Protein Folding and Modeling
... Assumes that proteins with similar sequences have similar structures, alignments ...
... Assumes that proteins with similar sequences have similar structures, alignments ...
Review for Final Summer 2011
... Chapter 3 Biological Molecules Define: organic inorganic monomer polymer dehydration synthesis vs. hydrolysis carbohydrates (1C:2H:1O) o monosaccharide (glucose fructose galactose) o disaccharides (glucose + glucose = maltose; glucose + fructose = sucrose; glucose + galactose = lactose) o poly ...
... Chapter 3 Biological Molecules Define: organic inorganic monomer polymer dehydration synthesis vs. hydrolysis carbohydrates (1C:2H:1O) o monosaccharide (glucose fructose galactose) o disaccharides (glucose + glucose = maltose; glucose + fructose = sucrose; glucose + galactose = lactose) o poly ...
Proteins - Lectures For UG-5
... eat a burger (vege or beef), you break the proteins down into single amino acids ready for use in building new proteins. And yes, proteins have the job of digesting proteins, they are known as proteases. There are only 20 different amino acids but they can be joined together in many different combin ...
... eat a burger (vege or beef), you break the proteins down into single amino acids ready for use in building new proteins. And yes, proteins have the job of digesting proteins, they are known as proteases. There are only 20 different amino acids but they can be joined together in many different combin ...
DNA, Transcription and Translation
... Transcription = rewriting or copying of information from DNA to ribonucleic acid ( RNA). Occurs in the nucleus. RNA is a single stranded molecule containing the sugar ribose, phosphate and the bases Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil. The synthesised RNA is complementary to one strand of DNA. In ...
... Transcription = rewriting or copying of information from DNA to ribonucleic acid ( RNA). Occurs in the nucleus. RNA is a single stranded molecule containing the sugar ribose, phosphate and the bases Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil. The synthesised RNA is complementary to one strand of DNA. In ...
Biochemistry Objectives 43
... a. Ebb phase (acute response): think of this phase as an urgent call for glucose and fuel use; glucagon, cortisol, epinephrine, and thyroid hormone (increased metabolism) increase while insulin decreases. Also, ADH and aldosterone increase to control fluids and sodium, respectively, while sex hormon ...
... a. Ebb phase (acute response): think of this phase as an urgent call for glucose and fuel use; glucagon, cortisol, epinephrine, and thyroid hormone (increased metabolism) increase while insulin decreases. Also, ADH and aldosterone increase to control fluids and sodium, respectively, while sex hormon ...
Macromolecules
... Essential nutrients must be obtained from food sources, because the body either does not produce them or produces them in amounts too small to maintain growth and health. Essential nutrients include water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. ...
... Essential nutrients must be obtained from food sources, because the body either does not produce them or produces them in amounts too small to maintain growth and health. Essential nutrients include water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. ...
DNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... What Codes For A Protein? A. The genetic code allows for almost an infinite amount of different proteins. B. Every 3 bases of DNA (or mRNA) is referred to as a CODON. - Each codon codes for 1 amino acid. ...
... What Codes For A Protein? A. The genetic code allows for almost an infinite amount of different proteins. B. Every 3 bases of DNA (or mRNA) is referred to as a CODON. - Each codon codes for 1 amino acid. ...
biology 422 - TeacherWeb
... pyruvate (pyruvic acid) during the Krebs cycle? In what molecules is that energy contained? 27.What are the reduction forms of NAD+ and FAD? 28.What is the function of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration and state where in the eukaryotic cell it is found? ...
... pyruvate (pyruvic acid) during the Krebs cycle? In what molecules is that energy contained? 27.What are the reduction forms of NAD+ and FAD? 28.What is the function of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration and state where in the eukaryotic cell it is found? ...
Worked solutions to textbook questions 1 Chapter 12 Pathways to
... DNA polymerase – which replicates and repairs DNA lactase – which breaks down the sugar lactose in the small intestine salivary amylase – which breaks down polysaccharides in the mouth. Almost all the chemical reactions occurring in living creatures are controlled by enzymes. Enzymes speed up the re ...
... DNA polymerase – which replicates and repairs DNA lactase – which breaks down the sugar lactose in the small intestine salivary amylase – which breaks down polysaccharides in the mouth. Almost all the chemical reactions occurring in living creatures are controlled by enzymes. Enzymes speed up the re ...
Protein foods - Deans Community High School
... They need to eat lots of different plants to make sure they get enough protein. Soya is a protein that comes from a plant and it is used in different foods for example soya milk. Beans also contain protein. Write a heading and try the work below. 1. Our bodies need protein for ___________ and ______ ...
... They need to eat lots of different plants to make sure they get enough protein. Soya is a protein that comes from a plant and it is used in different foods for example soya milk. Beans also contain protein. Write a heading and try the work below. 1. Our bodies need protein for ___________ and ______ ...
B1510F10_Exam3V1
... Please make sure that your copy of the exam includes all 10 pages of questions. • Write your name at the bottom of each exam page. • Please think through each answer carefully. None of these are intended to be trick questions, so try to answer only the question asked. Choose the best answer among th ...
