+ E A.
... Endopeptidases – hydrolyse the peptide bond inside a chain Pepsin, trypsin, chymotrypsin Exopeptidases – split the peptide bond at the end of a protein molecule Aminopeptidase, carboxypeptidases ...
... Endopeptidases – hydrolyse the peptide bond inside a chain Pepsin, trypsin, chymotrypsin Exopeptidases – split the peptide bond at the end of a protein molecule Aminopeptidase, carboxypeptidases ...
AQA Biology - Centre of the Cell
... 3.4.1 DNA, genes and chromosomes In the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, DNA molecules are very long, linear and associated with proteins, called histones. Together a DNA molecule and its associated proteins form a chromosome. A gene is a base sequence of DNA that codes for: • the amino acid sequence of ...
... 3.4.1 DNA, genes and chromosomes In the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, DNA molecules are very long, linear and associated with proteins, called histones. Together a DNA molecule and its associated proteins form a chromosome. A gene is a base sequence of DNA that codes for: • the amino acid sequence of ...
Biology Unit 2
... You only need one version of the allele to be a sufferer. The extra digit can be removed ...
... You only need one version of the allele to be a sufferer. The extra digit can be removed ...
B2 mindmaps File
... You only need one version of the allele to be a sufferer. The extra digit can be removed ...
... You only need one version of the allele to be a sufferer. The extra digit can be removed ...
The Chemical Level of Organization
... • Main function is source of energy for ATP formation • Forms only 2-3 % of total body weight – glycogen is storage in liver and muscle tissue – sugar building blocks of DNA & RNA (deoxyribose & ribose sugars) – Only plants produce starch for energy storage ...
... • Main function is source of energy for ATP formation • Forms only 2-3 % of total body weight – glycogen is storage in liver and muscle tissue – sugar building blocks of DNA & RNA (deoxyribose & ribose sugars) – Only plants produce starch for energy storage ...
Biology Unit 2
... You only need one version of the allele to be a sufferer. The extra digit can be removed ...
... You only need one version of the allele to be a sufferer. The extra digit can be removed ...
Lect4 Proteins
... Hydrogen bonds: weak electrostatic attractions between electronegative atom (O or N). Van der Waals forces: can be attractive or repulsive, depends on distance Electrostatic interactions or ionic bonds: weak bonds that form between charged groups in aqueous environments Hydrophobic effects: arise be ...
... Hydrogen bonds: weak electrostatic attractions between electronegative atom (O or N). Van der Waals forces: can be attractive or repulsive, depends on distance Electrostatic interactions or ionic bonds: weak bonds that form between charged groups in aqueous environments Hydrophobic effects: arise be ...
Biological Basis PDF worksheet - UNC
... The sequence of bases from one nucleotide to the next in line is the code for the assembly of specific amino acids to make specific types of proteins. Therefore, a gene is essentially a specific sequence of these base pairs. The sequence need not be continuous but can be divided into different secti ...
... The sequence of bases from one nucleotide to the next in line is the code for the assembly of specific amino acids to make specific types of proteins. Therefore, a gene is essentially a specific sequence of these base pairs. The sequence need not be continuous but can be divided into different secti ...
Science, Matter, Energy, and Systems Key Terms
... Nitrogen fixation-‐ Process by which free nitrogen (N2) is extracted from the atmosphere and converted (fixed) into nitrogen compounds which are plant nutrients (fertilizer). In nature, this process is carried ...
... Nitrogen fixation-‐ Process by which free nitrogen (N2) is extracted from the atmosphere and converted (fixed) into nitrogen compounds which are plant nutrients (fertilizer). In nature, this process is carried ...
Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... The Relationship between Cellular Respiration and Breathing Cellular respiration requires a cell to exchange gases with its surroundings. Breathing exchanges these gases between the blood and outside air. Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... The Relationship between Cellular Respiration and Breathing Cellular respiration requires a cell to exchange gases with its surroundings. Breathing exchanges these gases between the blood and outside air. Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Metabolism Fact Sheet - Barth Syndrome Foundation
... production. Summarizing: a gene named TAZ encodes a protein called tafazzin that probably functions as an enzyme to help make mature cardiolipin. Cardiolipin is made first with one kind of fatty acids attached to it which are mostly saturated, then the original fatty acids are removed and other fatt ...
... production. Summarizing: a gene named TAZ encodes a protein called tafazzin that probably functions as an enzyme to help make mature cardiolipin. Cardiolipin is made first with one kind of fatty acids attached to it which are mostly saturated, then the original fatty acids are removed and other fatt ...
UNIT I - apbiologypathways
... consists of a carbon backbone of three or more carbon atoms with either an aldehyde or carbonyl group on one carbon and hydroxyl groups on each of the other carbons. The most common monosaccharide is glucose, C6H12O6. Glucose is the form of sugar generally transported in the human body. A disacchari ...
