File - Mrs. Barrett`s Biology Site
... There are 20 common and several rare amino acids found in proteins • Amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds • This results in the formation of polypeptide chains ...
... There are 20 common and several rare amino acids found in proteins • Amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds • This results in the formation of polypeptide chains ...
A1985ASW1100001
... —CCA end) and also considerable labeling by amino acids, particularly in the pH 5 fraction. We found the amino acid label to be in “soluble” mRNA. The cited studies indicated that each of the amino acids was bound to the new RNA reversibly and at a separate site. The clincher as to its role in prote ...
... —CCA end) and also considerable labeling by amino acids, particularly in the pH 5 fraction. We found the amino acid label to be in “soluble” mRNA. The cited studies indicated that each of the amino acids was bound to the new RNA reversibly and at a separate site. The clincher as to its role in prote ...
Mutations Powerpoint
... The cell cycle is regulated by proteins. If these proteins are defective, cells divide prolifically. ...
... The cell cycle is regulated by proteins. If these proteins are defective, cells divide prolifically. ...
26,6 Synthesis of omino ocids
... Tyrosine,the only nonessential amino acid with an aromatic side chain, is produced from the essential amino acid phenylalanine. The conversion requires a single oxidation step catalyzed by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. Phenylalanine ...
... Tyrosine,the only nonessential amino acid with an aromatic side chain, is produced from the essential amino acid phenylalanine. The conversion requires a single oxidation step catalyzed by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. Phenylalanine ...
Functions of proteins
... Involves the folding of secondary structures to form a globular (round, compact) protein shape Caused by interactions between the R groups in the amino acids Held together by many bonds (H-bonds, dipole-dipole, London, ionic, covalent) (ex of covalent = disulfide bride bond forms between S o ...
... Involves the folding of secondary structures to form a globular (round, compact) protein shape Caused by interactions between the R groups in the amino acids Held together by many bonds (H-bonds, dipole-dipole, London, ionic, covalent) (ex of covalent = disulfide bride bond forms between S o ...
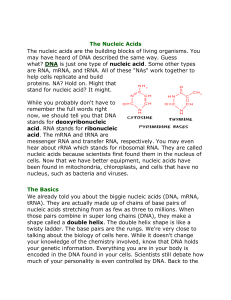
Introduction to Nucleic Acids
... There are five easy parts of nucleic acids. All nucleic acids are made up of the same building blocks (monomers). Chemists call the monomers "nucleotides." The five pieces are uracil, cytosine, thymine,a denine, and guanine. No matter what science class you are in, you will always hear about ATCG wh ...
... There are five easy parts of nucleic acids. All nucleic acids are made up of the same building blocks (monomers). Chemists call the monomers "nucleotides." The five pieces are uracil, cytosine, thymine,a denine, and guanine. No matter what science class you are in, you will always hear about ATCG wh ...
Properties of the Major Biological Molecules
... protein. So, ultimately any two proteins are different from one another due to the shape they form from the sequence of their amino acid monomers. What is the difference between a polypeptide and a protein? A polypeptide is a short, straight chain of amino acids. A protein is a very long polymer t ...
... protein. So, ultimately any two proteins are different from one another due to the shape they form from the sequence of their amino acid monomers. What is the difference between a polypeptide and a protein? A polypeptide is a short, straight chain of amino acids. A protein is a very long polymer t ...
Name__________________________________________
... Proteins are a major part of every living cell and have many different functions within each cell. Carbohydrates also perform numerous roles in living things. Part A: Describe the general composition of a protein molecule. A protein is a polymer made of amino acid monomers. Proteins contain the elem ...
... Proteins are a major part of every living cell and have many different functions within each cell. Carbohydrates also perform numerous roles in living things. Part A: Describe the general composition of a protein molecule. A protein is a polymer made of amino acid monomers. Proteins contain the elem ...
Curriculum for Excellence Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Nature`s Che
... The hydrocarbon tail is hydrophobic (water-hating) and dissolves well in grease and oil. How to explain the cleaning action of soap. Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions which form a scum with soap. Detergents were developed to combat hard-water conditions. Detergents clean in th ...
... The hydrocarbon tail is hydrophobic (water-hating) and dissolves well in grease and oil. How to explain the cleaning action of soap. Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions which form a scum with soap. Detergents were developed to combat hard-water conditions. Detergents clean in th ...
Amino Acids 2
... Unlike the alpha helix, composed of two or more peptide chains Polypeptide chains are joined by hydrogen bonds When the hydrogen bonds are formed between the polypeptide chains they are termed interchains. The polypeptide chains can run parallel to each other or antiparallel – Recall the “ends” of a ...
... Unlike the alpha helix, composed of two or more peptide chains Polypeptide chains are joined by hydrogen bonds When the hydrogen bonds are formed between the polypeptide chains they are termed interchains. The polypeptide chains can run parallel to each other or antiparallel – Recall the “ends” of a ...
