PowerPoint Presentation - Biochemistry
... Amino acid structural components can be divided into four parts that are illustrated below. Only the side chain varies among the alpha (α-) amino acids. ...
... Amino acid structural components can be divided into four parts that are illustrated below. Only the side chain varies among the alpha (α-) amino acids. ...
Unit 1: Biology Review
... some is kept in the body for blood pH (carbon dioxide) and hydrolysis reactions (water). - The most important product of respiration is the production of ATP (stored chemical potential energy). - Cell respiration occurs in your mitochondria (remember). - There are actually three stages to respiratio ...
... some is kept in the body for blood pH (carbon dioxide) and hydrolysis reactions (water). - The most important product of respiration is the production of ATP (stored chemical potential energy). - Cell respiration occurs in your mitochondria (remember). - There are actually three stages to respiratio ...
APDC Unit IV Biochem
... Energy can be transferred and transformed Energy cannot be created or destroyed Also called the principle of Conservation of ...
... Energy can be transferred and transformed Energy cannot be created or destroyed Also called the principle of Conservation of ...
Amino acids, introduction
... There are many ways to characterize the properties of amino acids. The ones most useful and most commonly used are: Hydrophobicity Size Charge Secondary structure preference Alcoholicity Aromaticity And on top of that there are some special characteristics like bridge forming by cysteines, rigidity ...
... There are many ways to characterize the properties of amino acids. The ones most useful and most commonly used are: Hydrophobicity Size Charge Secondary structure preference Alcoholicity Aromaticity And on top of that there are some special characteristics like bridge forming by cysteines, rigidity ...
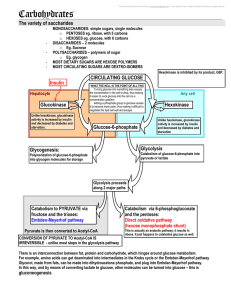
Fate of glucose:
... The brain is the main glucose hog and the reason glucose is so important The brain uses 2/3 of the glucose consumed The rest of your body’s energy reserves are 78% in body fat and 21% in proteins. Diabetes is a problem with insulin so diabetic’s cells can’t uptake and efficiently use glucose so bloo ...
... The brain is the main glucose hog and the reason glucose is so important The brain uses 2/3 of the glucose consumed The rest of your body’s energy reserves are 78% in body fat and 21% in proteins. Diabetes is a problem with insulin so diabetic’s cells can’t uptake and efficiently use glucose so bloo ...
Cellular Respiration Stations Worksheet Station 1: Overview Why is
... 3. True or false? If false, make it so that the answer is true: Glycolysis occurs in the mitochondria. 4. Is oxygen needed in order for glycolysis to occur? 5. Fill in the blanks below with regards to the steps of glycolysis: Step 1: Glucose is phosphorylated with _____________ phosphates; these pho ...
... 3. True or false? If false, make it so that the answer is true: Glycolysis occurs in the mitochondria. 4. Is oxygen needed in order for glycolysis to occur? 5. Fill in the blanks below with regards to the steps of glycolysis: Step 1: Glucose is phosphorylated with _____________ phosphates; these pho ...
File
... CoA is released to go back to the outer compartment. • This entire process consumes water (to get oxygen, making the process aerobic), and releases 6 NADH + H+ & 2 FADH2 molecules, 4 CO2 molecules per glucose molecule that we started with, and produces 2 ATP per glucose molecule that we started with ...
... CoA is released to go back to the outer compartment. • This entire process consumes water (to get oxygen, making the process aerobic), and releases 6 NADH + H+ & 2 FADH2 molecules, 4 CO2 molecules per glucose molecule that we started with, and produces 2 ATP per glucose molecule that we started with ...
melgarejo richard
... Carbon’s electron configuration is one that has two valence electrons in the first level and four on the next level giving it the ability to do covalent bonds because Carbon cannot form ionic bonds. It is not allowed to lose or gain electrons. It can form four covalent bonds. Carbon skeletons can ha ...
... Carbon’s electron configuration is one that has two valence electrons in the first level and four on the next level giving it the ability to do covalent bonds because Carbon cannot form ionic bonds. It is not allowed to lose or gain electrons. It can form four covalent bonds. Carbon skeletons can ha ...
1. Why is cellular respiration called an aerobic process? 2. What
... Define the words in the boxes. On the line across each arrow, write a phrase that describes how the words in the boxes are related to one another. ...
... Define the words in the boxes. On the line across each arrow, write a phrase that describes how the words in the boxes are related to one another. ...
You should be able to identify each of the following functional
... You should be able to identify each of the following functional groups within organic molecules: amino group within an amine molecule (both the form found at low pH and high pH) carbonyl group within an aldehyde molecule (you need to know it is within an aldehyde vs a ketone) carbonyl group within a ...
