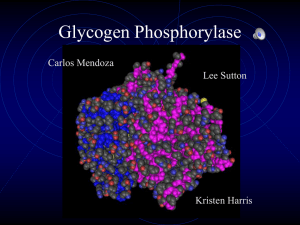
Glycogen Phosphorylase
... •There is more variation in bacteria glycogen phosphorylase than in vertebrates •This might be to the fact that bacteria has been around much longer and has had more time to change •Or it might be that Glycogen phosphorylase in vertebrates is unable to change with out causing major problems changes ...
... •There is more variation in bacteria glycogen phosphorylase than in vertebrates •This might be to the fact that bacteria has been around much longer and has had more time to change •Or it might be that Glycogen phosphorylase in vertebrates is unable to change with out causing major problems changes ...
HYDROLYSIS OF THE PEPTIDE BOND AND AMINO ACID
... proteins have shown that it can be used profitably as an alternative to hydrochloric acid. Like hydrochloric acid, it is readily available and can be purified by distillation. Moreover, the hydrolysis conditions are not as exacting-the reducing nature of the acid is apparently safeguard enough again ...
... proteins have shown that it can be used profitably as an alternative to hydrochloric acid. Like hydrochloric acid, it is readily available and can be purified by distillation. Moreover, the hydrolysis conditions are not as exacting-the reducing nature of the acid is apparently safeguard enough again ...
Chapter 2 - Tribiana.com
... 20 different amino acids can be used Amino acids contain an amino group (NH2) at one end; carboxyl group (COOH) at other end Differences between amino acids are due to differences in functional groups (“R”) ...
... 20 different amino acids can be used Amino acids contain an amino group (NH2) at one end; carboxyl group (COOH) at other end Differences between amino acids are due to differences in functional groups (“R”) ...
Final Exam Chemistry B2A Mr. Kimball`s Class 2003
... 22. Which of the following is FALSE regarding an electron? a) has a relative charge of -1 b) is abbreviated ec) has a mass of approximately 1 amu d) exists outside the nucleus e) exists in energy levels 23. Which of the following is FALSE regarding the nucleus of an atom? a) a small, low density reg ...
... 22. Which of the following is FALSE regarding an electron? a) has a relative charge of -1 b) is abbreviated ec) has a mass of approximately 1 amu d) exists outside the nucleus e) exists in energy levels 23. Which of the following is FALSE regarding the nucleus of an atom? a) a small, low density reg ...
Chemical Biology I (DM)
... 3. Optimize your initial lead compound by making analogs (SAR) and by using any additional biochemical/structural information. In parallel, screen optimized analogs against other targets (selectivity) ...
... 3. Optimize your initial lead compound by making analogs (SAR) and by using any additional biochemical/structural information. In parallel, screen optimized analogs against other targets (selectivity) ...
Relative Reactivity of Amino Acids with Chlorine
... Proline was the least reactive in mixture III (Figure 1c). As was shown for glycine, chlorination experiments of proline alone demonstrated that the higher residual percentages of proline in the chlorination experiments of mixture III were not due to interference from chlorinated proline. By conside ...
... Proline was the least reactive in mixture III (Figure 1c). As was shown for glycine, chlorination experiments of proline alone demonstrated that the higher residual percentages of proline in the chlorination experiments of mixture III were not due to interference from chlorinated proline. By conside ...
Lecture 4: bioenergetics and metabolism (mitochondria and
... These disorders are associated with dysfunction of the respiratory chain because all 13 subunits encoded by mtDNA are subunits of respiratory chain complexes. Diseases due to point mutations are transmitted by ...
... These disorders are associated with dysfunction of the respiratory chain because all 13 subunits encoded by mtDNA are subunits of respiratory chain complexes. Diseases due to point mutations are transmitted by ...
l a u n
... Ashleigh R. Borges, Karolina Z. Roszak, Christian D. Ziegler, Kevin Caran and Kevin Minbiole Molecular scaffolds, due to the highly symmetric orientation, can serve as functional points of attachment. The relative positioning of these functional groups can have a profound effect on the aggregation, ...
... Ashleigh R. Borges, Karolina Z. Roszak, Christian D. Ziegler, Kevin Caran and Kevin Minbiole Molecular scaffolds, due to the highly symmetric orientation, can serve as functional points of attachment. The relative positioning of these functional groups can have a profound effect on the aggregation, ...
Animal Transport and Exchange
... 0.5 litre more blood is supplied to the muscles than other parts of the body 1.0 litre less blood is supplied to the muscles than other parts of the body 0.5 litre less blood is supplied to the muscles than other parts of the body 1.0 litre more blood is supplied to the muscles than other parts of t ...
... 0.5 litre more blood is supplied to the muscles than other parts of the body 1.0 litre less blood is supplied to the muscles than other parts of the body 0.5 litre less blood is supplied to the muscles than other parts of the body 1.0 litre more blood is supplied to the muscles than other parts of t ...
RNA - Southgate Schools
... • Because there are four different bases, there are 64 possible, three-base codons ...
... • Because there are four different bases, there are 64 possible, three-base codons ...
invited talk
... (2004) SDPpred: a tool for prediction of amino acid residues that determine differences in functional specificity of homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids ...
... (2004) SDPpred: a tool for prediction of amino acid residues that determine differences in functional specificity of homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids ...
Chapter 6 Quiz
... c. linear d. trigonal-planar ______ 8. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of the chlorate ion, ClO3–. a. trigonal-planar b. bent c. octahedral d. trigonal-pyramidal ______ 9. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of carbon dioxide, CO2. a. tetrahedral b. bent c. linear d. octahedral ______10. Whe ...
... c. linear d. trigonal-planar ______ 8. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of the chlorate ion, ClO3–. a. trigonal-planar b. bent c. octahedral d. trigonal-pyramidal ______ 9. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of carbon dioxide, CO2. a. tetrahedral b. bent c. linear d. octahedral ______10. Whe ...
birkbeck college - Principles of Protein Structure
... The amino acid tyrosine can undertake four types of interaction with neighbouring atoms or groups within a protein molecule. Describe these interactions in detail. [10 Marks] ...
... The amino acid tyrosine can undertake four types of interaction with neighbouring atoms or groups within a protein molecule. Describe these interactions in detail. [10 Marks] ...
Lecture 9
... in solution • Crystals have 40-60% water content (similar to most cells) • Proteins may crystallize in of several forms depending on conditions. Different crystal forms of the same protein have identical conformations. • Many enzymes are catalytically active in the crystalline state. ...
... in solution • Crystals have 40-60% water content (similar to most cells) • Proteins may crystallize in of several forms depending on conditions. Different crystal forms of the same protein have identical conformations. • Many enzymes are catalytically active in the crystalline state. ...
Enzyme!
... • sucrase breaks down sucrose • proteases breakdown proteins • lipases breakdown lipids • DNA polymerase builds DNA Oh, I get it! They end in -ase ...
... • sucrase breaks down sucrose • proteases breakdown proteins • lipases breakdown lipids • DNA polymerase builds DNA Oh, I get it! They end in -ase ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.