The analysis of stress in natural populations
... determining how to analyse the effects of stress on a population. First, the persistence of a population is its continuance through time at some particular (equilibrial) abundance, or its return to that equilibrial abundance after changes. Persistence may occur simply because there are no perturbati ...
... determining how to analyse the effects of stress on a population. First, the persistence of a population is its continuance through time at some particular (equilibrial) abundance, or its return to that equilibrial abundance after changes. Persistence may occur simply because there are no perturbati ...
Alternative stable states in ecology
... under the same set of conditions and that the community of alternative states. The first considers alternative intebe conveyed from one state to another by a sufficiently rior states: “If the system of equations describing the translarge perturbation applied directly to the state variables formation ...
... under the same set of conditions and that the community of alternative states. The first considers alternative intebe conveyed from one state to another by a sufficiently rior states: “If the system of equations describing the translarge perturbation applied directly to the state variables formation ...
population
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Fishing Mortality - Measuring the Effects of Catch Shares
... yearly estimated fishing mortality compared to the current FMSY estimate. In order to track tends among groups of species, stocks that have required rebuilding plans are separated to observe trends in fishing mortality ratios among that group. These analyses are not intended as a measure of the appr ...
... yearly estimated fishing mortality compared to the current FMSY estimate. In order to track tends among groups of species, stocks that have required rebuilding plans are separated to observe trends in fishing mortality ratios among that group. These analyses are not intended as a measure of the appr ...
Journal of Herpetology
... S. grairimicus individuals appear (Ortega, 1986) just when prey ahundance is starting to be the highest (Ortega and Hernandez, 1983), perhaps allowing growth at the fastest rates. The growth rates observed for younger S. gramrnicus individuals at La ~ i c h i l í a (0.390 mmiday) are higher than tho ...
... S. grairimicus individuals appear (Ortega, 1986) just when prey ahundance is starting to be the highest (Ortega and Hernandez, 1983), perhaps allowing growth at the fastest rates. The growth rates observed for younger S. gramrnicus individuals at La ~ i c h i l í a (0.390 mmiday) are higher than tho ...
- DiscardLess
... country and the single most important economic activity in the area. The ecosystem and the fishery are highly dependent on the seasonal and inter‐annual fluctuations of the water levels (Kolding & van Zwieten, 2012), causing large areas of flood plains to be temporarily inundated. The amount of rai ...
... country and the single most important economic activity in the area. The ecosystem and the fishery are highly dependent on the seasonal and inter‐annual fluctuations of the water levels (Kolding & van Zwieten, 2012), causing large areas of flood plains to be temporarily inundated. The amount of rai ...
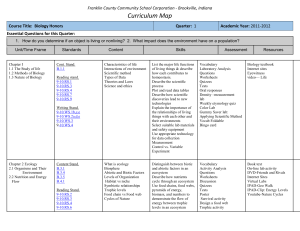
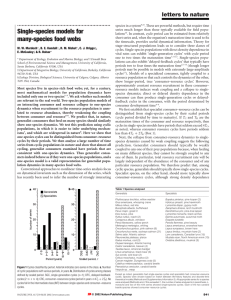
Q1 - FCCSC
... different biomes. Compare and Contrast the different biomes. Describe specific food chains and food webs in a particular biome. ...
... different biomes. Compare and Contrast the different biomes. Describe specific food chains and food webs in a particular biome. ...
Environmental variability and population dynamics: do European
... differences in life history strategies between dabbling (relatively “fast species” and governed by environmental variability) and diving (relatively “slow species” and governed by density) ducks. As expected, the variance component of population fluctuations caused by changes in breeding environment ...
... differences in life history strategies between dabbling (relatively “fast species” and governed by environmental variability) and diving (relatively “slow species” and governed by density) ducks. As expected, the variance component of population fluctuations caused by changes in breeding environment ...
Ecological and genetic models of diversity
... response to the rise of molecular biology during the 1960s, a group of leading researchers in ecology and evolution, including Robert MacArthur, Richard Levins, Richard Lewontin and Edward Wilson, made a concerted effort to draw the two disciplines together under the unifying banner of population bi ...
... response to the rise of molecular biology during the 1960s, a group of leading researchers in ecology and evolution, including Robert MacArthur, Richard Levins, Richard Lewontin and Edward Wilson, made a concerted effort to draw the two disciplines together under the unifying banner of population bi ...
