TAKS REVIEW
... 12. phylogeny - evolutionary history of a species based on comparative relationships of structures and on comparisons of modern life forms with fossils 13. speciation - the process by which a new species is formed when individuals of a population are unable to interbreed or produce fertile offspring ...
... 12. phylogeny - evolutionary history of a species based on comparative relationships of structures and on comparisons of modern life forms with fossils 13. speciation - the process by which a new species is formed when individuals of a population are unable to interbreed or produce fertile offspring ...
Part I: Anatomical Homologies, continued
... organisms. We also see this evidence in similarities in characteristics, known as homologies between organisms that originated from a common ancestor. A homologous structure is something that is similar in position, structure, or evolutionary origin. There are three main categories of homologies amo ...
... organisms. We also see this evidence in similarities in characteristics, known as homologies between organisms that originated from a common ancestor. A homologous structure is something that is similar in position, structure, or evolutionary origin. There are three main categories of homologies amo ...
PowerPoint
... amino acids (proteins/growth) lipids (cell membranes) pigments (energy/light capture) ...
... amino acids (proteins/growth) lipids (cell membranes) pigments (energy/light capture) ...
Protein mteabolism L..
... cholic acid giving taurocholate (see bile salts). 3- Formation of GSH: with glycine and glutamic acid ...
... cholic acid giving taurocholate (see bile salts). 3- Formation of GSH: with glycine and glutamic acid ...
A1980JQ46200001
... spectroscopy was at the Carlsberg Laboratory where I was a postdoctoral visitor with K. Linderstrøm-Lang. I applied the then rather new technique of difference spectroscopy in model compound studies to test Crammer and Neuberger’s suggestion that some of ovalbumin’s tyrosyl residues were Hbonded to ...
... spectroscopy was at the Carlsberg Laboratory where I was a postdoctoral visitor with K. Linderstrøm-Lang. I applied the then rather new technique of difference spectroscopy in model compound studies to test Crammer and Neuberger’s suggestion that some of ovalbumin’s tyrosyl residues were Hbonded to ...
L03_MitoOx
... – Adenine nucleotide attached back-toback with a nucleotide that has nicotinamide as the “base” ...
... – Adenine nucleotide attached back-toback with a nucleotide that has nicotinamide as the “base” ...
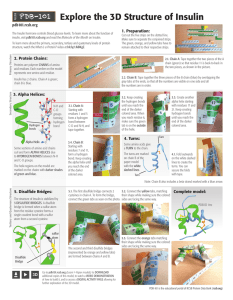
Explore the 3D Structure of Insulin
... gray tabs at the ends, so that all the numbers are visible on one side and all the numbers are in order. ...
... gray tabs at the ends, so that all the numbers are visible on one side and all the numbers are in order. ...
3.4: Transcription and Translation - ISM-Online
... discovered that some proteins are composed of more than one polypeptide subunit and that each subunit is coded for by its own specific gene. Hemoglobin is an example because it’s composed of two pairs of subunits and is coded for by two genes. ...
... discovered that some proteins are composed of more than one polypeptide subunit and that each subunit is coded for by its own specific gene. Hemoglobin is an example because it’s composed of two pairs of subunits and is coded for by two genes. ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... • Transfer of phosphoryl group from the energy-rich mixed anhydride 1,3BPG to ADP yields ATP and 3phosphoglycerate (3PG) • Substrate-level phosphorylation - Steps 6 and 7 couple oxidation of an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid with the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP Prentice Hall c2002 ...
... • Transfer of phosphoryl group from the energy-rich mixed anhydride 1,3BPG to ADP yields ATP and 3phosphoglycerate (3PG) • Substrate-level phosphorylation - Steps 6 and 7 couple oxidation of an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid with the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP Prentice Hall c2002 ...
best
... Leu: The enthalpy is lower, therefore fewer interactions need to be broken during unfolding (2 pts) The larger leucine sidechain must not quite fit in the core as well as the valine, disrupting van der Waals interactions (3 pts) Thr: The enthalpy is higher, therefore, more interactions have to be br ...
... Leu: The enthalpy is lower, therefore fewer interactions need to be broken during unfolding (2 pts) The larger leucine sidechain must not quite fit in the core as well as the valine, disrupting van der Waals interactions (3 pts) Thr: The enthalpy is higher, therefore, more interactions have to be br ...
Overall macromolecular composition of an average E. coli
... 1) Read “Order-of-Magnitude Biology Toolkit” and suggest one value you would like to see added to the list. 2) Choose one vignette to read from Chapter 2 of “Cell Biology by the Numbers” textbook, related to your research or to your fields of interest, and write us the title of the vignette you read ...
... 1) Read “Order-of-Magnitude Biology Toolkit” and suggest one value you would like to see added to the list. 2) Choose one vignette to read from Chapter 2 of “Cell Biology by the Numbers” textbook, related to your research or to your fields of interest, and write us the title of the vignette you read ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis Chapter 28, Stryer Short Course
... receptors in non-liver cells • HDLs are “good cholesterol” ...
... receptors in non-liver cells • HDLs are “good cholesterol” ...
Dietary Reference Intake Values
... fatlike substances that is found in the cells of all animals. • High cholesterol is associated with heart disease. ...
... fatlike substances that is found in the cells of all animals. • High cholesterol is associated with heart disease. ...
