Amino Acids and Proteins
... protein. The structural formulas of di- and tripeptides are written. The secondary forms of protein structure include the alpha helix, pleated sheet and collagen. The interaction of side groups to form the cross-links of tertiary structure is discussed. The breakdown in the secondary and tertiary st ...
... protein. The structural formulas of di- and tripeptides are written. The secondary forms of protein structure include the alpha helix, pleated sheet and collagen. The interaction of side groups to form the cross-links of tertiary structure is discussed. The breakdown in the secondary and tertiary st ...
Essential Amino Acids
... molecules, and any excess proteins you eat are broken down into their amino acids and used for energy or converted and stored as fat. Protein breakdown produces the waste urea, which is filtered from the blood by the kidneys. Urea is what gives your urine its yellow color. Why protein is needed Diet ...
... molecules, and any excess proteins you eat are broken down into their amino acids and used for energy or converted and stored as fat. Protein breakdown produces the waste urea, which is filtered from the blood by the kidneys. Urea is what gives your urine its yellow color. Why protein is needed Diet ...
b2-2biochemistryintroduction
... organisms is made of: carbon (C) oxygen (O) hydrogen (H) nitrogen (N) ...
... organisms is made of: carbon (C) oxygen (O) hydrogen (H) nitrogen (N) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 4. Define Gibb's free energy. 5. What are ketone bodies? 6. Give the energy value of one ATP molecule. 7. What is meant by β - oxidation? 8. What are porphyrins? 9. Mention the role of glutamate dehydrogenase. 10. What are primary metabolites? Part - B (8 x 5 = 40) Answer any five of the following q ...
... 4. Define Gibb's free energy. 5. What are ketone bodies? 6. Give the energy value of one ATP molecule. 7. What is meant by β - oxidation? 8. What are porphyrins? 9. Mention the role of glutamate dehydrogenase. 10. What are primary metabolites? Part - B (8 x 5 = 40) Answer any five of the following q ...
CHEM523 Final Exam
... 1) Below are seven amino acids. Indicate all characteristics that apply to each amino acid by writing the appropriate letter(s) in the blanks provided. Note: Each entry may have more than one letter associated with it. Amino acid ...
... 1) Below are seven amino acids. Indicate all characteristics that apply to each amino acid by writing the appropriate letter(s) in the blanks provided. Note: Each entry may have more than one letter associated with it. Amino acid ...
05 DetailLectOut 2012
... ○ A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ○ Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. The chemical mechanisms that cells use to mak ...
... ○ A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ○ Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. The chemical mechanisms that cells use to mak ...
Document
... v| Entry of substrates into mt Limit availability of substrates for ETC? …limit flux through ETC …limit ROS production/oxidative damage ...
... v| Entry of substrates into mt Limit availability of substrates for ETC? …limit flux through ETC …limit ROS production/oxidative damage ...
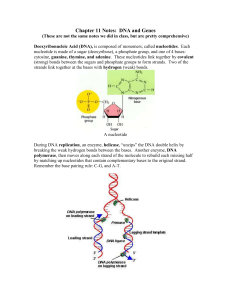
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... During DNA replication, an enzyme, helicase, “unzips” the DNA double helix by breaking the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase, then moves along each strand of the molecule to rebuild each missing half by matching up nucleotides that contain complementary bases to t ...
... During DNA replication, an enzyme, helicase, “unzips” the DNA double helix by breaking the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase, then moves along each strand of the molecule to rebuild each missing half by matching up nucleotides that contain complementary bases to t ...
Chapter 5
... of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most b ...
... of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most b ...
Document
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
Biochemistry - Ursuline High School
... • Similar to fats, but have only two fatty acids. • The third -OH of the glycerol is joined to a phosphate group replacing a fatty acid • Major component of the Plasma Membrane of all cells ...
... • Similar to fats, but have only two fatty acids. • The third -OH of the glycerol is joined to a phosphate group replacing a fatty acid • Major component of the Plasma Membrane of all cells ...
Document
... phosphate group (—OPO32–) is an ionized form of a phosphoric acid group (—OPO3H2; note the two hydrogens). ...
... phosphate group (—OPO32–) is an ionized form of a phosphoric acid group (—OPO3H2; note the two hydrogens). ...
IIIb
... 5. (12 Pts) Unlike most organs, muscle uses three specific amino acids as energy sources. What are these amino acids (structures)? Choose one and draw its degradation pathway. ...
