how do different measures of functional diversity perform?
... from individual plants. BIODEPTH monoculture measurements were the ecosystem-level properties that were also measured in species mixtures (measurements that contained missing values were not included as candidate traits). Monoculture measurements from all Northern European BIODEPTH sites were pooled ...
... from individual plants. BIODEPTH monoculture measurements were the ecosystem-level properties that were also measured in species mixtures (measurements that contained missing values were not included as candidate traits). Monoculture measurements from all Northern European BIODEPTH sites were pooled ...
Predation, seed size partitioning and the evolution of
... body mass increases more rapidly with bill depth among Kenya finches (Fringillidae, Passeridae, Estrildidae) than among Gal~ipagos finches (Geospiza; Emberizidae) (Schluter, 1988a). For large-billed finches, increased body size may improve predator evasion for at least two reasons. First, as body ma ...
... body mass increases more rapidly with bill depth among Kenya finches (Fringillidae, Passeridae, Estrildidae) than among Gal~ipagos finches (Geospiza; Emberizidae) (Schluter, 1988a). For large-billed finches, increased body size may improve predator evasion for at least two reasons. First, as body ma ...
Effects of landscape context on herbivory and parasitism at different
... experienced by an organism depends on its trophic level. We analyzed plant-herbivore and herbivore-parasitoid interactions in 15 agricultural landscapes differing in structural complexity using the rape pollen beetle (Meligethes aeneus), an important pest on oilseed rape (Brassica napus), and its pa ...
... experienced by an organism depends on its trophic level. We analyzed plant-herbivore and herbivore-parasitoid interactions in 15 agricultural landscapes differing in structural complexity using the rape pollen beetle (Meligethes aeneus), an important pest on oilseed rape (Brassica napus), and its pa ...
Theoretical Predictions for How Temperature Affects
... to be known to relate the metabolic model to environmental temperature. To test the effect of differential temperature dependence of primary and secondary production on consumer-prey model predictions, we assigned rates of primary producerand consumer-driven processes the activation energies that re ...
... to be known to relate the metabolic model to environmental temperature. To test the effect of differential temperature dependence of primary and secondary production on consumer-prey model predictions, we assigned rates of primary producerand consumer-driven processes the activation energies that re ...
Predation risk and nest-site selection in the Inca tern
... chamber. None of the interaction and quadratic terms significantly improved the model. Roof and walls had a significant influence on the selection pattern, although these variable were not significant in the stepwise model, presumably because they were correlated with number of cavities (Table 2), w ...
... chamber. None of the interaction and quadratic terms significantly improved the model. Roof and walls had a significant influence on the selection pattern, although these variable were not significant in the stepwise model, presumably because they were correlated with number of cavities (Table 2), w ...
ISBE Poster Abstract Book
... Agent-based models are increasingly used to generate and test mechanistic hypotheses about the emergence of complex group behaviors. However, the predictions from such models can be hard to compare to real world data, because emergent phenomena are difficult to quantify. We demonstrate how social ne ...
... Agent-based models are increasingly used to generate and test mechanistic hypotheses about the emergence of complex group behaviors. However, the predictions from such models can be hard to compare to real world data, because emergent phenomena are difficult to quantify. We demonstrate how social ne ...
Cost-efficient fenced reserves for conservation: single
... The day-to-day reality of management planning is complex, and short funding cycles from uncertain sources mean that building a single large fence is not always feasible. Additional funding following the demonstrated success of an exclosure can be used to leverage further investment to extend the ori ...
... The day-to-day reality of management planning is complex, and short funding cycles from uncertain sources mean that building a single large fence is not always feasible. Additional funding following the demonstrated success of an exclosure can be used to leverage further investment to extend the ori ...
A model for evaluating the `habitat potential` of a landscape for
... potential' of a landscape for capercaillie Tetrao urogallus: a tool for conservation planning. - Wildl. Biol. 13 (Suppl. 1): 21-33. Most habitat models developed for defining priority conservation sites target areas currently exhibiting suitable habitat conditions. For species whose habitats have be ...
