Computational Biology 1 - Bioinformatics Institute
... 1) How can a protein have two stable “lowest energy states”? 2) What is the rate of inter-conversion between them? 3) What does the auto-catalysis do? 4) How much inter-conversion leads to disease? 5) Under what conditions can the disease be transmitted? ...
... 1) How can a protein have two stable “lowest energy states”? 2) What is the rate of inter-conversion between them? 3) What does the auto-catalysis do? 4) How much inter-conversion leads to disease? 5) Under what conditions can the disease be transmitted? ...
Cellular Respiration Overview
... pumping H+ into the outer compartment of the mitochondria Where: The mitochondria A gradient is created to produce ATP • Electrons continue down the energy gradient ...
... pumping H+ into the outer compartment of the mitochondria Where: The mitochondria A gradient is created to produce ATP • Electrons continue down the energy gradient ...
Biochemistry Powerpoint - Glasgow Independent Schools
... • The main purpose of fats is to store energy. • Fats can store energy even more efficiently than carbohydrates. • The cell’s boundary is made of phospholipids. The structure of cell membranes depends on how this molecule interacts with water. • Waxes, found on the surfaces of plants and aquatic bir ...
... • The main purpose of fats is to store energy. • Fats can store energy even more efficiently than carbohydrates. • The cell’s boundary is made of phospholipids. The structure of cell membranes depends on how this molecule interacts with water. • Waxes, found on the surfaces of plants and aquatic bir ...
Final Respiration
... • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for bacteria, but more complex organisms need more of glucose’s energy. ...
... • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for bacteria, but more complex organisms need more of glucose’s energy. ...
cellrespdiagrams
... • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for bacteria, but more complex organisms need more of glucose’s energy. ...
... • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for bacteria, but more complex organisms need more of glucose’s energy. ...
Final Respiration
... • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for bacteria, but more complex organisms need more of glucose’s energy. ...
... • Where does the rest go? • It’s still in pyruvic acid • This small amount of energy is enough for bacteria, but more complex organisms need more of glucose’s energy. ...
Intro powerpoint Energy systems
... The amount of ATP produced by this process will allow an athlete to engage in a high level of performance for an additional 1-3 minutes ...
... The amount of ATP produced by this process will allow an athlete to engage in a high level of performance for an additional 1-3 minutes ...
Working with Data Primary Structure Specifies Tertiary Structure
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
[edit]More recent updates
... bonding, ionic interactions, Van Der Waals forces, and hydrophobicpacking. To understand the functions of proteins at a molecular level, it is often necessary to determine their three-dimensional structure. This is the topic of the scientific field of structural biology, which employs techniques suc ...
... bonding, ionic interactions, Van Der Waals forces, and hydrophobicpacking. To understand the functions of proteins at a molecular level, it is often necessary to determine their three-dimensional structure. This is the topic of the scientific field of structural biology, which employs techniques suc ...
The Molecular Basis of Life
... Test for macromolecules found in living organisms. Use three-dimensional models of important compounds. ...
... Test for macromolecules found in living organisms. Use three-dimensional models of important compounds. ...
Water molecule - Biology Courses Server
... What might be the factory doors? The power plant? The warehouse? Shipping and receiving? Recycling plant etc 8. Which amino acids are most likely to be found in each section of this transmembrane protein. Why? ...
... What might be the factory doors? The power plant? The warehouse? Shipping and receiving? Recycling plant etc 8. Which amino acids are most likely to be found in each section of this transmembrane protein. Why? ...
Table S1. - BioMed Central
... Key enzyme of the glycolysis; HK 2 is involved in increased utilization of glucose by cancer cells; target of new antineoplastic pharmacologic agents [35, 36]. Key enzyme of the glycolysis; PFK-1 is inhibited by ATP and citrate (from the citric acid cycle) [127]. Executes the final step of aerobic g ...
... Key enzyme of the glycolysis; HK 2 is involved in increased utilization of glucose by cancer cells; target of new antineoplastic pharmacologic agents [35, 36]. Key enzyme of the glycolysis; PFK-1 is inhibited by ATP and citrate (from the citric acid cycle) [127]. Executes the final step of aerobic g ...
