Bio 1 Unit 1 Answers
... Made up of nucleotides Most consist of three fatty acids bonded to a glycerol molecule DNA and RNA Contain peptide bonds Produce proteins Commonly called fats and oils Made up of amino acids Used for long-term energy storage, insulation, and protective coatings Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and ...
... Made up of nucleotides Most consist of three fatty acids bonded to a glycerol molecule DNA and RNA Contain peptide bonds Produce proteins Commonly called fats and oils Made up of amino acids Used for long-term energy storage, insulation, and protective coatings Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and ...
Genetics Lab - Identification of a Nucleic Acid
... Each group will be given a nucleic acid sample to analyze over the next few weeks. You must determine whether the nucleic acid is DNA or RNA, whether it is single-stranded or double-stranded. Based on this information, you should be able to identify the Virulent Virus. The following equipment and re ...
... Each group will be given a nucleic acid sample to analyze over the next few weeks. You must determine whether the nucleic acid is DNA or RNA, whether it is single-stranded or double-stranded. Based on this information, you should be able to identify the Virulent Virus. The following equipment and re ...
Overview of Aerobic Respiration
... So cell resp is up to 20 times more effective than glycolysis. - In faccccct cell resp is more efficient than human made machines like cars o Most of remaining energy in cars from gas is lost as heat OKKKKKKKKKKKK SOOOOO CELL RESPIRATION: GLYCOLYSIS & AEROBIC RESPIRATION ...
... So cell resp is up to 20 times more effective than glycolysis. - In faccccct cell resp is more efficient than human made machines like cars o Most of remaining energy in cars from gas is lost as heat OKKKKKKKKKKKK SOOOOO CELL RESPIRATION: GLYCOLYSIS & AEROBIC RESPIRATION ...
Alkaline Phosphatase
... Storage Buffer: 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0 at 22oC), 5 mM potassium phosphate, 100 mM KCl, 0.1 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM ZnCl2 and ...
... Storage Buffer: 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0 at 22oC), 5 mM potassium phosphate, 100 mM KCl, 0.1 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM ZnCl2 and ...
On the Propeller Structure of Isolated Watson
... The nucleotide sequence dependence of the D N A and R N A secondary structure is a problem of current interest in molecular biophysics. The key role of stacking interactions in determining this dependence is widely accepted [1, 2], It is be lieved that the propeller twisting of base pairs, ob serv ...
... The nucleotide sequence dependence of the D N A and R N A secondary structure is a problem of current interest in molecular biophysics. The key role of stacking interactions in determining this dependence is widely accepted [1, 2], It is be lieved that the propeller twisting of base pairs, ob serv ...
Ch. 7 Cellular Respiration
... At this point you should be able to write the cellular respiration chemical equation, which is a direct reversal of photosynthesis: (write it in the margin of your note sheet) ...
... At this point you should be able to write the cellular respiration chemical equation, which is a direct reversal of photosynthesis: (write it in the margin of your note sheet) ...
Protein Synthesis Practice
... Given the following mRNA strands, draw a circle around the START CODONS and the STOP CODONS. Number the 3-base pair codons in between. A whole protein need to have a series of codons between a start (AUG) and a stop codon (UGA, UAG or UAA). Which strands will build whole proteins? Example: This str ...
... Given the following mRNA strands, draw a circle around the START CODONS and the STOP CODONS. Number the 3-base pair codons in between. A whole protein need to have a series of codons between a start (AUG) and a stop codon (UGA, UAG or UAA). Which strands will build whole proteins? Example: This str ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... Four main types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things. • Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. – Carbohydrates include sugars and starches. – Monosaccharides are simple sugars. – Polysaccharides include starches, cellulose, and glycogen. ...
... Four main types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things. • Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. – Carbohydrates include sugars and starches. – Monosaccharides are simple sugars. – Polysaccharides include starches, cellulose, and glycogen. ...
National 4 Biology Unit 1 Cell Biology Summary Notes
... Amylase, Pepsin, Lipase and Catalase Some enzymes build-up molecules (synthesis). This happens when an enzyme links small molecules together to make a large molecule. A synthesising enzyme is : Phosphorylase Enzymes have conditions they work best at. These conditions are known as their optimum. An e ...
... Amylase, Pepsin, Lipase and Catalase Some enzymes build-up molecules (synthesis). This happens when an enzyme links small molecules together to make a large molecule. A synthesising enzyme is : Phosphorylase Enzymes have conditions they work best at. These conditions are known as their optimum. An e ...
LECT02 thermo
... Energy unavailable during a chemical transition “A spontaneous reaction is one that favors movement from order to disorder…occurs with a positive change in entropy” “To go from disorder back to order requires input of energy” Take Home: Living system take chemicals from their disordered environment ...
... Energy unavailable during a chemical transition “A spontaneous reaction is one that favors movement from order to disorder…occurs with a positive change in entropy” “To go from disorder back to order requires input of energy” Take Home: Living system take chemicals from their disordered environment ...
NAME AVERILL PARK HS THE LIVING ENVIRONMENT Worksheet
... 1. The function of cell respiration is to provide cells with __________________ 2. The most common food substance from which cells obtain energy is the monosaccharide known as ________________, which has the molecular formula _________________ 3. The difference between aerobic & anaerobic respiratio ...
... 1. The function of cell respiration is to provide cells with __________________ 2. The most common food substance from which cells obtain energy is the monosaccharide known as ________________, which has the molecular formula _________________ 3. The difference between aerobic & anaerobic respiratio ...
