The Gray Zone: Relationships between habitat loss and marine
... biology is the prediction of the decrease in species number and abundance in response to a reduction in the area of the habitat (Hanski, 2005). Additionally, there are other fundamental but often overlooked components of diversity (Gray, 1997), related to species identity (i.e. species are not equiv ...
... biology is the prediction of the decrease in species number and abundance in response to a reduction in the area of the habitat (Hanski, 2005). Additionally, there are other fundamental but often overlooked components of diversity (Gray, 1997), related to species identity (i.e. species are not equiv ...
Nature-based Solutions: New Influence for
... While we advocate that the open nature of the term NBS can favor its success, we contend that it is important to specify which solutions should and should not be considered as NBS. We illustrate this with the development of green roofs and walls in cities. Having in mind the sole objective of develo ...
... While we advocate that the open nature of the term NBS can favor its success, we contend that it is important to specify which solutions should and should not be considered as NBS. We illustrate this with the development of green roofs and walls in cities. Having in mind the sole objective of develo ...
NOBANIS – Invasive Alien Species Fact Sheet Procyon lotor
... consisting of four main components: monitoring, control, research and communication. The goal of control must be complete eradication of P. lotor from colonies and should be carried out in early stages of colonization, when P. lotor densities are low. The main method used to control P. lotor on rock ...
... consisting of four main components: monitoring, control, research and communication. The goal of control must be complete eradication of P. lotor from colonies and should be carried out in early stages of colonization, when P. lotor densities are low. The main method used to control P. lotor on rock ...
DOC file - City of Fort Collins Public Records
... fescue is considered an indicator of late successional forest stands within this ecosystem (Tirmenstein 1987). Pockets of spike fescue have survived on several ridgetops and slopes at the outer edges of the fire at the north end of the property. These areas are currently threatened by the invasion o ...
... fescue is considered an indicator of late successional forest stands within this ecosystem (Tirmenstein 1987). Pockets of spike fescue have survived on several ridgetops and slopes at the outer edges of the fire at the north end of the property. These areas are currently threatened by the invasion o ...
Predicting community structure of ground-foraging ant
... chemical contamination, we used a fresh piece of Tygon tubing for each trial, and washed and dried our hands before every trial. Ant workers were collected with an aspirator from tuna fish baits (which were not part of the abundance censuses), and were used in behavioral trials within 3 h of field c ...
... chemical contamination, we used a fresh piece of Tygon tubing for each trial, and washed and dried our hands before every trial. Ant workers were collected with an aspirator from tuna fish baits (which were not part of the abundance censuses), and were used in behavioral trials within 3 h of field c ...
Discoveries of new mammal species and their
... mammal species we found were of three types. The first was morphologically distinct species found in previously poorly surveyed areas. The second, the result of using molecular genetic techniques, was discoveries that the geographic range of a well-known organism was actually the combined ranges of ...
... mammal species we found were of three types. The first was morphologically distinct species found in previously poorly surveyed areas. The second, the result of using molecular genetic techniques, was discoveries that the geographic range of a well-known organism was actually the combined ranges of ...
species - TavistockCollegeScience
... interbreeding (mating) to produce fertile offspring (i.e. offspring that can breed to give rise to more offspring) and are reproductively isolated from other species Habitat The environment in which a particular organism (species) lives – e.g earthworm - soil; fish -pond. Organisms from a single spe ...
... interbreeding (mating) to produce fertile offspring (i.e. offspring that can breed to give rise to more offspring) and are reproductively isolated from other species Habitat The environment in which a particular organism (species) lives – e.g earthworm - soil; fish -pond. Organisms from a single spe ...
On the Use of Surrogate Species in Conservation Biology
... Surrogate species are employed to indicate the extent of various types of anthropogenic influence (e.g., Burdick et al. 1989; Stolte & Mangis 1992) or to track population changes of other species; these types of surrogate are by far the best worked examples (D. H. McKenzie et al. 1992). Surrogate sp ...
