Metabolism and Bioenergetics Fuel and Digestion
... • You can’t understand thermodynamics until we clear up some common misconceptions about equilibrium… • Is this reaction at equilibrium or not? • If not, in which direction does the equilibrium lie? ...
... • You can’t understand thermodynamics until we clear up some common misconceptions about equilibrium… • Is this reaction at equilibrium or not? • If not, in which direction does the equilibrium lie? ...
Lecture 2
... Illustration: Acid-base properties of amino acids Amino acids in acidic medium exist in the completely protonated form carrying a net positive charge, which can be confirmed by means of simple paper electrophoresis. The sample solution is applied at the centre of the strip and current is passed thro ...
... Illustration: Acid-base properties of amino acids Amino acids in acidic medium exist in the completely protonated form carrying a net positive charge, which can be confirmed by means of simple paper electrophoresis. The sample solution is applied at the centre of the strip and current is passed thro ...
Honors Biology Section 2 May 10, 2010 Chapter 14 History of Life
... organized as a membrane - Coacervates: collections of droplets that are composed of molecules of different types, including lipids, amino acids and sugars - Microspheres and coacervates do not have all of the properties of life ...
... organized as a membrane - Coacervates: collections of droplets that are composed of molecules of different types, including lipids, amino acids and sugars - Microspheres and coacervates do not have all of the properties of life ...
Handout 2 - CHO chemistry
... 2. Five-sided furanoses form when the C-2 keto group of a hexose reacts with one of the C-5 alcohol group to form another hemiacetal. ...
... 2. Five-sided furanoses form when the C-2 keto group of a hexose reacts with one of the C-5 alcohol group to form another hemiacetal. ...
Biogeochemical Cycles
... Sulfur (S) enters the atmosphere as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) during fossil fuel combustion, volcanic eruptions, gas exchange at ocean surfaces, and decomposition. SO2 and water vapor makes H2SO4 ( a weak sulfuric acid), which is then carried to Earth in rainfall. Sulfur in soluble form is taken up ...
... Sulfur (S) enters the atmosphere as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) during fossil fuel combustion, volcanic eruptions, gas exchange at ocean surfaces, and decomposition. SO2 and water vapor makes H2SO4 ( a weak sulfuric acid), which is then carried to Earth in rainfall. Sulfur in soluble form is taken up ...
The Proton Motive Force
... reactions occurring during growth Enzymes Typically proteins (some RNAs) Highly specific Typically rely on weak bonds Examples: hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, hydrophobic interactions Active site: region of enzyme that binds substrate Increase the rate of chemical reactions by 108 to 1020 tim ...
... reactions occurring during growth Enzymes Typically proteins (some RNAs) Highly specific Typically rely on weak bonds Examples: hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, hydrophobic interactions Active site: region of enzyme that binds substrate Increase the rate of chemical reactions by 108 to 1020 tim ...
Fibrous proteins
... classify proteins into two major groups: • Fibrous proteins, having polypeptide chains arranged in long strands or sheets. – Fibrous proteins usually consist largely of a single type of secondary structure. – Provide support, shape, and external protection to vertebrates ...
... classify proteins into two major groups: • Fibrous proteins, having polypeptide chains arranged in long strands or sheets. – Fibrous proteins usually consist largely of a single type of secondary structure. – Provide support, shape, and external protection to vertebrates ...
STEREOISOMERISM - OPTICAL ISOMERISM
... alanine, you still can't say which way it will rotate the plane of polarisation. The other amino acids, for example, have the same arrangement of groups as alanine does (all that changes is the CH3 group), but some are (+) forms and others are (-) forms. It's quite common for natural systems to only ...
... alanine, you still can't say which way it will rotate the plane of polarisation. The other amino acids, for example, have the same arrangement of groups as alanine does (all that changes is the CH3 group), but some are (+) forms and others are (-) forms. It's quite common for natural systems to only ...
Carbon Cycle and Nitrogen Cycle Readings
... We commonly think of the air that we breathe as being mostly oxygen. In fact it’s actually a mix of gasses and nearly 80% of that mix is nitrogen (N2). Nitrogen in the atmosphere comes in a chemical shape called diatomic, meaning that two nitrogen atoms are bonded together. Nitrogen is also one of t ...
... We commonly think of the air that we breathe as being mostly oxygen. In fact it’s actually a mix of gasses and nearly 80% of that mix is nitrogen (N2). Nitrogen in the atmosphere comes in a chemical shape called diatomic, meaning that two nitrogen atoms are bonded together. Nitrogen is also one of t ...
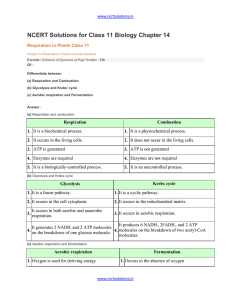
chapter_14_respiration_in_plants
... (c) Glucose molecule is assumed to be the only substrate while it is assumed that no other molecule enters the pathway at intermediate stages. (d) The intermediates produced during respiration are not utilized in any other process. ...
... (c) Glucose molecule is assumed to be the only substrate while it is assumed that no other molecule enters the pathway at intermediate stages. (d) The intermediates produced during respiration are not utilized in any other process. ...
ESSENTIAL VITAMINS
... folic acid, B6 and B12, are critical for proper methylation, a biochemical process that helps convert the problematic amino acid metabolite homocysteine into the amino acids methionine and cysteine. This process is vital for supporting cardiovascular and mental health, a healthy nervous system, regu ...
... folic acid, B6 and B12, are critical for proper methylation, a biochemical process that helps convert the problematic amino acid metabolite homocysteine into the amino acids methionine and cysteine. This process is vital for supporting cardiovascular and mental health, a healthy nervous system, regu ...
