1. Substrate level phosphorylation A) is part
... A) is a way the body moves nitrogen from muscle to liver B) involves the cyclic degradation of amino acids to urea and carbon skeletons C) includes an alternative to the Krebs cycle that allows acetate to be synthesized into glucose with no loss of carbons D) is a way the body moves carbon from musc ...
... A) is a way the body moves nitrogen from muscle to liver B) involves the cyclic degradation of amino acids to urea and carbon skeletons C) includes an alternative to the Krebs cycle that allows acetate to be synthesized into glucose with no loss of carbons D) is a way the body moves carbon from musc ...
Document
... Hydrophobic – “water hating”, non-polar amino acids that tend to orient themselves toward the interior of the protein Hyrophilic - “water loving”, polar amino acids that tend to orient themselves toward the exterior of the protein Alpha-helix – a spiral-shaped, motif in the secondary structure of a ...
... Hydrophobic – “water hating”, non-polar amino acids that tend to orient themselves toward the interior of the protein Hyrophilic - “water loving”, polar amino acids that tend to orient themselves toward the exterior of the protein Alpha-helix – a spiral-shaped, motif in the secondary structure of a ...
File
... 1. Most of the energy is acquired by NADH; three molecules are produced during each turn of the cycle. 2. The reactions of the electron transport chain occur in the inner mitochondrial membrane. 3. C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy 4. The mitochondrial membranes segregate the enzymes and reactant ...
... 1. Most of the energy is acquired by NADH; three molecules are produced during each turn of the cycle. 2. The reactions of the electron transport chain occur in the inner mitochondrial membrane. 3. C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy 4. The mitochondrial membranes segregate the enzymes and reactant ...
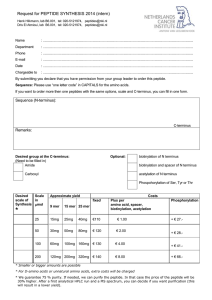
Scale - Netherlands Cancer Institute
... Henk Hilkmann, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] Dris El Atmioui, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] ...
... Henk Hilkmann, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] Dris El Atmioui, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] ...
Glycolysis Puzzle: Concept Map of "Splitting of Glucose"
... Pyruvate has two biochemical fates, depending upon whether or not oxygen is present. In the absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration (fermentation) occurs. In animal cells ________________________ is reduced to lactic acid (lactate) By the oxidation of the coenzyme __________________________ In yeas ...
... Pyruvate has two biochemical fates, depending upon whether or not oxygen is present. In the absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration (fermentation) occurs. In animal cells ________________________ is reduced to lactic acid (lactate) By the oxidation of the coenzyme __________________________ In yeas ...
3. Protein Structure and Function – Bio 20-1
... • Predictions of secondary structure of proteins adopted by a sequence of six or fewer residues have proved to be 60 to 70% accurate • Many protein chemists have tried to predict structure based on sequence ▫ Chou-Fasman: each amino acid is assigned a "propensity" for forming helices or sheets ▫ Cho ...
... • Predictions of secondary structure of proteins adopted by a sequence of six or fewer residues have proved to be 60 to 70% accurate • Many protein chemists have tried to predict structure based on sequence ▫ Chou-Fasman: each amino acid is assigned a "propensity" for forming helices or sheets ▫ Cho ...
word play - Discovery Education
... 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules to form the DNA helix. 12. A winding shape, simi ...
... 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules to form the DNA helix. 12. A winding shape, simi ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... group, deoxyribose (a sugar with 5 carbon atoms) and a nitrogenous base. Alternating phosphate groups and sugars form the skeleton of the ...
... group, deoxyribose (a sugar with 5 carbon atoms) and a nitrogenous base. Alternating phosphate groups and sugars form the skeleton of the ...
Example Problem Set for CHEM106 Section 002 Test 2
... 2) You are mutating amino acids in a protein to test predictions about which residues are important for a protein’s function. Which of each pair of amino acid substitutions listed below would you expect to disrupt protein structure the most? Explain. a) b) c) d) ...
... 2) You are mutating amino acids in a protein to test predictions about which residues are important for a protein’s function. Which of each pair of amino acid substitutions listed below would you expect to disrupt protein structure the most? Explain. a) b) c) d) ...
ppt
... citrate buildup • Citrate goes into cytoplasm – Begins fatty acid synthesis – Inactivates glycolysis ...
... citrate buildup • Citrate goes into cytoplasm – Begins fatty acid synthesis – Inactivates glycolysis ...
high energy bond
... Breakdown of larger molecules Products are small molecules Glycolysis, citric acid cycle Mediated by enzymes E released (exergonic) ...
... Breakdown of larger molecules Products are small molecules Glycolysis, citric acid cycle Mediated by enzymes E released (exergonic) ...
Attachment 3 Speakers(English version)
... acids as building blocks of foldamers. The group discovered a new series of peptidomimetics based on aminoxy acids (a class of unnatural amino acids). The group discovered a series of small molecules that self-assemble into ion channels for selective transport of cations or anions. The current focus ...