... Surrogate species are employed to indicate the extent of various types of anthropogenic influence (e.g., Burdick et al. 1989; Stolte & Mangis 1992) or to track population changes of other species; these types of surrogate are by far the best worked examples (D. H. McKenzie et al. 1992). Surrogate sp ...
Nitrogen enrichment and plant communities
... and mycorrhizal symbiosis.33 In addition to biological N fixation through symbiosis, plants can also exert feedback control over N cycling although effects of litter chemistry on decomposition and soil microorganism communities34,35 (but see Ref. 36). This concept of multiple resource limitation is ...
... and mycorrhizal symbiosis.33 In addition to biological N fixation through symbiosis, plants can also exert feedback control over N cycling although effects of litter chemistry on decomposition and soil microorganism communities34,35 (but see Ref. 36). This concept of multiple resource limitation is ...
Spatio-temporal community dynamics induced by frequency
... a growing body of evidence that frequency dependent effects mediated by both biotic and abiotic changes to the subsurface environment may play an important role in invasiveness by exotic plant species, and must be understood and considered for effective conservation and restoration of plant communit ...
... a growing body of evidence that frequency dependent effects mediated by both biotic and abiotic changes to the subsurface environment may play an important role in invasiveness by exotic plant species, and must be understood and considered for effective conservation and restoration of plant communit ...
The introduction of alien mammals into the broader Western and
... implications for the distribution of species, as well for the ecosystems that receive them. This process, referred to as the introduction of species, results in species being recognised as alien to an area (i.e. they did not arrive there through natural evolutionary or dispersal process) and such sp ...
... implications for the distribution of species, as well for the ecosystems that receive them. This process, referred to as the introduction of species, results in species being recognised as alien to an area (i.e. they did not arrive there through natural evolutionary or dispersal process) and such sp ...
America`s Least Wanted: Alien Species
... Introduced species may compete directly with natives for food or space, may compete indirectly by changing the food web or physical environment, or may prey on or hybridize with native species. Those natives whose natural range and population size already are limited, or have declined for other reas ...
... Introduced species may compete directly with natives for food or space, may compete indirectly by changing the food web or physical environment, or may prey on or hybridize with native species. Those natives whose natural range and population size already are limited, or have declined for other reas ...
Fitness and physiology in a variable environment
... small rain events and a greater number of days between precipitation pulse events tended to be worse, on average, for all desert annual species. Species with high relative growth rates and low water-use efficiency had greater standardized annual fitness than other species in years with greater numbe ...
... small rain events and a greater number of days between precipitation pulse events tended to be worse, on average, for all desert annual species. Species with high relative growth rates and low water-use efficiency had greater standardized annual fitness than other species in years with greater numbe ...
Using Historical and Experimental Data to Reveal
... activity and density because a change in either activity or density will affect the rate at which ants fall into the traps [34]. Despite this drawback, pitfall traps are commonly used in studies such as ours because they are easy to standardize and have little impact on soil, litter, or ant populati ...
... activity and density because a change in either activity or density will affect the rate at which ants fall into the traps [34]. Despite this drawback, pitfall traps are commonly used in studies such as ours because they are easy to standardize and have little impact on soil, litter, or ant populati ...
Abstract
... Successful recovery of threatened populations of Puget Sound steelhead (Oncorhynchus mykiss) will undoubtedly require knowledge of the predominant processes affecting population productivity. Here we utilize a 24 year data set of spawners and total resulting recruitment of adult wild winter run stee ...
... Successful recovery of threatened populations of Puget Sound steelhead (Oncorhynchus mykiss) will undoubtedly require knowledge of the predominant processes affecting population productivity. Here we utilize a 24 year data set of spawners and total resulting recruitment of adult wild winter run stee ...
