Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. ...
... Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. ...
Cell Respiration - Hollidaysburg Area School District
... Kilocalorie on food labels (1 Calorie = 1000 calories) When ...
... Kilocalorie on food labels (1 Calorie = 1000 calories) When ...
CHAPTER 2: CELL FUNCTION 2.1.
... Phosphorus. These few elements are combined as atoms into molecules that form different compounds. They are the building blocks of life and the ingredients of cell function. 2. What functions do proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids perform? Proteins are made of amino acids and control ...
... Phosphorus. These few elements are combined as atoms into molecules that form different compounds. They are the building blocks of life and the ingredients of cell function. 2. What functions do proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids perform? Proteins are made of amino acids and control ...
The Calvin Cycle
... decreases photosynthetic output by robbing Calvin cycle of organic material ...
... decreases photosynthetic output by robbing Calvin cycle of organic material ...
Ion exchange chromatography File
... Ion-exchangers made by co-polymerisation of styrene with divinyl benzene. Polystyrene itself is a linear polymer. Divinyl benzene, is a cross-linker Resins with low degree of cross-linking are more permeable to high molecular weight compounds, but they are less rigid and swell more when placed in bu ...
... Ion-exchangers made by co-polymerisation of styrene with divinyl benzene. Polystyrene itself is a linear polymer. Divinyl benzene, is a cross-linker Resins with low degree of cross-linking are more permeable to high molecular weight compounds, but they are less rigid and swell more when placed in bu ...
glycolysis
... What is Glycolysis? Term: from the Greek glykys, meaning “sweet,” And lysis, meaning “splitting”), Glycolysis (a sweet splitting process) is a central pathway for the catabolism of carbohydrates in which the six-carbon sugars are split to three-carbon compounds with subsequent release of energy ...
... What is Glycolysis? Term: from the Greek glykys, meaning “sweet,” And lysis, meaning “splitting”), Glycolysis (a sweet splitting process) is a central pathway for the catabolism of carbohydrates in which the six-carbon sugars are split to three-carbon compounds with subsequent release of energy ...
Chapter 5 Lecture Notes: Microbial Nutrition
... usually metals that serve structural and catalytic roles for some enzymes C. Growth factors = Organic compounds that are required for growth because they can not be synthesized by a particular organism and are part of essential cell components 1. Amino acids (for proteins) 2. Vitamins (small organic ...
... usually metals that serve structural and catalytic roles for some enzymes C. Growth factors = Organic compounds that are required for growth because they can not be synthesized by a particular organism and are part of essential cell components 1. Amino acids (for proteins) 2. Vitamins (small organic ...
Biomolecules
... What are some other names of polymers? HW:Textbook read page 63: 1- What are the parts of a nucleotide? 2- What does DNA stand for? RNA? 3- What is the function of DNA 4- Explain how ATP stores and releases energy ...
... What are some other names of polymers? HW:Textbook read page 63: 1- What are the parts of a nucleotide? 2- What does DNA stand for? RNA? 3- What is the function of DNA 4- Explain how ATP stores and releases energy ...
Theory21_30
... Insulin is essential for glycogen synthesis in muscle, but not liver The concentration of glucose 6-phosphate can rise high enough in liver to stimulate glycogen synthase, but this does not happen in muscle A build up of glucose 6-phosphate inhibits further glucose trapping in muscle, but not liver ...
... Insulin is essential for glycogen synthesis in muscle, but not liver The concentration of glucose 6-phosphate can rise high enough in liver to stimulate glycogen synthase, but this does not happen in muscle A build up of glucose 6-phosphate inhibits further glucose trapping in muscle, but not liver ...
Skill Builder _3a Cellular Respiration 10 Feb 2014
... one molecule to another in the chain of molecules. It occurs in the inner membrane (cristae) of the mitochondria. In a process known as chemiosmosis electrons move down the energy gradient in the inner membrane. Hydrogen ions are pumped across the membrane into the mitochondria matrix. An electroche ...
... one molecule to another in the chain of molecules. It occurs in the inner membrane (cristae) of the mitochondria. In a process known as chemiosmosis electrons move down the energy gradient in the inner membrane. Hydrogen ions are pumped across the membrane into the mitochondria matrix. An electroche ...
Cells are exposed to DNA damaging agents that can affect their
... In the recent years, our group has been working on the challenge of using single-particle EM to build 3D reconstructions of small and/or asymmetric macromolecules (1-5). These are important steps to solve because most of the molecules of interest in biology do not have any symmetry, especially those ...
