Exam 2
... PLP in glycogen phosphorylase is a co-factor enzyme but not a prosthetic group. In the glycogen phosphorylase reaction, the cleaved glucose is stabilized by having a half-chair conformation. e. None of the above. 14. The followings are some characteristics of glycogen metabolism. a. α-Adrenoreceptor ...
... PLP in glycogen phosphorylase is a co-factor enzyme but not a prosthetic group. In the glycogen phosphorylase reaction, the cleaved glucose is stabilized by having a half-chair conformation. e. None of the above. 14. The followings are some characteristics of glycogen metabolism. a. α-Adrenoreceptor ...
SAM Teacher`s Guide Four Levels of Protein Structure - RI
... • Identify the primary structure of a protein as a linear sequence of amino acids. • Identify the unique side chains of amino acids that give them their properties. • Explore how amino acids interact with water and how that affects the way proteins fold. • Differentiate among the common seconda ...
... • Identify the primary structure of a protein as a linear sequence of amino acids. • Identify the unique side chains of amino acids that give them their properties. • Explore how amino acids interact with water and how that affects the way proteins fold. • Differentiate among the common seconda ...
oxidation reduction
... Reduced NADH and FADH2 are important as they carry electrons which power other stages of respiration. ...
... Reduced NADH and FADH2 are important as they carry electrons which power other stages of respiration. ...
PPT
... • Any process that produces alcoholic beverages or acidic dairy products (general use) • Any large-scale microbial process occurring with or without air (common definition used in industry) ...
... • Any process that produces alcoholic beverages or acidic dairy products (general use) • Any large-scale microbial process occurring with or without air (common definition used in industry) ...
AminoAcidMetabolismFIN2011
... 1. In peripheral tissues,the a-amino groups of the amino acids are transferred to glutamate by a transamination reaction, as in the liver. 2. However, rather than oxidatively deaminating glutamate to form ammonium ion, the a-amino group is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. 3. The liver takes ...
... 1. In peripheral tissues,the a-amino groups of the amino acids are transferred to glutamate by a transamination reaction, as in the liver. 2. However, rather than oxidatively deaminating glutamate to form ammonium ion, the a-amino group is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. 3. The liver takes ...
Lecture 11 (Parker) - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... Vitamins are organic molecules that are needed in small amounts in the diets of higher animals as higher animals have lost the capacity to synthesize these molecules during the course of evoluBon ...
... Vitamins are organic molecules that are needed in small amounts in the diets of higher animals as higher animals have lost the capacity to synthesize these molecules during the course of evoluBon ...
SAM Teachers Guide - RI
... Identify the primary structure of a protein as a linear sequence of amino acids. Identify the unique side chains of amino acids that give them their properties. Explore how amino acids interact with water and how that affects the way proteins fold. Differentiate among the common secondary st ...
... Identify the primary structure of a protein as a linear sequence of amino acids. Identify the unique side chains of amino acids that give them their properties. Explore how amino acids interact with water and how that affects the way proteins fold. Differentiate among the common secondary st ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... cephalosporins. They have good antimicrobial activity against gram-positive bacteria but limited activity against gram-negative species. The chemical structures of the first generation cephalosporins are fairly simple. As an example three drugs of this class (Cephalexin, Cephradine and Cefadroxil), ...
... cephalosporins. They have good antimicrobial activity against gram-positive bacteria but limited activity against gram-negative species. The chemical structures of the first generation cephalosporins are fairly simple. As an example three drugs of this class (Cephalexin, Cephradine and Cefadroxil), ...
Amino Acids and Their Properties
... Connecting macroscopic properties of substances with their molecular properties ...
... Connecting macroscopic properties of substances with their molecular properties ...
Chapter 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ion
... If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole ...
... If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole ...
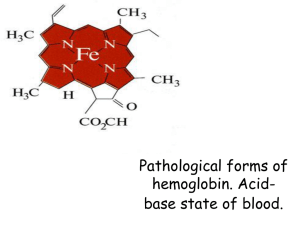
Pathological forms of hemoglobin. Acid
... balance between acids and bases, in other words, the pH. The body is very sensitive to its pH level, so strong mechanisms exist to maintain it. Outside the acceptable range of pH, proteins are denatured and digested, enzymes lose their ability to function, and death may occur. ...