Energy Metabolism - Rajarata University of Sri Lanka
... entitled: 'What is the relationship between the metabolism of the preimplantation embryos and their developmental competence?' these distinctions have become blurred since it became apparent that the traditional nutrients have multiple, overlapping functions, and that other nutrients, particularly, ...
... entitled: 'What is the relationship between the metabolism of the preimplantation embryos and their developmental competence?' these distinctions have become blurred since it became apparent that the traditional nutrients have multiple, overlapping functions, and that other nutrients, particularly, ...
continued
... – Triglycerides stored in fat cells can be broken down by hormone-sensitive lipase. This releases free fatty acids from the fat cells into the blood, where they can circulate and enter muscle fibers. ...
... – Triglycerides stored in fat cells can be broken down by hormone-sensitive lipase. This releases free fatty acids from the fat cells into the blood, where they can circulate and enter muscle fibers. ...
Sticky end in protein synthesis - The School of Molecular and
... coding for alanyl-tRNA synthetase (AlaRS), a component of the gene-expression machinery by which aminoacyl-transfer RNAs translate messenger RNA into an amino-acid sequence on the ribosome. Closer inspection revealed that this mutation increases the frequency of errors during translation, leading to ...
... coding for alanyl-tRNA synthetase (AlaRS), a component of the gene-expression machinery by which aminoacyl-transfer RNAs translate messenger RNA into an amino-acid sequence on the ribosome. Closer inspection revealed that this mutation increases the frequency of errors during translation, leading to ...
Chapter 8: CELL MEMBRANE
... ● the cell membrane forms spontaneously in water because the nonpolar lipid “tails” are repelled by polar water molecules; the polar “heads” of the molecules form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. ...
... ● the cell membrane forms spontaneously in water because the nonpolar lipid “tails” are repelled by polar water molecules; the polar “heads” of the molecules form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. ...
Activity
... In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this information in the form of a code to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis ta ...
... In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this information in the form of a code to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis ta ...
Chapter 8: CELL MEMBRANE
... ● the cell membrane forms spontaneously in water because the nonpolar lipid “tails” are repelled by polar water molecules; the polar “heads” of the molecules form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. ...
... ● the cell membrane forms spontaneously in water because the nonpolar lipid “tails” are repelled by polar water molecules; the polar “heads” of the molecules form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. ...
best
... Leu: The enthalpy is lower, therefore fewer interactions need to be broken during unfolding (2 pts) The larger leucine sidechain must not quite fit in the core as well as the valine, disrupting van der Waals interactions (3 pts) Thr: The enthalpy is higher, therefore, more interactions have to be br ...
... Leu: The enthalpy is lower, therefore fewer interactions need to be broken during unfolding (2 pts) The larger leucine sidechain must not quite fit in the core as well as the valine, disrupting van der Waals interactions (3 pts) Thr: The enthalpy is higher, therefore, more interactions have to be br ...
Replication/ Transcription/Translation Review
... sequence. One side of the DNA is used to make RNA using RNA nucleotides. 4. Describe the different types of RNA, their names and their roles in transcription & translation. mRNA: Messenger RNA: Contains the code transcribed from the DNA. It is used as the code to make the amino acid chains of a prot ...
... sequence. One side of the DNA is used to make RNA using RNA nucleotides. 4. Describe the different types of RNA, their names and their roles in transcription & translation. mRNA: Messenger RNA: Contains the code transcribed from the DNA. It is used as the code to make the amino acid chains of a prot ...
CH 3 COO
... Control the supply of H2CO3 in the blood by controlling the amount of CO2 exhaled. When the blood level of HCO3- decreases, the breathing rate is increased, increasing amount of CO2 expelled, decreasing H2CO3. If H2CO3 (CO2) increases it is called respiratory acidosis. If H2CO3 (CO2) decreases it is ...
... Control the supply of H2CO3 in the blood by controlling the amount of CO2 exhaled. When the blood level of HCO3- decreases, the breathing rate is increased, increasing amount of CO2 expelled, decreasing H2CO3. If H2CO3 (CO2) increases it is called respiratory acidosis. If H2CO3 (CO2) decreases it is ...
Document
... Kazal inhibitor, that inhibits any small amounts of activated trypsin which may find its way into the ducts, by forming a complex with it Enzyme Y is also exhibiting a protective function, which is activated by traces of active trypsin degrades zymogen The alkaline pH (8.0-9.5) and low Ca2+ concentr ...
... Kazal inhibitor, that inhibits any small amounts of activated trypsin which may find its way into the ducts, by forming a complex with it Enzyme Y is also exhibiting a protective function, which is activated by traces of active trypsin degrades zymogen The alkaline pH (8.0-9.5) and low Ca2+ concentr ...
BIOCHEMISTRY Carbohydrate Metabolism
... • Begins in the mouth – salivary α-amylase catalyzes hydrolysis of αglycosidic bonds of starch – producing smaller polysaccharides & disaccharide (maltose). • No digestion in stomach. • Small intestine – most carbs digestion – pancreatic α-amylase catalyzes hydrolysis of α-glycosidic bonds in polysa ...
... • Begins in the mouth – salivary α-amylase catalyzes hydrolysis of αglycosidic bonds of starch – producing smaller polysaccharides & disaccharide (maltose). • No digestion in stomach. • Small intestine – most carbs digestion – pancreatic α-amylase catalyzes hydrolysis of α-glycosidic bonds in polysa ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.