Final exam
... Overriding topic for this portion of the class: ecology (what living things are doing out there); remember, 25 questions on the exam will come from this portion of the class! I. Definition of ecology II. Definitions of ecosystem, community, and population III. Population dynamics A. What population ...
... Overriding topic for this portion of the class: ecology (what living things are doing out there); remember, 25 questions on the exam will come from this portion of the class! I. Definition of ecology II. Definitions of ecosystem, community, and population III. Population dynamics A. What population ...
APES POPULATION PATTERNS
... The Change in Population Allele Frequencies Allele frequency refers to the proportion of a population that has a particular allele. Natural selection alters the proportions of alleles, making those that give an advantage to a population higher. Natural selection puts genetic pressure on the populat ...
... The Change in Population Allele Frequencies Allele frequency refers to the proportion of a population that has a particular allele. Natural selection alters the proportions of alleles, making those that give an advantage to a population higher. Natural selection puts genetic pressure on the populat ...
Limiting Factors
... be in the form of animals or plants) as well as water and carbon supply. 1. Food Chains: Populations at one trophic level are ...
... be in the form of animals or plants) as well as water and carbon supply. 1. Food Chains: Populations at one trophic level are ...
NOTES: Chapter 8.1 - How Populations Change In Size
... Carrying capacity is the largest population that an environment can support at any given time. ...
... Carrying capacity is the largest population that an environment can support at any given time. ...
Population Ecology
... This helps to determine what particular aspects of the habitat are favored over others. One way to retrieve information from populations is to sample them. Sampling involves collecting data about features of the population from samples of that population (since populations are usually too large ...
... This helps to determine what particular aspects of the habitat are favored over others. One way to retrieve information from populations is to sample them. Sampling involves collecting data about features of the population from samples of that population (since populations are usually too large ...
population ecology 2010
... • Consists of all the factors acting jointly to limit the growth of a population • Population size of species in a given place and time is determined by interplay between biotic potential and environmental resistance. • Affects the young more than the elderly in a population, thereby affecting recru ...
... • Consists of all the factors acting jointly to limit the growth of a population • Population size of species in a given place and time is determined by interplay between biotic potential and environmental resistance. • Affects the young more than the elderly in a population, thereby affecting recru ...
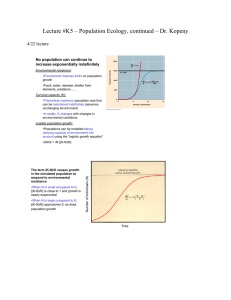
Lecture #K5 – Population Ecology, continued – Dr
... – Overshooting K •Lag time in many populations before negative effects of increasing population are realized ...
... – Overshooting K •Lag time in many populations before negative effects of increasing population are realized ...
Lecture - Chapter 11 - Population Regulation
... Chapter #11 – Population Regulation (pg. 223 – 237) 11.10 – Plants Preempt Space and ...
... Chapter #11 – Population Regulation (pg. 223 – 237) 11.10 – Plants Preempt Space and ...
Populations - Mrs. GM Biology 200
... Developed Countries – slightly wider base, width is same, or inverted pyramid – lower #s of pre- & reproductive age – low birth rates • slow growth, zero growth, negative growth (pop. shrinks) ...
... Developed Countries – slightly wider base, width is same, or inverted pyramid – lower #s of pre- & reproductive age – low birth rates • slow growth, zero growth, negative growth (pop. shrinks) ...
Ch 8 Lecture 10-11 - myersparkenvironmental
... increasingly severe. (2) Population is declining, and density-dependent factors are increasingly relaxed. ...
... increasingly severe. (2) Population is declining, and density-dependent factors are increasingly relaxed. ...
Ch 05 - Evolution Biodiversity and Population Ecology
... 1. Every population is eventually contained by limiting factors, which are physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the environment. 2. The interaction of the limiting factors determines the carrying capacity. 3. The logistic growth curve shows a population that increases sharply at fir ...
... 1. Every population is eventually contained by limiting factors, which are physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the environment. 2. The interaction of the limiting factors determines the carrying capacity. 3. The logistic growth curve shows a population that increases sharply at fir ...
05_3eOutline
... 1. Every population is eventually contained by limiting factors, which are physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the environment. 2. The interaction of the limiting factors determines the carrying capacity. 3. The logistic growth curve shows a population that increases sharply at fir ...
... 1. Every population is eventually contained by limiting factors, which are physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the environment. 2. The interaction of the limiting factors determines the carrying capacity. 3. The logistic growth curve shows a population that increases sharply at fir ...
AP BiologyEcology Unit Study QuestionsMs. Dolce CHAPTER 53
... 2. What are some possible difficulties in counting populations? 3. Describe three patterns of dispersal. 4. Compare the survival strategies of species and give an example of each type. a. Type I b. Type II c. Type III 5. Write the formula for population growth without limits. Define the terms. 6. De ...
