produce fertile offspring ...
... Basic unit of biological classification Organisms that resemble each other, that are similar in genetic makeup, chemistry, and behavior, and that are able to interbreed and produce fertile offspring ...
Populations 2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... -factors that affect biotic pot.: age at reproduction, freq. of reprod., # of offspring, life span, death rate ...
... -factors that affect biotic pot.: age at reproduction, freq. of reprod., # of offspring, life span, death rate ...
Niches PPT - Staff Web Pages
... – interactions among organisms of same species, – interactions among organisms of different species, – effects of abiotic factors on interacting species ...
... – interactions among organisms of same species, – interactions among organisms of different species, – effects of abiotic factors on interacting species ...
Presentation
... Explain the relationship between the three populations of organisms and how their growth or decline rate are related to each other. Explain what density dependent factor might have influenced the two animal populations. ...
... Explain the relationship between the three populations of organisms and how their growth or decline rate are related to each other. Explain what density dependent factor might have influenced the two animal populations. ...
Energy in an Ecosystem Summary Notes
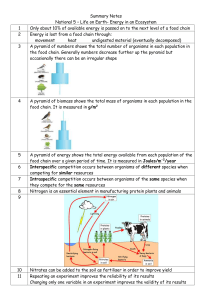
... food chain over a given period of time. It is measured in Joules/m-2/year Interspecific competition occurs between organisms of different species when competing for similar resources Intraspecific competition occurs between organisms of the same species when they compete for the same resources Nitro ...
... food chain over a given period of time. It is measured in Joules/m-2/year Interspecific competition occurs between organisms of different species when competing for similar resources Intraspecific competition occurs between organisms of the same species when they compete for the same resources Nitro ...
Biology 35I - Science-with
... G.1.1 Outline the factors that affect the distribution of plant species, including temperature, water, light, soil pH, salinity and mineral nutrients. G.1.2 ...
... G.1.1 Outline the factors that affect the distribution of plant species, including temperature, water, light, soil pH, salinity and mineral nutrients. G.1.2 ...
summary notes the biosphere
... food or water, disease, build up of toxic wastes and lack of space. Competition occurs when 2 or more individuals need a resource (like food or shelter) that is in short supply. When 2 species compete for a resource the result will be a reduction in the population size of the poorer competitor. Nutr ...
... food or water, disease, build up of toxic wastes and lack of space. Competition occurs when 2 or more individuals need a resource (like food or shelter) that is in short supply. When 2 species compete for a resource the result will be a reduction in the population size of the poorer competitor. Nutr ...
Ecology
... • Any substance that contaminates any part of an environment • The presence in or introduction into the environment of a substance or thing that has harmful or poisonous effects. ...
... • Any substance that contaminates any part of an environment • The presence in or introduction into the environment of a substance or thing that has harmful or poisonous effects. ...
Jeopardy-Ecology
... • What are photosynthesis and chemosynthesis? (Photosynthesis is by far the most common) ...
... • What are photosynthesis and chemosynthesis? (Photosynthesis is by far the most common) ...
Organismal and Community Ecology
... offspring will be even more difficult for the wolves to catch, and only the fastest wolves (or perhaps the wolves who are genetically capable of devising strategies to hunt very fast prey) will get enough food to survive. An evolutionary “Cold War” ensues. Example: Flowers compete for pollinators. T ...
... offspring will be even more difficult for the wolves to catch, and only the fastest wolves (or perhaps the wolves who are genetically capable of devising strategies to hunt very fast prey) will get enough food to survive. An evolutionary “Cold War” ensues. Example: Flowers compete for pollinators. T ...
Unit 2: Multi-cellular organisms
... 12. Biologists investigate an ecosystem’s community by SAMPLING its plants and animals. To do this, they often use quantitative techniques such as PITFALL traps and QUADRATS. 13. For sampling to give a VALID representation of the community, MANY samples must be taken and mean results calculated. ...
... 12. Biologists investigate an ecosystem’s community by SAMPLING its plants and animals. To do this, they often use quantitative techniques such as PITFALL traps and QUADRATS. 13. For sampling to give a VALID representation of the community, MANY samples must be taken and mean results calculated. ...
Key Unit 9 Study Guide
... 4. The niche of an organism is the place in which it lives, and the role that it plays in its environment. Explain the niche of a honeybee in its environment AND what would happen if all the bees died: The honeybee collects nectar from flowers to take back to the hive for food. It pollinates flower ...
... 4. The niche of an organism is the place in which it lives, and the role that it plays in its environment. Explain the niche of a honeybee in its environment AND what would happen if all the bees died: The honeybee collects nectar from flowers to take back to the hive for food. It pollinates flower ...
File
... Length of Reproductive Life – the age of sexual maturity and the number of years the individual can reproduce Example: African elephants reach sexual maturity at about 15 years of age, but may reproduce until they are 90! ...
... Length of Reproductive Life – the age of sexual maturity and the number of years the individual can reproduce Example: African elephants reach sexual maturity at about 15 years of age, but may reproduce until they are 90! ...
Lecture notes for r and K selection and pests and weeds
... What regulates species abundance? population size fluctuates, but extinction is rare and uncontrolled (exponential) growth is rare examples of extinctions and uncontrolled growth? ...
... What regulates species abundance? population size fluctuates, but extinction is rare and uncontrolled (exponential) growth is rare examples of extinctions and uncontrolled growth? ...
1 Community Ecology
... and resource requirements. Manifest in the absence of other organisms. b) realized: niche space determined by combined physical and biological factors. Realized in presence of other organisms fundamental ...
... and resource requirements. Manifest in the absence of other organisms. b) realized: niche space determined by combined physical and biological factors. Realized in presence of other organisms fundamental ...
Lesson 6.2
... 1. Intraspecific: between the same species Ex. Hermit crabs compete for the biggest shell 2. Interspecific: between different species Ex. Sponges & coral compete for plankton ...
... 1. Intraspecific: between the same species Ex. Hermit crabs compete for the biggest shell 2. Interspecific: between different species Ex. Sponges & coral compete for plankton ...
Interactions among species
... Niche = what an organisms does and how it interacts with the environment (Job) ...
... Niche = what an organisms does and how it interacts with the environment (Job) ...
Interactions and Ecosystems Review JEOPARDY
... Both hungry, you and your friend both get to the fridge at the same time…but there’s only one piece of cake! This is an example of… ...
... Both hungry, you and your friend both get to the fridge at the same time…but there’s only one piece of cake! This is an example of… ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.