1. Introduction
... glyoxylate cycle (see paragraph 1.3.4). With the exception of isocitrate, every TCA cycle intermediate is commonly used by other metabolic reactions. In fact, the citric acid cycle is an amphibolic pathway, since it combines both catabolic and anabolic functions. The latter results, for example, f ...
... glyoxylate cycle (see paragraph 1.3.4). With the exception of isocitrate, every TCA cycle intermediate is commonly used by other metabolic reactions. In fact, the citric acid cycle is an amphibolic pathway, since it combines both catabolic and anabolic functions. The latter results, for example, f ...
Biology First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... The biomolecule classified as a nucleic acid and composed of nucleotides; genetic material shaped like a double helix A five carbon sugar found as part of the structural components of a nucleotide of DNA The process in which the DNA sequence is copied to form an additional DNA molecule A segment of ...
... The biomolecule classified as a nucleic acid and composed of nucleotides; genetic material shaped like a double helix A five carbon sugar found as part of the structural components of a nucleotide of DNA The process in which the DNA sequence is copied to form an additional DNA molecule A segment of ...
Preview Sample 1
... 30) Magnesium atoms have two electrons in the outermost shell. As a result, you would expect magnesium to form ions with a charge of A) -1. B) +1. C) -2. D) +2. E) either +2 or -2 ...
... 30) Magnesium atoms have two electrons in the outermost shell. As a result, you would expect magnesium to form ions with a charge of A) -1. B) +1. C) -2. D) +2. E) either +2 or -2 ...
File
... Lesson 3- Energy for Life Where does our energy come from? From the food we eat! The chemical energy stored in food molecules is changed inside of cells into forms needed to perform all the activities necessary for life. In every cell, these changes involve chemical reaction. All of the activiti ...
... Lesson 3- Energy for Life Where does our energy come from? From the food we eat! The chemical energy stored in food molecules is changed inside of cells into forms needed to perform all the activities necessary for life. In every cell, these changes involve chemical reaction. All of the activiti ...
Cellular Respiration
... used by humans and other organisms to release the energy stored in the food they consume ...
... used by humans and other organisms to release the energy stored in the food they consume ...
acetyl-CoA - Winona State University
... • 4) Beta-hydroxybutyric acid • Why do we see ketoacidosis during a diabetic crisis? – Blood acidity reduces ability of hemoglobin to carry oxygen! – Ketones react readily with DNA (mutations) and proteins (denaturation) ...
... • 4) Beta-hydroxybutyric acid • Why do we see ketoacidosis during a diabetic crisis? – Blood acidity reduces ability of hemoglobin to carry oxygen! – Ketones react readily with DNA (mutations) and proteins (denaturation) ...
ATP and Sources of Energy
... Energy is depleted and a new molecule ADP is formed. Energy is created by using energy released from other chemical reactions to bond a phosphate group to ADP...making ATP. ...
... Energy is depleted and a new molecule ADP is formed. Energy is created by using energy released from other chemical reactions to bond a phosphate group to ADP...making ATP. ...
Dna Mutations
... These are called silent mutations. • change an amino-acid-coding codon to a single "stop" codon and cause an incomplete protein. This can have serious effects since the incomplete protein probably won't function. ...
... These are called silent mutations. • change an amino-acid-coding codon to a single "stop" codon and cause an incomplete protein. This can have serious effects since the incomplete protein probably won't function. ...
How life evolved: 10 steps to the first cells
... hydrothermal vents deep under the sea. Not in the superhot black smokers, but more placid affairs known as alkaline hydrothermal vents. This theory can explain life’s strangest feature, and there is growing evidence to support it. Earlier this year, for instance, lab experiments confirmed that condi ...
... hydrothermal vents deep under the sea. Not in the superhot black smokers, but more placid affairs known as alkaline hydrothermal vents. This theory can explain life’s strangest feature, and there is growing evidence to support it. Earlier this year, for instance, lab experiments confirmed that condi ...
student notes protein synthesis mutation
... Transcription: A Deep look A. RNA is made from the DNA nucleotide sequence during transcription. 1. __________________attaches to the beginning of one gene or a group of genes, called the ___________, on the DNA molecule. 2. DNA separates at the______________________ 3. half the DNA serves as a tem ...
... Transcription: A Deep look A. RNA is made from the DNA nucleotide sequence during transcription. 1. __________________attaches to the beginning of one gene or a group of genes, called the ___________, on the DNA molecule. 2. DNA separates at the______________________ 3. half the DNA serves as a tem ...
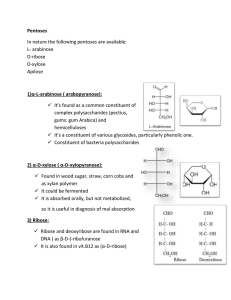
2) α-D-xylose
... To differentiate between Glucose & Fructose: (1) Br2 in water oxidizes only glucose (2) Reaction with resorcinol (3) Raction with Methylphenylhydrazine * Note: Both are reducing sugars and form the same osazone with phenylhydrazine ...
... To differentiate between Glucose & Fructose: (1) Br2 in water oxidizes only glucose (2) Reaction with resorcinol (3) Raction with Methylphenylhydrazine * Note: Both are reducing sugars and form the same osazone with phenylhydrazine ...
Glossary (PDF file)
... reactions between many small molecules. Poly means “many.” When many monomers react with each other, they form a polymer. A polymer can contain just a few monomer units, or it can contain tens of thousands of them. Carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch are polymers of certain sugars, which are ...
... reactions between many small molecules. Poly means “many.” When many monomers react with each other, they form a polymer. A polymer can contain just a few monomer units, or it can contain tens of thousands of them. Carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch are polymers of certain sugars, which are ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.