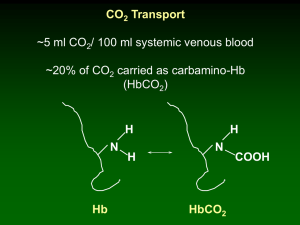
Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) (isolate 216.94.A2) gp120
... < 1.0 EU per μg protein as determined by the LAL method. ...
... < 1.0 EU per μg protein as determined by the LAL method. ...
2013
... 11. [7 points] Indicate the location each of the following components in the photosynthetic electron transport pathway of plants by placing the numbers corresponding to the components in the spaces provided. ...
... 11. [7 points] Indicate the location each of the following components in the photosynthetic electron transport pathway of plants by placing the numbers corresponding to the components in the spaces provided. ...
Cellular Respiration
... where pyruvate can be regenerated Lactic acid is also important in the making of cheese and yogurt ...
... where pyruvate can be regenerated Lactic acid is also important in the making of cheese and yogurt ...
Where are enzymes?
... Where are enzymes? Enzymes are usually in cells. They can be: •proteins in the cytoplasm •proteins in an organelle •proteins in the membranes of cells or organelles. •Enzymes can also be secreted by cells into an organism’s body, such as those in your mouth, your stomach, and your intestines. ...
... Where are enzymes? Enzymes are usually in cells. They can be: •proteins in the cytoplasm •proteins in an organelle •proteins in the membranes of cells or organelles. •Enzymes can also be secreted by cells into an organism’s body, such as those in your mouth, your stomach, and your intestines. ...
AAA-Direct Amino Acid Analysis System
... cell culture. The insert is the IPAD waveform used in the analysis with the integration period indicated by the heavy blue line. Using this waveform, common sugars and amino acids present in the sample can be determined simultaneously. If the integration period is shifted to a lower potential, the r ...
... cell culture. The insert is the IPAD waveform used in the analysis with the integration period indicated by the heavy blue line. Using this waveform, common sugars and amino acids present in the sample can be determined simultaneously. If the integration period is shifted to a lower potential, the r ...
this lecture as PDF here
... to grow). How to get NADPH? The redox potential is much higher than nitrite. • Solution: Reverse electron transport. Accumulate enough proton gradient by oxidation of nitrite to force electrons back to carriers with higher redox potentials, all the way back to NADH ---> NADPH. This works as long as ...
... to grow). How to get NADPH? The redox potential is much higher than nitrite. • Solution: Reverse electron transport. Accumulate enough proton gradient by oxidation of nitrite to force electrons back to carriers with higher redox potentials, all the way back to NADH ---> NADPH. This works as long as ...
Cellular Respiration
... Used to charge up ATP (for cell to use) Series of reactions (can’t release all at once) Glycolysis, ...
... Used to charge up ATP (for cell to use) Series of reactions (can’t release all at once) Glycolysis, ...
Enzymes - NVHSIntroBioPiper1
... breaking of bonds in reactants and the formation of new bonds in products Reactants Products ...
... breaking of bonds in reactants and the formation of new bonds in products Reactants Products ...
Anaerobic Respiration - Deans Community High School
... A second type of RNA is found in the cell’s cytoplasm. This is called ____________ _____ (______). Each molecule of tRNA has an exposed triplet of bases, known as an anticodon. This anticodon corresponds to a particular amino acid. Each tRNA molecule picks up the appropriate amino acid from the cyto ...
... A second type of RNA is found in the cell’s cytoplasm. This is called ____________ _____ (______). Each molecule of tRNA has an exposed triplet of bases, known as an anticodon. This anticodon corresponds to a particular amino acid. Each tRNA molecule picks up the appropriate amino acid from the cyto ...
Problem Set 3 (Due February 4th) 1. In 1896, Christiaan Eijkman
... this). E. coli, which lack mitochondria, rely on a different mechanism to regulate enzyme activity. Please read the attached paper and discuss how this E. coli enzyme is regulated and how this mechanism relates to the ‘dietary’ carbon source. E. coli Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (IDH) can be inhibited b ...
... this). E. coli, which lack mitochondria, rely on a different mechanism to regulate enzyme activity. Please read the attached paper and discuss how this E. coli enzyme is regulated and how this mechanism relates to the ‘dietary’ carbon source. E. coli Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (IDH) can be inhibited b ...
SPRGM Teacher Notes - 3D Molecular Designs
... HS-PS 1-6: Refine the design of a chemical system by specifying a change in conditions that would produce increased amounts of products at equilibrium. ...
... HS-PS 1-6: Refine the design of a chemical system by specifying a change in conditions that would produce increased amounts of products at equilibrium. ...