... potential' of a landscape for capercaillie Tetrao urogallus: a tool for conservation planning. - Wildl. Biol. 13 (Suppl. 1): 21-33. Most habitat models developed for defining priority conservation sites target areas currently exhibiting suitable habitat conditions. For species whose habitats have be ...
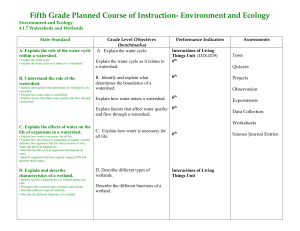
Environment and Ecology
... B. Explain how species of living organisms adapt to their environment. • Explain the role of individual variations in natural selection. • Explain how an adaptation is an inherited structure or behavior that helps an organism survive and reproduce. • Describe how a particular trait may be selected o ...
... B. Explain how species of living organisms adapt to their environment. • Explain the role of individual variations in natural selection. • Explain how an adaptation is an inherited structure or behavior that helps an organism survive and reproduce. • Describe how a particular trait may be selected o ...
the Dark Side of Black Bass
... fish species, creating more homogeneous fish communities, increasing competition among small-bodied fish, reducing energy flow to other game fishes, alterating planktonic and benthic communities, and potentially changing habitat complexity. Discussed within is also the fact that, although there is p ...
... fish species, creating more homogeneous fish communities, increasing competition among small-bodied fish, reducing energy flow to other game fishes, alterating planktonic and benthic communities, and potentially changing habitat complexity. Discussed within is also the fact that, although there is p ...
Macroecological patterns of species richness in parasite assemblages
... richness should be higher in large-bodied, longlived host species with dense populations, broad geographical ranges and broad diets. As a rule, these predictions are qualitative rather than quantitative, i.e. we can predict a general increase in parasite species richness with increasing host body si ...
... richness should be higher in large-bodied, longlived host species with dense populations, broad geographical ranges and broad diets. As a rule, these predictions are qualitative rather than quantitative, i.e. we can predict a general increase in parasite species richness with increasing host body si ...
Ecological replacement of native red squirrels by invasive greys
... modelled as causing density-dependent effects on reproduction but not on adult mortality. At least two lines of evidence justify this. First, Kenward et al. (1998) documented negative correlations between squirrel density and squirrel productivity (but not adult survival) for both species while, sec ...
... modelled as causing density-dependent effects on reproduction but not on adult mortality. At least two lines of evidence justify this. First, Kenward et al. (1998) documented negative correlations between squirrel density and squirrel productivity (but not adult survival) for both species while, sec ...
Evaluating MPA effectiveness
... the degree of linkage between sub-populations at different sites. The required targets for percentage of stock protected are themselves subject to uncertainty. How well, for example, would 35% stock protection safeguard against a fisheries collapse? If MPA’s have local effects on species size-struct ...
... the degree of linkage between sub-populations at different sites. The required targets for percentage of stock protected are themselves subject to uncertainty. How well, for example, would 35% stock protection safeguard against a fisheries collapse? If MPA’s have local effects on species size-struct ...
Competitive avoidance not edaphic specialization drives vertical
... Along with changing abiotic resources and conditions, there are important differences in biotic factors with soil depth that may also play a role in driving the differential vertical distribution of EM fungi. It is widely recognized that the plant root density declines with increasing depth (Jackson ...
... Along with changing abiotic resources and conditions, there are important differences in biotic factors with soil depth that may also play a role in driving the differential vertical distribution of EM fungi. It is widely recognized that the plant root density declines with increasing depth (Jackson ...
pdf here
... bear scent in a forest-dominated landscape, except when the habitat was opened up through human activities. We are, however, only beginning to understand how human modifications to landscapes affect predator –prey interactions. The direct effects of human activity on the behaviour of carnivores and ...