... balance between acids and bases, in other words, the pH. The body is very sensitive to its pH level, so strong mechanisms exist to maintain it. Outside the acceptable range of pH, proteins are denatured and digested, enzymes lose their ability to function, and death may occur. ...
Collision Theory
... • Before atoms/molecules/ions can react, they must first collide • An effective collision between two species puts enough energy to break key bonds • The activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy that must be supplied by collisions to trigger a reaction • A certain fraction of all molecules in a ...
... • Before atoms/molecules/ions can react, they must first collide • An effective collision between two species puts enough energy to break key bonds • The activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy that must be supplied by collisions to trigger a reaction • A certain fraction of all molecules in a ...
Final Exam, Chem 111 2012 Study Guide
... a) State the combining power for elements C, N, O, H, halogens, P, and S. b) Explain the difference between various types of structural formulas (normal, condensed, and expanded). c) Translate given structural ...
... a) State the combining power for elements C, N, O, H, halogens, P, and S. b) Explain the difference between various types of structural formulas (normal, condensed, and expanded). c) Translate given structural ...
the krebs cycle
... Stage 3: If there is energy present, ADP + Pi can become bonded back together again to form ATP. This process requires energy and will no t occur without it. This shows that the formation of ATP from ADP + Pi is a reversible process ...
... Stage 3: If there is energy present, ADP + Pi can become bonded back together again to form ATP. This process requires energy and will no t occur without it. This shows that the formation of ATP from ADP + Pi is a reversible process ...
PowerPoint Slides
... They provide a detailed picture of interesting biological features, such as active site, substrate specificity, allosteric regulation etc. They aid in rational drug design and protein ...
... They provide a detailed picture of interesting biological features, such as active site, substrate specificity, allosteric regulation etc. They aid in rational drug design and protein ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
... Digestion breaks down the large molecules in food into smaller compounds that can be absorbed by the body. Hydrolysis is the main reaction involved in the digestion of carbohydrates. The _-amylase is produced by the salivary glands to begin the hydrolysis of the _-glycosidic bonds in the polysacchar ...
... Digestion breaks down the large molecules in food into smaller compounds that can be absorbed by the body. Hydrolysis is the main reaction involved in the digestion of carbohydrates. The _-amylase is produced by the salivary glands to begin the hydrolysis of the _-glycosidic bonds in the polysacchar ...
Document
... To do either process – break down VLCFA or make them from LCFA – the FAs first need to be “activated” Activation means attaching the FA to a helper molecule called “Coenzyme A” (or CoA for short) We would write this as “LCFA-CoA” or “VLCFA-CoA” (Remember this when we get to Part 2!) ...
... To do either process – break down VLCFA or make them from LCFA – the FAs first need to be “activated” Activation means attaching the FA to a helper molecule called “Coenzyme A” (or CoA for short) We would write this as “LCFA-CoA” or “VLCFA-CoA” (Remember this when we get to Part 2!) ...
History—One gene, one polypeptide hypothesis The Overall
... · Transfer RNAs have a special role in bringing amino acids to line up properly as directed by messenger RNA during polypeptide synthesis. ...
... · Transfer RNAs have a special role in bringing amino acids to line up properly as directed by messenger RNA during polypeptide synthesis. ...
Where can water be found?
... We then eat plants and break down that glucose for energy (ATP) in a process called cellular respiration. The carbon molecules we take from the glucose are then exhaled as carbon dioxide that plants can use. Plants also give off the oxygen we need to perform cellular respiration because it is a ...
... We then eat plants and break down that glucose for energy (ATP) in a process called cellular respiration. The carbon molecules we take from the glucose are then exhaled as carbon dioxide that plants can use. Plants also give off the oxygen we need to perform cellular respiration because it is a ...
Honors Biology A 4W5 Respiration (divide by
... formation of ATP is called ______________________________. is the enzyme that helps convert a 2 carbon molecule with a 4 carbon molecule to make citric acid. ______________________________ is the organelle that contains the enzymes for ...
... formation of ATP is called ______________________________. is the enzyme that helps convert a 2 carbon molecule with a 4 carbon molecule to make citric acid. ______________________________ is the organelle that contains the enzymes for ...
Nucleic Acids and Genetics - Travis Science TAKS Practice
... Nucleic Acids and Genetics A Adenine B ...
... Nucleic Acids and Genetics A Adenine B ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.