1st lecture CELLS
... and ribosomes. Cell Size and Shape The shapes of cells are quite varied with some, such as neurons, being longer than they are wide and others, such as parenchyma (a common type of plant cell) and erythrocytes (red blood cells) being equidimensional. Some cells are encased in a rigid wall, which con ...
... and ribosomes. Cell Size and Shape The shapes of cells are quite varied with some, such as neurons, being longer than they are wide and others, such as parenchyma (a common type of plant cell) and erythrocytes (red blood cells) being equidimensional. Some cells are encased in a rigid wall, which con ...
review topics to prepare for the health biology proficiency exam
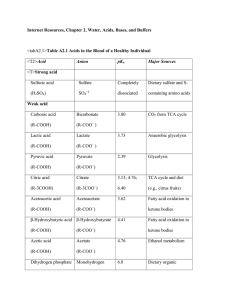
... mass, isotopes, chemical symbols b. atoms and molecules ionization, anions, cations, bonding: ionic, covalent (polar, non-polar), hydrogen c. acids, bases, pH, buffers Organic a. functional groups, example: amino group, carboxyl group, hydroxyl group b. biologically important molecules: carbohydrate ...
... mass, isotopes, chemical symbols b. atoms and molecules ionization, anions, cations, bonding: ionic, covalent (polar, non-polar), hydrogen c. acids, bases, pH, buffers Organic a. functional groups, example: amino group, carboxyl group, hydroxyl group b. biologically important molecules: carbohydrate ...
LS1a Fall 2014 Lab 2 (PyMOL- Protein) question sheet Q1) (10 points)
... residues away? Hydrogen atoms bound to the backbone nitrogens of the peptide bonds act as the H-bond donors (the entire N-H group can also be considered the donor). Carbonyl oxygen atoms of the backbone peptide bonds act as the acceptors. The H-bond donating residue is 4 residues away from the H-bon ...
... residues away? Hydrogen atoms bound to the backbone nitrogens of the peptide bonds act as the H-bond donors (the entire N-H group can also be considered the donor). Carbonyl oxygen atoms of the backbone peptide bonds act as the acceptors. The H-bond donating residue is 4 residues away from the H-bon ...
Name Date
... 8. In alcoholic fermentation, _______ is the final acceptor of the electrons stripped from glucose. a. oxygen c. acetaldehyde b. kinase d. sulfate 9. Fermentation produces no more ATP beyond the small yield from glycolysis, but the remaining reactions a. regenerate ADP c. dump electrons on an inorga ...
... 8. In alcoholic fermentation, _______ is the final acceptor of the electrons stripped from glucose. a. oxygen c. acetaldehyde b. kinase d. sulfate 9. Fermentation produces no more ATP beyond the small yield from glycolysis, but the remaining reactions a. regenerate ADP c. dump electrons on an inorga ...
Organization: The 6 Essential Elements
... There are several types of lipids, but all contain subunits of glycerol and fatty acids made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It is different from a carbohydrate because of the ratio and because the smaller units do not link together to form a chemical chain ...
... There are several types of lipids, but all contain subunits of glycerol and fatty acids made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It is different from a carbohydrate because of the ratio and because the smaller units do not link together to form a chemical chain ...
Notes - Learner
... Further processing of pyruvate depends on the aerobic or anaerobic nature of an organism. In anaerobic respiration, pyruvate is further processed to produce either lactic acid or ethyl alcohol. There is incomplete oxidation of glucose in anaerobic respiration. In aerobic respiration, pyruvate is fur ...
... Further processing of pyruvate depends on the aerobic or anaerobic nature of an organism. In anaerobic respiration, pyruvate is further processed to produce either lactic acid or ethyl alcohol. There is incomplete oxidation of glucose in anaerobic respiration. In aerobic respiration, pyruvate is fur ...
Unit 1 – Life on Earth
... 3: The ribosome reads 3 bases (called a codon) at a time and brings the amino acid associated with that codon into position to form a polypeptide chain. ...
... 3: The ribosome reads 3 bases (called a codon) at a time and brings the amino acid associated with that codon into position to form a polypeptide chain. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.







![[edit]More recent updates](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022145907_1-8f0620400434ad236b249c9cd08f1aa3-300x300.png)