... bear scent in a forest-dominated landscape, except when the habitat was opened up through human activities. We are, however, only beginning to understand how human modifications to landscapes affect predator –prey interactions. The direct effects of human activity on the behaviour of carnivores and ...
Ecological Heterogeneity in the Effects of Grazing and Fire on
... recent years, the maintenance of appropriate disturbance regimes has also become recognized as a general principle in conservation biology (e.g., Meffe & Carroll 1997 ). Yet in a world of ever-increasing movement of propagules across former biotic boundaries, wildlands managers face a fundamental di ...
... recent years, the maintenance of appropriate disturbance regimes has also become recognized as a general principle in conservation biology (e.g., Meffe & Carroll 1997 ). Yet in a world of ever-increasing movement of propagules across former biotic boundaries, wildlands managers face a fundamental di ...
Dynamics of Single Neurons
... excitable. • We want to understand what makes different neurons behave in different ways. • Going model-by-model is difficult and not at all general: – there are hundreds of channel types in nature – any cell expresses a few or ten or so of them ...
... excitable. • We want to understand what makes different neurons behave in different ways. • Going model-by-model is difficult and not at all general: – there are hundreds of channel types in nature – any cell expresses a few or ten or so of them ...
Real Business Cycle Theory
... therefore the welfare theorems apply to these models: 1) the competitive equilibrium is pareto-optimal 2) a pareto-optimal allocation can be decentralized as a competitive equilibrium The social planner equilibrium and the competitive equilibrium are identical and admit a unique solution ...
... therefore the welfare theorems apply to these models: 1) the competitive equilibrium is pareto-optimal 2) a pareto-optimal allocation can be decentralized as a competitive equilibrium The social planner equilibrium and the competitive equilibrium are identical and admit a unique solution ...
Global networks for invasion science: benefits, challenges and
... 2006). The current distribution of most invasive organisms, in both their native and introduced ranges, spans two or more continents but rarely covers the entire globe (cf. Rejmánek and Richardson 2013). Limiting the selection of focal taxa to those that have a large global range would focus resear ...
... 2006). The current distribution of most invasive organisms, in both their native and introduced ranges, spans two or more continents but rarely covers the entire globe (cf. Rejmánek and Richardson 2013). Limiting the selection of focal taxa to those that have a large global range would focus resear ...
1 THEME: BIODIVERSITY 1.1 Introduction
... for South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland (Mucina and Rutherford, 2006) took a number of years to collect. It is likely that further loss of natural habitat has taken place since then, but these are the best available data. By using land classes incorporating expert knowledge about biological characte ...
... for South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland (Mucina and Rutherford, 2006) took a number of years to collect. It is likely that further loss of natural habitat has taken place since then, but these are the best available data. By using land classes incorporating expert knowledge about biological characte ...
The food limitation hypothesis for juvenile marine fish
... Coastal zones are productive areas that serve as nursery grounds for a large number of marine species. However, the processes involved in survival success during the juvenile phase are not wellknown. Some authors suggest that the availability of prey is important to support the production of prerecr ...
... Coastal zones are productive areas that serve as nursery grounds for a large number of marine species. However, the processes involved in survival success during the juvenile phase are not wellknown. Some authors suggest that the availability of prey is important to support the production of prerecr ...
Refocusing Ecocentrism: De-emphasizing Stability
... scale at which the system is described. Vernal pools that exist for perhaps a dozen weeks each year and then dry up are ephemeral on a time scale of months but constant if the scale is years. Integrity is also used in a variety of senses. The general idea is that the elements of the ecosystem are bl ...
... scale at which the system is described. Vernal pools that exist for perhaps a dozen weeks each year and then dry up are ephemeral on a time scale of months but constant if the scale is years. Integrity is also used in a variety of senses. The general idea is that the elements of the ecosystem are bl ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.