... 5. (12 Pts) Unlike most organs, muscle uses three specific amino acids as energy sources. What are these amino acids (structures)? Choose one and draw its degradation pathway. ...
Answers to Exam 1 multiple choice, TF and short answer questions
... 13. Which of the following statements is(are) FALSE? a. Peptide bonds are the covalent bonds that link together two amino acids in proteins. b. The polypeptide backbone is free to rotate about each peptide bond. c. Nonpolar amino acids tend to be found in the interior of cytosolic proteins. d. The s ...
... 13. Which of the following statements is(are) FALSE? a. Peptide bonds are the covalent bonds that link together two amino acids in proteins. b. The polypeptide backbone is free to rotate about each peptide bond. c. Nonpolar amino acids tend to be found in the interior of cytosolic proteins. d. The s ...
Amino Acids - Shelton State
... Proline is unique among the amino acids because its "branch" and amino group are linked forming a ring. The presence of proline in a peptide usually creates a bend in the chain. ...
... Proline is unique among the amino acids because its "branch" and amino group are linked forming a ring. The presence of proline in a peptide usually creates a bend in the chain. ...
Chapter 5 Notes:
... A. Photosynthesis Transforms Solar Energy into the chemical bond energy of Glucose B. Organic molecules built by photosynthesis provide both the building blocks and energy for cells. C. Plants use the raw materials: carbon dioxide and water D. Chloroplasts carry out photosynthesis E. Chlorophylls an ...
... A. Photosynthesis Transforms Solar Energy into the chemical bond energy of Glucose B. Organic molecules built by photosynthesis provide both the building blocks and energy for cells. C. Plants use the raw materials: carbon dioxide and water D. Chloroplasts carry out photosynthesis E. Chlorophylls an ...
PPT_Biochemistry_Short_Course
... Polysaccharides Storage forms of sugars (cellular fuel & some structural components) = larger size so lower solubility (doesn’t break down as easily) Starch • Type of polysaccharide found in Plants • Cellulose & lignin indigestible by humans • Used for FIBER (drink lots of water!!) ...
... Polysaccharides Storage forms of sugars (cellular fuel & some structural components) = larger size so lower solubility (doesn’t break down as easily) Starch • Type of polysaccharide found in Plants • Cellulose & lignin indigestible by humans • Used for FIBER (drink lots of water!!) ...
DNA to Proteins
... it to hold information * The order of the bases is the code that carries the information * A gene is a string or group of nucleotides that give the cell information on how to make a protein. * Humans have over 30,000 genes ...
... it to hold information * The order of the bases is the code that carries the information * A gene is a string or group of nucleotides that give the cell information on how to make a protein. * Humans have over 30,000 genes ...
Ch 2 PowerPoint Notes
... •In an unsaturated fatty acid, some of the carbon atoms are linked by a ―double‖ covalent bond, each with only one hydrogen atom, producing kinks in the molecule. Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Acids •Saturated fats, such as butter, are solid at room temperature. •Unsaturated fats, such as olive oi ...
... •In an unsaturated fatty acid, some of the carbon atoms are linked by a ―double‖ covalent bond, each with only one hydrogen atom, producing kinks in the molecule. Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Acids •Saturated fats, such as butter, are solid at room temperature. •Unsaturated fats, such as olive oi ...
Protein Synthesis - OpotikiCollegeBiology
... and proteins are built out of amino acids. • How does the chromosome alphabet get changed into structures that join up to make proteins? ...
... and proteins are built out of amino acids. • How does the chromosome alphabet get changed into structures that join up to make proteins? ...
HMH 2.3 notes
... Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. • Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. ...
... Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. • Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. ...
Chap02 ed11
... composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. b. Carbohydrates are made from monosaccharides (simple sugars); disaccharides are two monosaccharides joined together; complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides), such as starch, are built of many sugars. c. Humans synthesize the polysaccharide glycogen. Lipids ...
... composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. b. Carbohydrates are made from monosaccharides (simple sugars); disaccharides are two monosaccharides joined together; complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides), such as starch, are built of many sugars. c. Humans synthesize the polysaccharide glycogen. Lipids ...
cell membranes gs
... The membrane that surrounds every cell, forming the selectively permeable boundary between the cell and its environment. It is made up of a double layer of phospholipids with embedded proteins. ...
... The membrane that surrounds every cell, forming the selectively permeable boundary between the cell and its environment. It is made up of a double layer of phospholipids with embedded proteins. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.