Manier MK., and SJ. Arnold. 2006. Ecological correlates of population genetic structure: a comparative approach using a vertebrate metacommunity. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 273:3001-3009.
... Ecological correlates of population genetic structure: a comparative approach using a vertebrate metacommunity Mollie K. Manier* and Stevan J. Arnold Department of Zoology, 3029 Cordley Hall, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331-2914, USA Identifying ecological factors associated with popula ...
... Ecological correlates of population genetic structure: a comparative approach using a vertebrate metacommunity Mollie K. Manier* and Stevan J. Arnold Department of Zoology, 3029 Cordley Hall, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR 97331-2914, USA Identifying ecological factors associated with popula ...
Comparing growth patterns among field populations of cereal
... dirhodum (Walker), which is the dominant species on leaves and avoids the ears, Sitobion avenae (Fabricius), dominant on ears but also lives on leaves and Rhopalosiphum padi (Linnaeus), which can colonize the whole plant. These aphids migrate to wheat, around mid-May, from their winter hosts: Rosa s ...
... dirhodum (Walker), which is the dominant species on leaves and avoids the ears, Sitobion avenae (Fabricius), dominant on ears but also lives on leaves and Rhopalosiphum padi (Linnaeus), which can colonize the whole plant. These aphids migrate to wheat, around mid-May, from their winter hosts: Rosa s ...
The impact of fox and feral cat predation
... MUZAFFAR, S.B., BENJAMIN, S.D. & GUBIANI, R. 2013. The impact of fox and feral cat predation on the population viability of the threatened, endemic Socotra Cormorant on Siniya Island, United Arab Emirates. Marine Ornithology 41: 171–177. Seabirds are vulnerable to a variety of threats occurring at b ...
... MUZAFFAR, S.B., BENJAMIN, S.D. & GUBIANI, R. 2013. The impact of fox and feral cat predation on the population viability of the threatened, endemic Socotra Cormorant on Siniya Island, United Arab Emirates. Marine Ornithology 41: 171–177. Seabirds are vulnerable to a variety of threats occurring at b ...
a 09 Population limit factrs carr cap ppt
... •Increase in prey means more food for predators. •Predator population will increase until there is not enough food . . . and the cycle repeats itself. •Rabbit/Wolf simulation: http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/activities/RabbitsAndWolves/ ...
... •Increase in prey means more food for predators. •Predator population will increase until there is not enough food . . . and the cycle repeats itself. •Rabbit/Wolf simulation: http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/activities/RabbitsAndWolves/ ...
Comparative analysis of the interaction between habitat
... et al., 2013). For example, the gain of coloniality proceeds through two rate parameters: 0S-1S in the slow rate class and 0F-1F in the fast rate class (Figures 1b and c). Transitions between rate classes are modeled analogously with 0S-0F when the lineage is solitary and 1S-1F when the lineage is c ...
... et al., 2013). For example, the gain of coloniality proceeds through two rate parameters: 0S-1S in the slow rate class and 0F-1F in the fast rate class (Figures 1b and c). Transitions between rate classes are modeled analogously with 0S-0F when the lineage is solitary and 1S-1F when the lineage is c ...
Single-species models for many
... shown that the cycle period approaches six for large l only if b ¼ 0 and S C ¼ 0. If either b . 0 (as with a type 2 functional response) or S C . 0 (adult consumers may live for more than a year), the limiting period is greater than six. Cycle period increases as l decreases from the limit to lower, ...
... shown that the cycle period approaches six for large l only if b ¼ 0 and S C ¼ 0. If either b . 0 (as with a type 2 functional response) or S C . 0 (adult consumers may live for more than a year), the limiting period is greater than six. Cycle period increases as l decreases from the limit to lower, ...
Population demographics and trade
... 1998; Sakai et al. 2001). Fast growth rates reflect rapid acquisition and allocation of resources, which enable a species to swiftly establish a population following colonization. While life-history theory predicts a trade-off between high reproduction and growth rates (Stearns 1992), research examini ...
... 1998; Sakai et al. 2001). Fast growth rates reflect rapid acquisition and allocation of resources, which enable a species to swiftly establish a population following colonization. While life-history theory predicts a trade-off between high reproduction and growth rates (Stearns 1992), research examini ...
size-selective harvesting alters life histories of a temperate sex
... structure and growth rates, and the timing of maturation. For sex-changing species, selective fishing practices can affect additional traits such as the mature population sex ratio and the timing of sexual transformation. Using historical comparisons, we examined the effects of exploitation on life h ...