... consists of a carbon backbone of three or more carbon atoms with either an aldehyde or carbonyl group on one carbon and hydroxyl groups on each of the other carbons. The most common monosaccharide is glucose, C6H12O6. Glucose is the form of sugar generally transported in the human body. A disacchari ...
From DNA to Protein
... guanine and cytosine, abbreviated with letters A, T, G, C - the first letters of their names). Three nucleotides make a codon for an amino acid. A codon in the genetic code can be compared with a single letter in our human alphabet. These letters are combined in separate "words" - genes, each "remem ...
... guanine and cytosine, abbreviated with letters A, T, G, C - the first letters of their names). Three nucleotides make a codon for an amino acid. A codon in the genetic code can be compared with a single letter in our human alphabet. These letters are combined in separate "words" - genes, each "remem ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... We will also study the process where RNA is used to make proteins. Specifically, we will study each part (transcription and translation), the steps involved and the enzymes involved. We will also look more specifically at mutations; how they can occur and what effects they might have. Pages in the b ...
... We will also study the process where RNA is used to make proteins. Specifically, we will study each part (transcription and translation), the steps involved and the enzymes involved. We will also look more specifically at mutations; how they can occur and what effects they might have. Pages in the b ...
Gene Action
... Translation 2. The large ribosomal subunit attaches to the small subunit, creating a functional ribosome – The initiator tRNA binds to the start codon – One end of the tRNA carries a specific amino acid, the other consists of a triplet of bases ...
... Translation 2. The large ribosomal subunit attaches to the small subunit, creating a functional ribosome – The initiator tRNA binds to the start codon – One end of the tRNA carries a specific amino acid, the other consists of a triplet of bases ...
Cellular Energy hbio 09 tri 1
... categories and write down what each item in the category shares in common. 2. Why did you put them in those categories and what do they have in common. ...
... categories and write down what each item in the category shares in common. 2. Why did you put them in those categories and what do they have in common. ...
the krebs cycle by stef worrall
... 5. 4 carbon compound is changed into another 4 carbon compound 6. ADP is phosphorylated to produce a molecule of ATP 7. The second 4 carbon compound is changed into another 4 carbon compound 8. Coenzyme FAD is reduced – due to accepting a pair of hydrogen atoms that have been removed 9. The resulti ...
... 5. 4 carbon compound is changed into another 4 carbon compound 6. ADP is phosphorylated to produce a molecule of ATP 7. The second 4 carbon compound is changed into another 4 carbon compound 8. Coenzyme FAD is reduced – due to accepting a pair of hydrogen atoms that have been removed 9. The resulti ...
A1983RE63700001
... causes less stringent control by amino acids over ribosomal RNA synthesis than its normal, or ‘stringent, allele [The SCI~indicates that this paper has been cited in over 535 publications since ...
... causes less stringent control by amino acids over ribosomal RNA synthesis than its normal, or ‘stringent, allele [The SCI~indicates that this paper has been cited in over 535 publications since ...
Nonessential Amino Acid Metabolism in Healthy Adult Males Using
... Need all 20 in correct proportions for protein synthesis to occur in the body www.onlymyhealth.com ...
... Need all 20 in correct proportions for protein synthesis to occur in the body www.onlymyhealth.com ...
complete
... • Review the basic structure of proteins and their component amino acids • Learn which are the essential amino acids and why • Understand that there are various amino acid “pools” within the body including dietary and body tissue pools • Learn how amino acids can be used for The synthesis of new p ...
... • Review the basic structure of proteins and their component amino acids • Learn which are the essential amino acids and why • Understand that there are various amino acid “pools” within the body including dietary and body tissue pools • Learn how amino acids can be used for The synthesis of new p ...
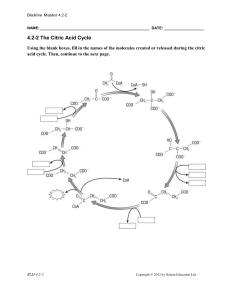
Blackline Master 4.2-2 NAME: DATE: 4.2
... ________________enters the cycle and then combines with ________________ to make the six-carbon compound ________________. During the eight steps of the citric cycle, ________________ undergoes a number of reactions, releasing _______ and ______ in a number of steps. ________________ is eventually c ...
... ________________enters the cycle and then combines with ________________ to make the six-carbon compound ________________. During the eight steps of the citric cycle, ________________ undergoes a number of reactions, releasing _______ and ______ in a number of steps. ________________ is eventually c ...
CHEMISTRY 112 - LECTURE NOTES
... dissolves in the fat while the negatively-charged side chain interacts with water molecules. The mutual repulsion of these negatively-charged droplets keeps them from coalescing. Thus large globules of fat (liquid at body temperature) are emulsified into tiny droplets (about 1 µm in diameter) that c ...
... dissolves in the fat while the negatively-charged side chain interacts with water molecules. The mutual repulsion of these negatively-charged droplets keeps them from coalescing. Thus large globules of fat (liquid at body temperature) are emulsified into tiny droplets (about 1 µm in diameter) that c ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.