... You should be able to identify each of the following functional groups within organic molecules: amino group within an amine molecule (both the form found at low pH and high pH) carbonyl group within an aldehyde molecule (you need to know it is within an aldehyde vs a ketone) carbonyl group within a ...
Biological Molecules: Structure and Methods of Analysis
... a substance changes form a solid to a liquid. Molecules in a solid state are packed together in an orderly fashion with very much movement, while molecules in a liquid state are moving around in a random pattern termed Brownian motion. Therefore, the melting point is affected by anything that affect ...
... a substance changes form a solid to a liquid. Molecules in a solid state are packed together in an orderly fashion with very much movement, while molecules in a liquid state are moving around in a random pattern termed Brownian motion. Therefore, the melting point is affected by anything that affect ...
week-1-2 - WordPress.com
... 1.All cells are bounded by a plasma membrane; have a cytosol containing metabolites, coenzymes, inorganic ions, and enzymes; and have a set of genes contained within a nucleoid (prokaryotes) or nucleus (eukaryotes). 2.Phototrophs use sunlight to do work; chemotrophs oxidize fuels, passing electrons ...
... 1.All cells are bounded by a plasma membrane; have a cytosol containing metabolites, coenzymes, inorganic ions, and enzymes; and have a set of genes contained within a nucleoid (prokaryotes) or nucleus (eukaryotes). 2.Phototrophs use sunlight to do work; chemotrophs oxidize fuels, passing electrons ...
Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) Human E. coli
... kingdom. The three known mammalian Hh proteins, Sonic (Shh), Desert (Dhh) and Indian (Ihh), are structurally related, and share a high degree of amino acid sequence identity (e.g. Shh and Ihh are 93% identical). The biologically active form of each Hh molecule is obtained by autocatalytic cleavage o ...
... kingdom. The three known mammalian Hh proteins, Sonic (Shh), Desert (Dhh) and Indian (Ihh), are structurally related, and share a high degree of amino acid sequence identity (e.g. Shh and Ihh are 93% identical). The biologically active form of each Hh molecule is obtained by autocatalytic cleavage o ...
Nitrogen Anabolism
... by the nitrogenase complex, which uses ATP to transfer electrons from a donor (harvested from a redox protein such as ferredoxin). Nitrogenase Complex ...
... by the nitrogenase complex, which uses ATP to transfer electrons from a donor (harvested from a redox protein such as ferredoxin). Nitrogenase Complex ...
here - Biology 100
... For each NADH that enters the electron transport chain, two molecules of ATP are produced. b. The products of glycolysis include ATP, NADH, and pyruvate. c. Aerobic respiration requires the presence of oxygen. d. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells while aerobic respiration occurs ...
... For each NADH that enters the electron transport chain, two molecules of ATP are produced. b. The products of glycolysis include ATP, NADH, and pyruvate. c. Aerobic respiration requires the presence of oxygen. d. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells while aerobic respiration occurs ...
chapter20
... Formation of Cells First cell membranes may have formed before the beginning of life: Single amino acids can be assembled into long protein-like molecules, which form microspheres when they cool in water. Cell membranes ...
... Formation of Cells First cell membranes may have formed before the beginning of life: Single amino acids can be assembled into long protein-like molecules, which form microspheres when they cool in water. Cell membranes ...
MITOCHONDRIA
... produce the majority of the cell's ATP. The cellular respiration reactions that occur in the mitochondria are: Pyruvate Oxidation (Link reaction), Krebs Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) They require oxygen and are considered aerobic. Prokaryotes do these reactions in the cytoplasm with m ...
... produce the majority of the cell's ATP. The cellular respiration reactions that occur in the mitochondria are: Pyruvate Oxidation (Link reaction), Krebs Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) They require oxygen and are considered aerobic. Prokaryotes do these reactions in the cytoplasm with m ...
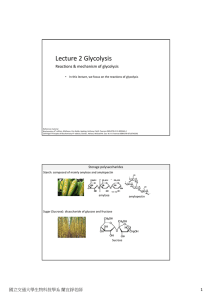
Lecture 2 Glycolysis
... Cellulose: polymers of glucose Hemicellulose: Copolymers of various sugars including, glucose xylose arabinose glucuronic acid etc.. Lignin: polymers of aromatic alcohols which provides structure strength for the cellulose and hemicellulose fibers ...
... Cellulose: polymers of glucose Hemicellulose: Copolymers of various sugars including, glucose xylose arabinose glucuronic acid etc.. Lignin: polymers of aromatic alcohols which provides structure strength for the cellulose and hemicellulose fibers ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.