... Please make sure that your copy of the exam includes all 10 pages of questions. • Write your name at the bottom of each exam page. • Please think through each answer carefully. None of these are intended to be trick questions, so try to answer only the question asked. Choose the best answer among th ...
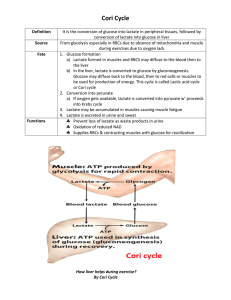
Cori Cycle - COFFEE BREAK CORNER
... or Cori cycle 2. Conversion into pyruvate a) If oxygen gets available, lactate is converted into pyruvate w’ proceeds into Krebs cycle 3. Lactate may be accumulated in muscles causing muscle fatigue ...
... or Cori cycle 2. Conversion into pyruvate a) If oxygen gets available, lactate is converted into pyruvate w’ proceeds into Krebs cycle 3. Lactate may be accumulated in muscles causing muscle fatigue ...
Document
... There is an aminoacyltRNA synthetase for each amino acid. The carboxyl end of an amino acid is attached to the 3’ end of the tRNA. ...
... There is an aminoacyltRNA synthetase for each amino acid. The carboxyl end of an amino acid is attached to the 3’ end of the tRNA. ...
class01-m
... • Proteins are polypeptides of 703000 amino-acids • This structure is (mostly) determined by the sequence of amino-acids that make up the protein ...
... • Proteins are polypeptides of 703000 amino-acids • This structure is (mostly) determined by the sequence of amino-acids that make up the protein ...
question bank acids, bases and salts
... 3. How can the effect of china rose on acids and bases be seem ? 4. What happens when a concentrated acid gets accidentally spilled on cloth or wool ? 5. What happen when metals and non metals combined with oxygen, also write chemical equation ? ...
... 3. How can the effect of china rose on acids and bases be seem ? 4. What happens when a concentrated acid gets accidentally spilled on cloth or wool ? 5. What happen when metals and non metals combined with oxygen, also write chemical equation ? ...
3. CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... • 6. Conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinate Succinyl-CoA is converted to succinate by the enzyme succinate thiokinase (succiny1CoA synthetase). High-energy phosphate (ATP) is synthesized at the substrate level because the release of free energy from the oxidative decarboxylation of α- ketoglutarat ...
... • 6. Conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinate Succinyl-CoA is converted to succinate by the enzyme succinate thiokinase (succiny1CoA synthetase). High-energy phosphate (ATP) is synthesized at the substrate level because the release of free energy from the oxidative decarboxylation of α- ketoglutarat ...
Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry
... • Made of amino acids- 20 different ones • Contain carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur • Each amino acid differs from others by a variable “R” group • Form peptide bonds through dehydration synthesis Slide 2.33a ...
... • Made of amino acids- 20 different ones • Contain carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur • Each amino acid differs from others by a variable “R” group • Form peptide bonds through dehydration synthesis Slide 2.33a ...
The Respiratory System
... • During this process carbon dioxide and water are made. These products are then carried by the blood back to the lungs to be exhaled. ...
... • During this process carbon dioxide and water are made. These products are then carried by the blood back to the lungs to be exhaled. ...
SBI-4U1 Exam Review
... 6. Give an example of a pair of structural isomers. Write their chemical formulas, and draw their structural formulas. Glucose and fructose, C6H12O6 7. Name and describe the biological macromolecules discussed in class. Include the following: constituent monomers, linkages that join the monomers, an ...
... 6. Give an example of a pair of structural isomers. Write their chemical formulas, and draw their structural formulas. Glucose and fructose, C6H12O6 7. Name and describe the biological macromolecules discussed in class. Include the following: constituent monomers, linkages that join the monomers, an ...
Exam 1 with Key
... 6. (12 pts) The mass of a protein was determined by gel filtration chromatography to be 60 kd. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30 kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM β-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. ...
... 6. (12 pts) The mass of a protein was determined by gel filtration chromatography to be 60 kd. Chromatography in the presence of 6 M urea yields a 30 kd species. When the chromatography is repeated in the presence of 6 M urea and 10 mM β-mercaptoethanol, a single molecular species of 15 kd results. ...
Slide 1
... When DNA is replicated (doubled) in a cell, you make another DNA helix In mitosis both helices attach to each other at the centromere forming sister chromatids….which makes the X-shaped chromosome you normally think of when thinking about chromosomes. The kinetochore is a complex of proteins formed ...
... When DNA is replicated (doubled) in a cell, you make another DNA helix In mitosis both helices attach to each other at the centromere forming sister chromatids….which makes the X-shaped chromosome you normally think of when thinking about chromosomes. The kinetochore is a complex of proteins formed ...
Paper chromatography and electrophoresis
... their differential solubility between the stationary phase, represented by the water bonded to the cellulose molecules of paper, and the moving phase, the solvent. • As the solvent front advances it carried the components at different rates. ...
... their differential solubility between the stationary phase, represented by the water bonded to the cellulose molecules of paper, and the moving phase, the solvent. • As the solvent front advances it carried the components at different rates. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.