... structure and growth rates, and the timing of maturation. For sex-changing species, selective fishing practices can affect additional traits such as the mature population sex ratio and the timing of sexual transformation. Using historical comparisons, we examined the effects of exploitation on life h ...
View or download: Introduction, methods, results
... (Appendix 1) because of fluctuations in oceanographic conditions affecting food supply (Warham 1990). A practical outcome of this variation is that it may make a small population more susceptible to extinction (i.e. several ‘bad’ years in a row). For our modeling purpose ...
... (Appendix 1) because of fluctuations in oceanographic conditions affecting food supply (Warham 1990). A practical outcome of this variation is that it may make a small population more susceptible to extinction (i.e. several ‘bad’ years in a row). For our modeling purpose ...
Applications of Sustainable Management Practices
... Objectives: from Maximum Sustainable Yield to Optimal Sustainable Yield Where the objectives of fisheries management are concerned, the concept of Maximum Sustainable Yield (MSY) was dominant from the 1930s to the 1970s. The basic idea behind MSY will only be summarised here (for more detailed descr ...
... Objectives: from Maximum Sustainable Yield to Optimal Sustainable Yield Where the objectives of fisheries management are concerned, the concept of Maximum Sustainable Yield (MSY) was dominant from the 1930s to the 1970s. The basic idea behind MSY will only be summarised here (for more detailed descr ...
Predicting changes in the distribution and abundance of species
... may not yet have reached their equilibrium abundance. Persistent life stages, such as long-lived adults or seeds in a seed bank, or slow life histories may introduce time lags between environmental change and population responses. Such time lags may cause the equilibrium to over- or under-estimate t ...
... may not yet have reached their equilibrium abundance. Persistent life stages, such as long-lived adults or seeds in a seed bank, or slow life histories may introduce time lags between environmental change and population responses. Such time lags may cause the equilibrium to over- or under-estimate t ...
Colonization in metapopulations: a review of
... The Leigh model is also a Markovian birth-and-death process model, relating and T , to r, K, and the amount of environmental variation in r. All three parameters were found to influence time to extinction, but variance in r was the most important one, through its effect on the amplitude of populatio ...
... The Leigh model is also a Markovian birth-and-death process model, relating and T , to r, K, and the amount of environmental variation in r. All three parameters were found to influence time to extinction, but variance in r was the most important one, through its effect on the amplitude of populatio ...
Benthic amphipod community in the northern
... Therefore, the larger ampeliscids, which are actually dominant, must not only live in a highly productive environment, they must also have a lower mortality rate than smaller ampeliscids. One advantage of larger size is the ability to defend limiting resources against smaller competitors. Competitiv ...
... Therefore, the larger ampeliscids, which are actually dominant, must not only live in a highly productive environment, they must also have a lower mortality rate than smaller ampeliscids. One advantage of larger size is the ability to defend limiting resources against smaller competitors. Competitiv ...
Summary
... The expected higher densities of previously-exploited species in MPAs may produce an augmentation of intraspecific and interspecific competition as biomass of the populations approaches the carrying capacity of the area. The importance of taking proper account of density-dependent changes in life-hi ...
... The expected higher densities of previously-exploited species in MPAs may produce an augmentation of intraspecific and interspecific competition as biomass of the populations approaches the carrying capacity of the area. The importance of taking proper account of density-dependent changes in life-hi ...
Higher Biology - Kelso High School
... Deletion: base/bases deleted from chromosome/removed/taken out Previous point may be shown as suitably labelled diagrams with only bases A, T, G and C used Insertion: base/bases inserted into chromosome/added/put in Deletion/insertion changes codons/triplets after the mutation Deletion/insertion cha ...
... Deletion: base/bases deleted from chromosome/removed/taken out Previous point may be shown as suitably labelled diagrams with only bases A, T, G and C used Insertion: base/bases inserted into chromosome/added/put in Deletion/insertion changes codons/triplets after the mutation Deletion/insertion cha ...
Mathematical Modelling Of Ecological Networks, Structure and
... Ecological interactions are the relationships between two species in anecosystem [2]. Based on either effects, or on mechanisms, these relationships can be categorized into many different classes of interactions as shown in Fig. 1. ...
... Ecological interactions are the relationships between two species in anecosystem [2]. Based on either effects, or on mechanisms, these relationships can be categorized into many different classes of interactions as shown in Fig. 1. ...