... acids as building blocks of foldamers. The group discovered a new series of peptidomimetics based on aminoxy acids (a class of unnatural amino acids). The group discovered a series of small molecules that self-assemble into ion channels for selective transport of cations or anions. The current focus ...
Chapter 9 - Cellular Respiration
... If molecular oxygen is present……. Each pyruvate is converted into acetyl CoA (begin w/ 2): CO2 is released; NAD+ --> NADH; coenzyme A (from B vitamin), makes molecule very reactive From this point, each turn 2 C atoms enter (pyruvate) and 2 exit (carbon dioxide) Oxaloacetate is regenerated (the “cyc ...
... If molecular oxygen is present……. Each pyruvate is converted into acetyl CoA (begin w/ 2): CO2 is released; NAD+ --> NADH; coenzyme A (from B vitamin), makes molecule very reactive From this point, each turn 2 C atoms enter (pyruvate) and 2 exit (carbon dioxide) Oxaloacetate is regenerated (the “cyc ...
SECTION 2 - CELL FUNCTION AND BIOCHEMICAL MEASUREMENT
... 10. “All fats are lipids” because fats are organic molecules that are relatively insoluble in water. Fats (triglycerides) represent a subcategory of lipids; “not all lipids are fats” because the term lipids includes other subcategories such as phospholipids and steroids, that are not triglycerides. ...
... 10. “All fats are lipids” because fats are organic molecules that are relatively insoluble in water. Fats (triglycerides) represent a subcategory of lipids; “not all lipids are fats” because the term lipids includes other subcategories such as phospholipids and steroids, that are not triglycerides. ...
SECTION 2 - CELL FUNCTION AND BIOCHEMICAL MEASUREMENT
... 10. “All fats are lipids” because fats are organic molecules that are relatively insoluble in water. Fats (triglycerides) represent a subcategory of lipids; “not all lipids are fats” because the term lipids includes other subcategories such as phospholipids and steroids, that are not triglycerides. ...
... 10. “All fats are lipids” because fats are organic molecules that are relatively insoluble in water. Fats (triglycerides) represent a subcategory of lipids; “not all lipids are fats” because the term lipids includes other subcategories such as phospholipids and steroids, that are not triglycerides. ...
Exam 3
... 13. ______The hormone glucagon will lead to A. increased concentrations of phosphorylase a in muscle B. decreased concentrations of phosphorylase a in muscle C. increased concentrations of phosphorylase a in liver D. decreased concentrations of phosphorylase a in liver 14. ______ To store a dietary ...
... 13. ______The hormone glucagon will lead to A. increased concentrations of phosphorylase a in muscle B. decreased concentrations of phosphorylase a in muscle C. increased concentrations of phosphorylase a in liver D. decreased concentrations of phosphorylase a in liver 14. ______ To store a dietary ...
Aerobic Respiration
... Advantages of ATP as an intermediate energy carrier Only one enzyme is required to release ...
... Advantages of ATP as an intermediate energy carrier Only one enzyme is required to release ...
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
... • Therefore, the two NADH molecules produce six ATP molecules total. So, the total number of ATP molecules formed from glycolysis is eight. When each molecule of pyruvic acid is oxidized, one molecule of NADH is produced. This occurs twice, since one glucose molecule splits into two molecules of py ...
... • Therefore, the two NADH molecules produce six ATP molecules total. So, the total number of ATP molecules formed from glycolysis is eight. When each molecule of pyruvic acid is oxidized, one molecule of NADH is produced. This occurs twice, since one glucose molecule splits into two molecules of py ...
o"', ,jl w - 'J'
... regulation of metabolic pathways, evolution of metabolic pathways-RNA world. ...
... regulation of metabolic pathways, evolution of metabolic pathways-RNA world. ...
here
... This is NOT a complete listing of what you need to know for the exam--consider this a guide. Also, do NOT consider all topics listed here as equally important. Use your own judgement, based on how much time we spent on these topics in class, to plan your studying time. Good luck!!! Scale, Organelles ...
... This is NOT a complete listing of what you need to know for the exam--consider this a guide. Also, do NOT consider all topics listed here as equally important. Use your own judgement, based on how much time we spent on these topics in class, to plan your studying time. Good luck!!! Scale, Organelles ...
Proteins
... • > 50% of the dry mass of a cell is protein Proteins are used for: • Structural support • Energy storage • Transport of other substances • Signalling from one part of the ...
... • > 50% of the dry mass of a cell is protein Proteins are used for: • Structural support • Energy storage • Transport of other substances • Signalling from one part of the ...
Computational Biology 1 - Bioinformatics Institute
... 1) How can a protein have two stable “lowest energy states”? 2) What is the rate of inter-conversion between them? 3) What does the auto-catalysis do? 4) How much inter-conversion leads to disease? 5) Under what conditions can the disease be transmitted? ...
... 1) How can a protein have two stable “lowest energy states”? 2) What is the rate of inter-conversion between them? 3) What does the auto-catalysis do? 4) How much inter-conversion leads to disease? 5) Under what conditions can the disease be transmitted? ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.