... 2. What are some possible difficulties in counting populations? 3. Describe three patterns of dispersal. 4. Compare the survival strategies of species and give an example of each type. a. Type I b. Type II c. Type III 5. Write the formula for population growth without limits. Define the terms. 6. De ...
natural population
... Only write the answer! You may use your notes. Place in basket with name when finished. No talking!!!! 1. List 3 factors that affect population growth. 2. What are 3 characteristics of a population? 3. What type of growth goes through a period of rapid growth, and slows down or stops? 4. What is the ...
... Only write the answer! You may use your notes. Place in basket with name when finished. No talking!!!! 1. List 3 factors that affect population growth. 2. What are 3 characteristics of a population? 3. What type of growth goes through a period of rapid growth, and slows down or stops? 4. What is the ...
Chapter 5: Biodiversity, Species Interaction, Population Control
... • Intrinsic Rate of Increase (r): rate at which population would increase if unlimited resources are available • High r value: reproduce early, often, short generation time, produce many offspring • Scientific Principles of Sustainability – always limits population growth ...
... • Intrinsic Rate of Increase (r): rate at which population would increase if unlimited resources are available • High r value: reproduce early, often, short generation time, produce many offspring • Scientific Principles of Sustainability – always limits population growth ...
lecture_ch14_Population Ecology1
... ecology is the study of the interaction between populations of organisms and their environment, particularly their patterns of growth and how they are influenced by other species and by environmental factors. ...
... ecology is the study of the interaction between populations of organisms and their environment, particularly their patterns of growth and how they are influenced by other species and by environmental factors. ...
Ecology - 國立陽明大學
... – Maximum number of sustainable individuals – Results in intra-specific competition – Two types Scramble competition – Growth and reproduction depressed for all individuals Can result in local extinction or population crash ...
... – Maximum number of sustainable individuals – Results in intra-specific competition – Two types Scramble competition – Growth and reproduction depressed for all individuals Can result in local extinction or population crash ...
Chapter 4 notepacket
... b. Abiotic factors: Parts of an ecosystem that have NEVER been ________________________. i. Ex: _______________________, _______________________________________ 3. _______________________________ is a specific environment in which an organism lives. a. Consist of _________________________ and ______ ...
... b. Abiotic factors: Parts of an ecosystem that have NEVER been ________________________. i. Ex: _______________________, _______________________________________ 3. _______________________________ is a specific environment in which an organism lives. a. Consist of _________________________ and ______ ...
Benchmark SC.912.L.17.5
... – Birds/rhinos- nutrition and protection – Clownfish/sea anemones – Inhabitant mutualism – Vast amount of organisms like bacteria in an animal’s digestive tract – Termites and bacteria in gut ...
... – Birds/rhinos- nutrition and protection – Clownfish/sea anemones – Inhabitant mutualism – Vast amount of organisms like bacteria in an animal’s digestive tract – Termites and bacteria in gut ...
Populations
... 10. Tolerance Range: the minimum and maximum levels of an environmental factor that can support population growth 11. Law of the Minimum: of the number of essential substances required for growth, the one with the least concentration is the controlling factor 12. Open or Closed: an open population i ...
... 10. Tolerance Range: the minimum and maximum levels of an environmental factor that can support population growth 11. Law of the Minimum: of the number of essential substances required for growth, the one with the least concentration is the controlling factor 12. Open or Closed: an open population i ...
Primary Succession
... Carrying Capacitythe maximum population size that can be supported by the available resources ...
... Carrying Capacitythe maximum population size that can be supported by the available resources ...
Density-independent
... Factors that Regulate Population Growth Various factors regulate population growth, primarily by affecting natality or mortality and can be classified in different ways. • Intrinsic: operating within individual organisms or between organisms in the same species. • Extrinsic: imposed from outside th ...
... Factors that Regulate Population Growth Various factors regulate population growth, primarily by affecting natality or mortality and can be classified in different ways. • Intrinsic: operating within individual organisms or between organisms in the same species. • Extrinsic: imposed from outside th ...
Ecology - TeacherWeb
... productivity of the ecosystem in which the organism lives. The area they live is its habitat. Niche – the full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism uses those conditions. (an organisms job in the environment.) ...
... productivity of the ecosystem in which the organism lives. The area they live is its habitat. Niche – the full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism uses those conditions. (an organisms job in the environment.) ...
Which is r-strategy?
... Density-dependent Growth Compared to Exponential Growth Populations will not increase forever. Ignoring all interactions with other species (competition, predation, parasites, herbivory), resources will still limit growth food resources and space resources. (Remember the flies data from previous sl ...
... Density-dependent Growth Compared to Exponential Growth Populations will not increase forever. Ignoring all interactions with other species (competition, predation, parasites, herbivory), resources will still limit growth food resources and space resources. (Remember the flies data from previous sl ...