... In the recent years, our group has been working on the challenge of using single-particle EM to build 3D reconstructions of small and/or asymmetric macromolecules (1-5). These are important steps to solve because most of the molecules of interest in biology do not have any symmetry, especially those ...
For teachers: Get four colours of beads or rubber bands. You can
... rubber bands together with S-hooks. If you want, you can get your class to string together a bracelet. Just stick to the four colours below and make sure there are multiples of 3. remember 3 DNA letters = one word (an amino acid). DNA Our bodies are made up of trillions of different cells — bone cel ...
... rubber bands together with S-hooks. If you want, you can get your class to string together a bracelet. Just stick to the four colours below and make sure there are multiples of 3. remember 3 DNA letters = one word (an amino acid). DNA Our bodies are made up of trillions of different cells — bone cel ...
Cellular Respiration
... Kreb’s Cycle What Happens? = If oxygen IS available, fermentation does NOT happen. 1. Pyruvic Acid is converted into Acetyl CoA. 2. This joins with oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid. 3. Citric Acid goes through a cycle where CO2 and electron carriers are formed. 4. The 2 original pyruvic acid mo ...
... Kreb’s Cycle What Happens? = If oxygen IS available, fermentation does NOT happen. 1. Pyruvic Acid is converted into Acetyl CoA. 2. This joins with oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid. 3. Citric Acid goes through a cycle where CO2 and electron carriers are formed. 4. The 2 original pyruvic acid mo ...
The Cell in Motion
... have severe symptoms like mental retardation. This example illustrates how a gene is linked to a disease. ...
... have severe symptoms like mental retardation. This example illustrates how a gene is linked to a disease. ...
Slide 1
... The food is made by combining small molecules of water with small molecules of carbon dioxide to make larger molecules of starch and sugar. (Oxygen is released as a byproduct of photosynthesis.) The starch and sugar are stored by the plant then used by us when we eat plants. But feeding us is not wh ...
... The food is made by combining small molecules of water with small molecules of carbon dioxide to make larger molecules of starch and sugar. (Oxygen is released as a byproduct of photosynthesis.) The starch and sugar are stored by the plant then used by us when we eat plants. But feeding us is not wh ...
Unit 2 ~ Learning Guide Name
... ____________________________________. This narrows the pathway for blood so the heart has to pump harder to push the blood through the body (i.e., increase ___________________________). Cholesterol is the imporant part of the cell membrane and the protective cover around nerve fibres. ______________ ...
... ____________________________________. This narrows the pathway for blood so the heart has to pump harder to push the blood through the body (i.e., increase ___________________________). Cholesterol is the imporant part of the cell membrane and the protective cover around nerve fibres. ______________ ...
Ch 9 Power Point - Cellular Respiration
... – Remember: have 2 pyruvate from 1 glucose • All of the numbers will be doubled ...
... – Remember: have 2 pyruvate from 1 glucose • All of the numbers will be doubled ...
•What makes up an atom? Draw an atom
... • Isotope: different number of neutrons changes the mass, but NOT the element • EX. C12 vs C14 • Carbon 14 is heavier since it has two more neutrons ...
... • Isotope: different number of neutrons changes the mass, but NOT the element • EX. C12 vs C14 • Carbon 14 is heavier since it has two more neutrons ...
Nutrients Outline
... b. turns into ____________________ - collects inside blood vessels c. Ex: meat, cheese, butter 2. ____________________ a. Most come from plants - veg. & nuts b. body can't build some unsaturated fats so you need to eat them V. Vitamins A. Definition 1. Chemicals made by ________________ ____________ ...
... b. turns into ____________________ - collects inside blood vessels c. Ex: meat, cheese, butter 2. ____________________ a. Most come from plants - veg. & nuts b. body can't build some unsaturated fats so you need to eat them V. Vitamins A. Definition 1. Chemicals made by ________________ ____________ ...
Biological Molecules: Water and Carbohydrates
... main biological molecules it is appropriate to gain an understanding of the cell membrane before going on to the last important biochemical molecule. ...
... main biological molecules it is appropriate to gain an understanding of the cell membrane before going on to the last important biochemical molecule. ...
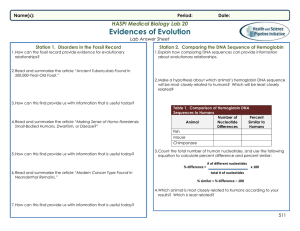
Evidence for Evolution Student Answer Sheet
... 1. How can comparing similarities and differences in anatomy provide evidence for evolution? ...
... 1. How can comparing similarities and differences in anatomy provide evidence for evolution? ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.