Chapter 1
... Chemical components Molecular structures Structure-function relationship Physical and chemical properties Exploration of proteins ...
... Chemical components Molecular structures Structure-function relationship Physical and chemical properties Exploration of proteins ...
Chapter 6
... a. The body NEEDS another source of energy, for example if you are fasting or starving. In this case, structural and functional proteins- like the contractile proteins in your muscles- will be sacrificed, digested, and their amino acids used for energy. b. The body needs glucose specifically. Rememb ...
... a. The body NEEDS another source of energy, for example if you are fasting or starving. In this case, structural and functional proteins- like the contractile proteins in your muscles- will be sacrificed, digested, and their amino acids used for energy. b. The body needs glucose specifically. Rememb ...
Question 2. Which of the following statements about G proteins are
... Question 2. Which of the following statements about G proteins are correct? a) G proteins are activated by twelve-membrane receptors only b) G proteins make up a large family of proteins that are involved in regulating enzymes, chemotaxis, visual excitation, and ion channels. c) G proteins cycle bet ...
... Question 2. Which of the following statements about G proteins are correct? a) G proteins are activated by twelve-membrane receptors only b) G proteins make up a large family of proteins that are involved in regulating enzymes, chemotaxis, visual excitation, and ion channels. c) G proteins cycle bet ...
peak glossary of terms
... The sensation felt by marathon runners when they deplete their body's glycogen stores and begin running primarily on stored body fat. Homeostasis The tendency of the body to maintain an internal equilibrium. Hyaluronic acid The principal glycosaminoglycan in proteoglycan. Hydrogenation The process i ...
... The sensation felt by marathon runners when they deplete their body's glycogen stores and begin running primarily on stored body fat. Homeostasis The tendency of the body to maintain an internal equilibrium. Hyaluronic acid The principal glycosaminoglycan in proteoglycan. Hydrogenation The process i ...
Time: 1.5 hour
... (a) H2O, CO2 and energy are the only end products (b) H2O, C6H12O6 and energy are the end products (c) CO2, C2H5OH and energy are the end products (d) Water and CO2 are the end products 21. R.Q. value of 4 may be expected for the complete oxidation of which one of the following? (a) Glucose (b) Mali ...
... (a) H2O, CO2 and energy are the only end products (b) H2O, C6H12O6 and energy are the end products (c) CO2, C2H5OH and energy are the end products (d) Water and CO2 are the end products 21. R.Q. value of 4 may be expected for the complete oxidation of which one of the following? (a) Glucose (b) Mali ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... 22. Describe the effect on the overall shape of a large molecule due to a great number of hydrogen bonds between different parts of that molecule. 23. Explain how hydrogen bonds result in the cohesion of water molecules and how this cohesion creates a high surface tension which is very important to ...
... 22. Describe the effect on the overall shape of a large molecule due to a great number of hydrogen bonds between different parts of that molecule. 23. Explain how hydrogen bonds result in the cohesion of water molecules and how this cohesion creates a high surface tension which is very important to ...
IB BIO II Cell Respiration Van Roekel Cell Respiration Review
... 5. What occurs (what is gained/lost) during oxidation? Reduction? Oxidation is the loss of electrons/hydrogens. Reduction is the gain of electrons/hydrogens Oxidation is the gain of oxygen. Reduction is the loss of oxygen. Glycolysis 1. Where does glycolysis occur? Why does this make Glycolysis the ...
... 5. What occurs (what is gained/lost) during oxidation? Reduction? Oxidation is the loss of electrons/hydrogens. Reduction is the gain of electrons/hydrogens Oxidation is the gain of oxygen. Reduction is the loss of oxygen. Glycolysis 1. Where does glycolysis occur? Why does this make Glycolysis the ...
Gene Expression Worksheet
... 2. Where does the replication of DNA occur inside the cell and what part of the cell cycle? ...
... 2. Where does the replication of DNA occur inside the cell and what part of the cell cycle? ...
Water, Ph, and Macromolecules PPT
... • Living things are made of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosporus, and Sulfur (CHONPS) with a few other elements in small amounts. • These create carboyhdrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins, which are taken in from/with food and used to build new cells/tissues • Most macromolecules ar ...
... • Living things are made of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosporus, and Sulfur (CHONPS) with a few other elements in small amounts. • These create carboyhdrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins, which are taken in from/with food and used to build new cells/tissues • Most macromolecules ar ...
Available
... The Urea Cycle Earlier it was noted that kidney glutaminase was responsible for converting excess glutamine from the liver to urine ammonium. However, about 80% of the excreted nitrogen is in the form of urea which is produced exclusively in the liver, in a series of reactions that are distributed b ...
... The Urea Cycle Earlier it was noted that kidney glutaminase was responsible for converting excess glutamine from the liver to urine ammonium. However, about 80% of the excreted nitrogen is in the form of urea which is produced exclusively in the liver, in a series of reactions that are distributed b ...