Predictors of species sensitivity to fragmentation
... size provide indirect empirical evidence for the increased survival of larger populations (reviewed by Diamond 1984; see also Sarre et al. 1996; Bolger et al. 1997; Warburton 1997), very few studies have tested this prediction directly. This is due to the fact that in the case of fragmentation drive ...
... size provide indirect empirical evidence for the increased survival of larger populations (reviewed by Diamond 1984; see also Sarre et al. 1996; Bolger et al. 1997; Warburton 1997), very few studies have tested this prediction directly. This is due to the fact that in the case of fragmentation drive ...
Interactions among invaders: community and ecosystem effects of
... health and the economy. Despite recent progress in invasion biology, a more complete understanding of invader impacts and the mechanisms through which they occur is essential to effective management and remediation of biological invasions. From well-studied cases, it is clear that invasions can lead ...
... health and the economy. Despite recent progress in invasion biology, a more complete understanding of invader impacts and the mechanisms through which they occur is essential to effective management and remediation of biological invasions. From well-studied cases, it is clear that invasions can lead ...
Biology special study material
... Ans: Primary, secondary, tertiary and graafian follicles(4 part to be labeled) ½X4=2 4. Draw the microscopic structure of human sperm and relate its different parts with their functions. 5 Ans: Plasma membrane-envelops the whole body of sperm; Acrosome – filled with enzymes that help in fertilizatio ...
... Ans: Primary, secondary, tertiary and graafian follicles(4 part to be labeled) ½X4=2 4. Draw the microscopic structure of human sperm and relate its different parts with their functions. 5 Ans: Plasma membrane-envelops the whole body of sperm; Acrosome – filled with enzymes that help in fertilizatio ...
hau_vivian_tbio_brief1
... number of species and their populations (Venier et al.). By changing the demographics of the population there could be shifts for the worst. If the young are wiped out, there will not be a next generation. If the adults are gone, the young may die. Some agriculture methods can be more damaging than ...
... number of species and their populations (Venier et al.). By changing the demographics of the population there could be shifts for the worst. If the young are wiped out, there will not be a next generation. If the adults are gone, the young may die. Some agriculture methods can be more damaging than ...
140818 PPR Redef of Anthroposphere R7.1
... In the case of BE, the biologist H.T. Odum studied the stocks and flows of mass and energy in a large number of ecosystems. He also postulated that the insights gained there were directly applicable to human economic systems. This view was further developed by his student C.A.S. Hall who undertook e ...
... In the case of BE, the biologist H.T. Odum studied the stocks and flows of mass and energy in a large number of ecosystems. He also postulated that the insights gained there were directly applicable to human economic systems. This view was further developed by his student C.A.S. Hall who undertook e ...
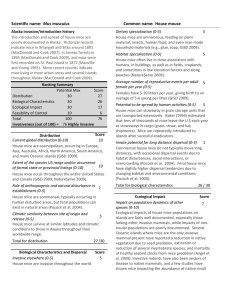
House mouse Scientific name: Mus musculus
... species threatened (0‐3) House mice usually inhabit disturbed areas and have not been reported to threaten any valuable native species. Insular populations of mice are more likely to impact natural areas and native species (Angel et al. 2009). No impacts to that degree have been reported in A ...
... species threatened (0‐3) House mice usually inhabit disturbed areas and have not been reported to threaten any valuable native species. Insular populations of mice are more likely to impact natural areas and native species (Angel et al. 2009). No impacts to that degree have been reported in A ...
Social Evolution and Inclusive Fitness Theory: An Introduction
... Other individual behaviors seem to impact on the reproduction of others in a much more “deliberate” manner, however. Examples of such social behaviors abound in the natural world. Quite possibly the most well-known examples are among the social insects, considered by Darwin himself [Darwin, 1859]. I ...
... Other individual behaviors seem to impact on the reproduction of others in a much more “deliberate” manner, however. Examples of such social behaviors abound in the natural world. Quite possibly the most well-known examples are among the social insects, considered by Darwin himself [Darwin, 1859]. I ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.