Biophysics : Aspects of Amino Acids Sequence in Proteins and
... The gene is a part of DNA macromolecule reactions to accelerate the rate of reaction but responsible for the synthesis of protein chain. The their amount is always conserved i.e. they change genetic codes are triplets i.e. one coding includes substrate without changing themselves. three nucleotides ...
... The gene is a part of DNA macromolecule reactions to accelerate the rate of reaction but responsible for the synthesis of protein chain. The their amount is always conserved i.e. they change genetic codes are triplets i.e. one coding includes substrate without changing themselves. three nucleotides ...
Biology Mid Year Exam Revision
... Hormone – Chemical messengers that cause certain parts of the body to respond to their presence. E.g. Human Growth Hormone causes bones and muscles to grow at a faster rate during puberty. Endocrine glands – Glands that produce and release hormones. Target organ – an organ on which a hormone has an ...
... Hormone – Chemical messengers that cause certain parts of the body to respond to their presence. E.g. Human Growth Hormone causes bones and muscles to grow at a faster rate during puberty. Endocrine glands – Glands that produce and release hormones. Target organ – an organ on which a hormone has an ...
Review [Life] - Mahopac Voyagers!
... catalysts of chemical reactions D) catalysts of chemical reactions and components of cellular membranes ...
... catalysts of chemical reactions D) catalysts of chemical reactions and components of cellular membranes ...
Cellular Respiration
... Electron transport and pumping of protons (H+), ATP synthesis powered by the flow which create an H+ gradient across the membrane Of H+ back across the membrane ...
... Electron transport and pumping of protons (H+), ATP synthesis powered by the flow which create an H+ gradient across the membrane Of H+ back across the membrane ...
artsy - sciencebugz
... Inheritance is based on complex mechanism for copying DNA The copy must be passed on from generation to generation All forms of life have the same 4 nucleotides ...
... Inheritance is based on complex mechanism for copying DNA The copy must be passed on from generation to generation All forms of life have the same 4 nucleotides ...
9.2 adaptions and support study guide
... Cellulose in cell walls & Lignin in xylem act together to provide support Stem cells, including xylem cells occur in within a plant. These act like to support plant during high winds. Cell turgidity and plant support: ...
... Cellulose in cell walls & Lignin in xylem act together to provide support Stem cells, including xylem cells occur in within a plant. These act like to support plant during high winds. Cell turgidity and plant support: ...
Lecture 8 - People Server at UNCW
... • Examine neural control of breathing • Respiratory centers in the brain • Peripheral input to respirator centers ...
... • Examine neural control of breathing • Respiratory centers in the brain • Peripheral input to respirator centers ...
Transcription and Translation
... • Other errors in replication may lead to a change in protein structure and be very harmful. ...
... • Other errors in replication may lead to a change in protein structure and be very harmful. ...
Lesson 12 Vocab
... When you light a candle, you see smoke. As you swirl the bromthymol blue in the beaker, the color changes to greenish-yellow. This is an indication that carbon dioxide was released during oxidation and that it was dissolved in the solution. This dissolved carbon dioxide forms carbonic acid, and the ...
... When you light a candle, you see smoke. As you swirl the bromthymol blue in the beaker, the color changes to greenish-yellow. This is an indication that carbon dioxide was released during oxidation and that it was dissolved in the solution. This dissolved carbon dioxide forms carbonic acid, and the ...
Chapter 6- Cell Structure and Function
... -The process of CO2 being converted to glucose is called “carbon fixation.” The initial step of merging CO2 with a larger carbon-based molecule called RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate) to begin the cycle is catalyzed (assisted) by an enzyme called RuBP carboxylase (aka Rubisco). By the end of the Calvin ...
... -The process of CO2 being converted to glucose is called “carbon fixation.” The initial step of merging CO2 with a larger carbon-based molecule called RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate) to begin the cycle is catalyzed (assisted) by an enzyme called RuBP carboxylase (aka Rubisco). By the end of the Calvin ...
Section 2-4 “Chemical Reactions and Enzymes”
... Energy must be added to break bonds that hold the reactant molecules together. This is called activation energy (Ae). This amount of energy is what “activates” or gets the reaction started. Once the bonds are broken, the atoms are freed up and can make new molecules. When bonds form between the atom ...
... Energy must be added to break bonds that hold the reactant molecules together. This is called activation energy (Ae). This amount of energy is what “activates” or gets the reaction started. Once the bonds are broken, the atoms are freed up and can make new molecules. When bonds form between the atom ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.













![Review [Life] - Mahopac Voyagers!](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015415087_1-086194e3d7adf4968e532aedfd1651a9-300x300.png)