Tentative exam questions on Food Biochemistry part - e
... Define gelation as a functional property of proteins Thermally reversible and irreversible gels Influence of pH on protein gel properties What is emulsion? Define emulsification capacity and stability Why can proteins serve as emulsifying agents? Any important protein features? Utilization of prote ...
... Define gelation as a functional property of proteins Thermally reversible and irreversible gels Influence of pH on protein gel properties What is emulsion? Define emulsification capacity and stability Why can proteins serve as emulsifying agents? Any important protein features? Utilization of prote ...
Chapter 8 - Energy and Enzymes
... Many enzymes require a cofactor to assist in the reaction. These "assistants" are nonprotein and may be metal ions such as magnesium (Mg++), potassium (K+), and calcium (Ca++). The cofactors bind to the enzyme and participate in the reaction by removing electrons, protons, or chemical groups from th ...
... Many enzymes require a cofactor to assist in the reaction. These "assistants" are nonprotein and may be metal ions such as magnesium (Mg++), potassium (K+), and calcium (Ca++). The cofactors bind to the enzyme and participate in the reaction by removing electrons, protons, or chemical groups from th ...
Metabolism
... Lipids are stored as droplets in the cytoplasm which make them more difficult to access than carbohydrate reserves ...
... Lipids are stored as droplets in the cytoplasm which make them more difficult to access than carbohydrate reserves ...
Fatty acid synthesis
... Fatty acid Synthesis • Known as lipogenesis • Extramitochondrial • Highly active process • Elongation takes place in microsomes •Takes place primarily in liver & lactating mammary glands • To lesser extent in adipose tissue & kidney ...
... Fatty acid Synthesis • Known as lipogenesis • Extramitochondrial • Highly active process • Elongation takes place in microsomes •Takes place primarily in liver & lactating mammary glands • To lesser extent in adipose tissue & kidney ...
I. Circulatory System
... A) Food is broken down so that it is small enough to enter the body tissues/cells. 1. Food is broken down mechanically and chemically. 2. Nutrients and water are absorbed into the body in the small and large intestines. B) The digestive system is a one way passage through the body that includes the ...
... A) Food is broken down so that it is small enough to enter the body tissues/cells. 1. Food is broken down mechanically and chemically. 2. Nutrients and water are absorbed into the body in the small and large intestines. B) The digestive system is a one way passage through the body that includes the ...
Amino acid sequence alignment of a `small` citrate synthase from
... Escherichia coli [4] and Bacillus subtilis [S], organisms considered for many years to contain a single molecular form of CS. There is also evidence that CS isoenzymes may have different metabolic roles [6]. Citrate synthase isoenzymes have recently been purified to homogeneity, from Pseudomonas aer ...
... Escherichia coli [4] and Bacillus subtilis [S], organisms considered for many years to contain a single molecular form of CS. There is also evidence that CS isoenzymes may have different metabolic roles [6]. Citrate synthase isoenzymes have recently been purified to homogeneity, from Pseudomonas aer ...
Chapter 01 Genetics: The Study of Biological
... Both molecules store information DNA in the order of its nucleetoides and proteins in the order of amino acids ...
... Both molecules store information DNA in the order of its nucleetoides and proteins in the order of amino acids ...
Chapter 3
... • Absorbed carbohydrates transported to _____. • ________ can be stored as glycogen in liver or transported to skeletal muscle (muscle glycogen). • Glyconeogenesis: Formation of glycogen from noncarbohydrate sources • ____________: Formation of glycogen from carbohydrate sources ...
... • Absorbed carbohydrates transported to _____. • ________ can be stored as glycogen in liver or transported to skeletal muscle (muscle glycogen). • Glyconeogenesis: Formation of glycogen from noncarbohydrate sources • ____________: Formation of glycogen from carbohydrate sources ...
Essential Chemistry for Biology
... Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of the atom Electrons orbit the nucleus Number of protons = atomic number This determines the chemical properties of the element Number of protons + neutrons = mass number Atoms are electrically neutral ...
... Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of the atom Electrons orbit the nucleus Number of protons = atomic number This determines the chemical properties of the element Number of protons + neutrons = mass number Atoms are electrically neutral ...
Protein Synthesis
... given on the mRNA into a sequence of amino acids Sequence of bases specifying one amino acid ...
... given on the mRNA into a sequence of amino acids Sequence of bases specifying one amino acid ...
biochemistry/docs/Protein structure 1
... Primary sequence- The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide, listed from N-terminus to C-terminus. Secondary structure- Recurring structural feature of proteins stabilized exclusively by hydrogen bonds between peptide bond elements. Supersecondary structure- Recurring structural feature of proteins c ...
... Primary sequence- The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide, listed from N-terminus to C-terminus. Secondary structure- Recurring structural feature of proteins stabilized exclusively by hydrogen bonds between peptide bond elements. Supersecondary structure- Recurring structural feature of proteins c ...
Protein - people.vcu.edu
... genetics text (which I can’t reproduce here owing to copyright restrictions, but I can show in class if you like). Protein - 4 ...
... genetics text (which I can’t reproduce here owing to copyright restrictions, but I can show in class if you like). Protein - 4 ...
Name__________________________ Period_______ Word
... Chemical formulas are used to represent the products and reactants in a reaction. Equations can also contain much more information. Conditions under which a reaction occurs are often found above the arrow. An example of a reaction condition is the heat symbol (∆ ), which indicates that the reactants ...
... Chemical formulas are used to represent the products and reactants in a reaction. Equations can also contain much more information. Conditions under which a reaction occurs are often found above the arrow. An example of a reaction condition is the heat symbol (∆ ), which indicates that the reactants ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.