Metabolism
... •When the 2 high-energy phosphate bonds in ATP are hydrolyzed – energy is released – phosphate is transferred to other molecules ...
... •When the 2 high-energy phosphate bonds in ATP are hydrolyzed – energy is released – phosphate is transferred to other molecules ...
Protein Synthesis
... and they are broken down during digestion. 8. tRNA pairs with mRNA and brings the correct amino acid with it to the ribosome. 9. Peptide bonds are formed between the amino acids, and voila, a protein is formed. ...
... and they are broken down during digestion. 8. tRNA pairs with mRNA and brings the correct amino acid with it to the ribosome. 9. Peptide bonds are formed between the amino acids, and voila, a protein is formed. ...
Cell Metabolism
... Thousands of molecules in each cell continually reacting with each other to maintain cell function DNA directs cell metabolism by instructing the cell to make proteins Do this now; hand it in Read: Whale book pg 1801 Answer these Q’s with complete thoughts & sentences: • What determines the shap ...
... Thousands of molecules in each cell continually reacting with each other to maintain cell function DNA directs cell metabolism by instructing the cell to make proteins Do this now; hand it in Read: Whale book pg 1801 Answer these Q’s with complete thoughts & sentences: • What determines the shap ...
Unit 2 Test Review
... 16. Which molecule is the most abundant in the human body? water 17. Enzymes only work with specific substrates because each enzyme — ...
... 16. Which molecule is the most abundant in the human body? water 17. Enzymes only work with specific substrates because each enzyme — ...
Chapter Two: Matter
... B. Macromolecules- very large molecules 1. monomers- smaller unit that can join together with other small ...
... B. Macromolecules- very large molecules 1. monomers- smaller unit that can join together with other small ...
Assignment 6 Cell Respiration
... transfer this energy into the molecule called Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP). The processes involved are Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) (also called the electron transport system or shuttle (ETS)). Glycolysis occurs as a series of enzymatically driven steps (10) w ...
... transfer this energy into the molecule called Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP). The processes involved are Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) (also called the electron transport system or shuttle (ETS)). Glycolysis occurs as a series of enzymatically driven steps (10) w ...
Section 6.1 Summary – pages 141-151
... molecules of other substances • Water has a greater resists to changes in temperature (boiling and feezing) • Found in all 3 states: gas, a liquid, and a solid – Less dense when in a solid state • Helps in temperature regulation of all organisms on ...
... molecules of other substances • Water has a greater resists to changes in temperature (boiling and feezing) • Found in all 3 states: gas, a liquid, and a solid – Less dense when in a solid state • Helps in temperature regulation of all organisms on ...
Introduction: Proteins are one of the three major classes of biological
... Proteins are one of the three major classes of biological macromolecules that perform a variety of functions in a cell. Among other things, they catalyze chemical reactions that drive biological processes. They also provide the physical support for life and pass signals that tell cells how to behave ...
... Proteins are one of the three major classes of biological macromolecules that perform a variety of functions in a cell. Among other things, they catalyze chemical reactions that drive biological processes. They also provide the physical support for life and pass signals that tell cells how to behave ...
Chapter 1
... Lipid, & Protein Metabolism • TCA cycle & electron transport chain - common to all 3 • This catabolic pathway also: – Produces CO2 for carboxylation & C for other needs – Provides common intermediates – Provides citrate & malate for lipogenesis 2009 Cengage-Wadsworth ...
... Lipid, & Protein Metabolism • TCA cycle & electron transport chain - common to all 3 • This catabolic pathway also: – Produces CO2 for carboxylation & C for other needs – Provides common intermediates – Provides citrate & malate for lipogenesis 2009 Cengage-Wadsworth ...
Translation
... In order for a cell to make a protein, DNA must be transcribed into ____________ and the mRNA must then be translated into _____________. The processes of transcription and translation together are called _________________________. The process of transcription occurs in the ____________ of a cell. T ...
... In order for a cell to make a protein, DNA must be transcribed into ____________ and the mRNA must then be translated into _____________. The processes of transcription and translation together are called _________________________. The process of transcription occurs in the ____________ of a cell. T ...
Characterization of AtAAP1 function in amino acid uptake by the root
... in expanding the range of nitrogen sources of their host plants to include organic forms. Many studies have examined the uptake of amino acids using specific 13C-labeled amino acids such as glycine but the generality of these results is questionable because microbes assimilate a broad range of amino ...
... in expanding the range of nitrogen sources of their host plants to include organic forms. Many studies have examined the uptake of amino acids using specific 13C-labeled amino acids such as glycine but the generality of these results is questionable because microbes assimilate a broad range of amino ...
Biochemistry Chp 3
... Lipids (CHO) 2x as many H as C, fewer O Proteins (CHONS) Nucleic Acids (CHONP) ...
... Lipids (CHO) 2x as many H as C, fewer O Proteins (CHONS) Nucleic Acids (CHONP) ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.