One Gene - One Polypeptide
... turn are made up of DNA. Each chromosome represents a single molecule of DNA tightly wound around sets of proteins called histones. Each DNA molecule (chromosome) is made up of sequences nucleotides in varying orders and lengths. A molecule of DNA may be hundreds of thousands of nucleotides long, bu ...
... turn are made up of DNA. Each chromosome represents a single molecule of DNA tightly wound around sets of proteins called histones. Each DNA molecule (chromosome) is made up of sequences nucleotides in varying orders and lengths. A molecule of DNA may be hundreds of thousands of nucleotides long, bu ...
DNA - BiologyProvidence
... protein, takes place in the cytoplasm The mRNA interacts with a specialized organelle in the rough ER called a ribosome, which “reads” the sequence of mRNA bases Each sequence of three bases, called a codon, codes for one particular amino acid (the building blocks of proteins). tRNA assembles the pr ...
... protein, takes place in the cytoplasm The mRNA interacts with a specialized organelle in the rough ER called a ribosome, which “reads” the sequence of mRNA bases Each sequence of three bases, called a codon, codes for one particular amino acid (the building blocks of proteins). tRNA assembles the pr ...
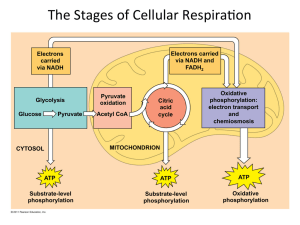
The Stages of Cellular RespiraWon
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
The amino acids
... Glycine is special because it is so flexible, so it can easily make the sharp turns and bends needed in a b-turn. Proline is special because it is so rigid; you could say that it is pre-bent for the turn. Aspartic acid, asparagine, and serine have in common that they have short side chains that can ...
... Glycine is special because it is so flexible, so it can easily make the sharp turns and bends needed in a b-turn. Proline is special because it is so rigid; you could say that it is pre-bent for the turn. Aspartic acid, asparagine, and serine have in common that they have short side chains that can ...
Lecture 2: Biological Side of Bioinformatics
... Pufferfish, fruit fly, mouse, chicken, yeast, bacteria ...
... Pufferfish, fruit fly, mouse, chicken, yeast, bacteria ...
here - Sites@PSU
... Lactococcus sp. Lactobacillus sp. Leuconostoc sp. Pediococcus sp. Oenococcus sp. Streptococcus sp. Enterococcus sp. Sporolactobacillus sp. Carnobacterium sp. Aerococcus sp. Tetragenococcus sp. Vagococcus sp. Weisella sp. ...
... Lactococcus sp. Lactobacillus sp. Leuconostoc sp. Pediococcus sp. Oenococcus sp. Streptococcus sp. Enterococcus sp. Sporolactobacillus sp. Carnobacterium sp. Aerococcus sp. Tetragenococcus sp. Vagococcus sp. Weisella sp. ...
Name Biology Chemistry of Life What can reduce the effect of a
... both have one oxygen atom in the ring; both have the same relative amounts of C, H and O; both have only –OH and –H linked to the carbon atoms; both are monosaccharides / sugars / reducing sugars; I and IV both have a carboxyl / COOH / acid group; I and IV both are linear; ...
... both have one oxygen atom in the ring; both have the same relative amounts of C, H and O; both have only –OH and –H linked to the carbon atoms; both are monosaccharides / sugars / reducing sugars; I and IV both have a carboxyl / COOH / acid group; I and IV both are linear; ...
LECTURE 2: Precambrian Era: Origin of Life
... RNA! Trapped inside a “protocell” by chance about 4.0 BYA RNA came 1st b/c has the following properties: _____________________________!!! Less complex/less stable than DNA RNA into protein more direct than DNA into Protein Has 3 different phenotypes (characteristics), can fold into diverse s ...
... RNA! Trapped inside a “protocell” by chance about 4.0 BYA RNA came 1st b/c has the following properties: _____________________________!!! Less complex/less stable than DNA RNA into protein more direct than DNA into Protein Has 3 different phenotypes (characteristics), can fold into diverse s ...
Energy Exam Review - Lewiston School District
... A).through the chloroplasts B).through the mesophyll C).through the thylakoids D).through the stomata E).through the vascular system D ...
... A).through the chloroplasts B).through the mesophyll C).through the thylakoids D).through the stomata E).through the vascular system D ...
Recitation 2 - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... After 10 rounds of amplification approximately how many molecules of the amplified region should you have theoretically. ...
... After 10 rounds of amplification approximately how many molecules of the amplified region should you have theoretically. ...
DNA
... • For ALL life! • Code has duplicates • several codons for each amino acid • mutation insurance! ...
... • For ALL life! • Code has duplicates • several codons for each amino acid • mutation insurance! ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.