DNA, RNA and Protein
... Organic Macromolecules Contain Carbon Question: How many electrons does carbon need to fill its outer energy level? Answer: Therefore, each carbon atom can make ____ covalent bonds with other types of atoms or additional carbons. ...
... Organic Macromolecules Contain Carbon Question: How many electrons does carbon need to fill its outer energy level? Answer: Therefore, each carbon atom can make ____ covalent bonds with other types of atoms or additional carbons. ...
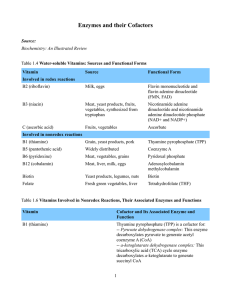
Enzymes and their Cofactors Source: Biochemistry: An Illustrated
... cofactors for: -- Methylmalonyl CoA mutase: This enzyme isomerizes methylmalonyl CoA into succinyl CoA in a reaction that is part of the pathway that degrades odd-numbered fatty acids -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrof ...
... cofactors for: -- Methylmalonyl CoA mutase: This enzyme isomerizes methylmalonyl CoA into succinyl CoA in a reaction that is part of the pathway that degrades odd-numbered fatty acids -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrof ...
Modern Taxonomy
... from a common ancestor without indication as to how far removed species are from each other • Clade – a group of related organisms representing a complete branch of a biological tree • Derived characters – a character shared by all members of a branch but not present before the branch in cladograms ...
... from a common ancestor without indication as to how far removed species are from each other • Clade – a group of related organisms representing a complete branch of a biological tree • Derived characters – a character shared by all members of a branch but not present before the branch in cladograms ...
Document
... ___________, diffuse through the cell membrane. Ammonia is very soluble in water, so it is easily excreted. Active transport – for those organisms that live in fresh water, they have a __________ contractile _______to vacuole pump out water that comes in the cell. ...
... ___________, diffuse through the cell membrane. Ammonia is very soluble in water, so it is easily excreted. Active transport – for those organisms that live in fresh water, they have a __________ contractile _______to vacuole pump out water that comes in the cell. ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... - cellulose: major component of plant cell walls - note: 2 ring structures of glucose (alpha (a) and beta (b)) - cellulose is composed of all b glucose ...
... - cellulose: major component of plant cell walls - note: 2 ring structures of glucose (alpha (a) and beta (b)) - cellulose is composed of all b glucose ...
APchapter5notes
... - cellulose: major component of plant cell walls - note: 2 ring structures of glucose (alpha (a) and beta (b)) - cellulose is composed of all b glucose ...
... - cellulose: major component of plant cell walls - note: 2 ring structures of glucose (alpha (a) and beta (b)) - cellulose is composed of all b glucose ...
Dr. Randall H. Goldsmith
... Single-Molecule measurements offer a wealth of detail about chemical diversity and unsynchronized dynamics, but only if the system under study is conducive to known methods of single-molecule fluoresence microscopy. I will present two cases where new measurement technology enables new observations o ...
... Single-Molecule measurements offer a wealth of detail about chemical diversity and unsynchronized dynamics, but only if the system under study is conducive to known methods of single-molecule fluoresence microscopy. I will present two cases where new measurement technology enables new observations o ...
Chapters 13 and 16
... Condensation reaction, Add the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA to oxaloacetate to form a 6C molecule (this step commits the acetyl group to the TCA cycle), ΔG=-31.4 kJ/mole (highly regulated enzyme), oxaloacetate must bind first, then acetyl-CoA can bind to the enzyme (sequential type mechanism), oxaloac ...
... Condensation reaction, Add the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA to oxaloacetate to form a 6C molecule (this step commits the acetyl group to the TCA cycle), ΔG=-31.4 kJ/mole (highly regulated enzyme), oxaloacetate must bind first, then acetyl-CoA can bind to the enzyme (sequential type mechanism), oxaloac ...
Slide 1
... There are 3 major differences between RNA and DNA. The sugar in RNA is ribose, not deoxyribose. RNA consists of a single strand of nucleotides, and DNA is double-stranded. The nitrogenous bases in RNA are different than DNA. RNA contains: Adenine ...
... There are 3 major differences between RNA and DNA. The sugar in RNA is ribose, not deoxyribose. RNA consists of a single strand of nucleotides, and DNA is double-stranded. The nitrogenous bases in RNA are different than DNA. RNA contains: Adenine ...
Mechanism of action of trypsin and chymotrypsin
... • All are endopeptidases, which means that they cleave protein chain at internal peptide bonds adjacent to particular type of amino acids. ...
... • All are endopeptidases, which means that they cleave protein chain at internal peptide bonds adjacent to particular type of amino acids. ...
Solgar® Earth Source® Organic Flaxseed Oil
... Solgar ® Earth Source® Organic Flaxseed Oil Solgar ® Earth Source ® Organic Flaxseed Oil provides one of the most concentrated vegan plant sources of omega-3 fatty acids found in nature. It also supplies the omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids linoleic acid and oleic acid. Fatty acids play a role in pro ...
... Solgar ® Earth Source® Organic Flaxseed Oil Solgar ® Earth Source ® Organic Flaxseed Oil provides one of the most concentrated vegan plant sources of omega-3 fatty acids found in nature. It also supplies the omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids linoleic acid and oleic acid. Fatty acids play a role in pro ...
Oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondria)
... Two primary forms of energy are: Nucleotide triphosphate (e.g. ATP, GTP) Reducing power (NADH, NADPH) Two ways to make them: Through glycolysis (cytosol) Oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondria) ...
... Two primary forms of energy are: Nucleotide triphosphate (e.g. ATP, GTP) Reducing power (NADH, NADPH) Two ways to make them: Through glycolysis (cytosol) Oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondria) ...
Essential Concept of Metabolism
... An amphibolic pathways is a metabolic pathway that can capture energy or synthesize substances needed by the cell. Figure 5.27 summarized the intermediate products of energy yielding metabolism and some of the building blocks for synthetic reactions that can be made from them. Bacteria synthesize a ...
... An amphibolic pathways is a metabolic pathway that can capture energy or synthesize substances needed by the cell. Figure 5.27 summarized the intermediate products of energy yielding metabolism and some of the building blocks for synthetic reactions that can be made from them. Bacteria synthesize a ...
Black-Chapter 5 – Essential Concept of Metabolism
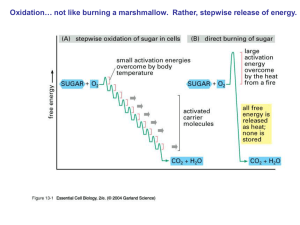
... Most of a cell’s energy is produced from the oxidation of carbohydrates. Glucose is the most commonly used carbohydrates. In aerobic,glucose is completely degrades through a). glycolysis; b). Kreb’s cycle (also known as tricarboxylic acid cycle c). Electron transport chain. Molecular oxygen is final ...
... Most of a cell’s energy is produced from the oxidation of carbohydrates. Glucose is the most commonly used carbohydrates. In aerobic,glucose is completely degrades through a). glycolysis; b). Kreb’s cycle (also known as tricarboxylic acid cycle c). Electron transport chain. Molecular oxygen is final ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Must-Knows: Unit 6 (Enzymes and Cell
... respiration (i.e. glycolysis, the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, the Krebs cycle, or the electron transport chain) occur during anaerobic respiration? ...
... respiration (i.e. glycolysis, the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, the Krebs cycle, or the electron transport chain) occur during anaerobic respiration? ...
Protein Folding and The Impact of Mutations
... The tertiary level is the combination of helices and sheets held together by hydrogen bonds. The final level, the quaternary level, is the mixture of proteins (subunits) to create a functional protein ...
... The tertiary level is the combination of helices and sheets held together by hydrogen bonds. The final level, the quaternary level, is the mixture of proteins (subunits) to create a functional protein ...
Amino Acid Sidechains
... Every acidic or basic group on a molecule has a different “pK” (K is the dissociation constant) value. The relationship between the pH of the solution it is in and the pK of the ionizable group will determine the predominant form of the ionizable group. Every acidic or basic group has an “acid form” ...
... Every acidic or basic group on a molecule has a different “pK” (K is the dissociation constant) value. The relationship between the pH of the solution it is in and the pK of the ionizable group will determine the predominant form of the ionizable group. Every acidic or basic group has an “acid form” ...
College Accounting: A Practical Approach, Cdn
... 1) Which of the following is true regarding the -carbon of an amino acid? A) there are always four different functional groups attached B) the most commonly occurring form of amino acids are the D-amino acids C) when assigning the R-S stereochemistry, the carboxylic acid is always the highest prior ...
... 1) Which of the following is true regarding the -carbon of an amino acid? A) there are always four different functional groups attached B) the most commonly occurring form of amino acids are the D-amino acids C) when assigning the R-S stereochemistry, the carboxylic acid is always the highest prior ...
C - Vanderbilt Center for Structural Biology
... How Does a Protein Find It’s Fold? Amino terminus ...
... How Does a Protein Find It’s Fold? Amino terminus ...
6. Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation
... Protein Hydrolysis Protein hydrolysis splits the peptide bonds to give smaller peptides and amino acids occurs in the digestion of proteins occurs in cells when amino acids are needed to synthesize new proteins and repair tissues ...
... Protein Hydrolysis Protein hydrolysis splits the peptide bonds to give smaller peptides and amino acids occurs in the digestion of proteins occurs in cells when amino acids are needed to synthesize new proteins and repair tissues ...
Fat - Food a fact of life
... Protein Protein is needed for growth and repair of the body. Excess protein can be broken down and used as a source of energy. Protein is made up of different combinations of amino acids. These are the building blocks of protein. Amino acids are compounds containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrog ...
... Protein Protein is needed for growth and repair of the body. Excess protein can be broken down and used as a source of energy. Protein is made up of different combinations of amino acids. These are the building blocks of protein. Amino acids are compounds containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrog ...
Presentation Package - faculty.coe.unt.edu
... carbon dioxide, and hydrogen. 3. Hydrogen in the cell combines with two coenzymes that carry it to the electron transport chain. 4. Electron transport chain recombines hydrogen atoms to produce ATP and water. 5. One molecule of glycogen can generate up to 39 molecules of ATP. ...
... carbon dioxide, and hydrogen. 3. Hydrogen in the cell combines with two coenzymes that carry it to the electron transport chain. 4. Electron transport chain recombines hydrogen atoms to produce ATP and water. 5. One molecule of glycogen can generate up to 39 molecules of ATP. ...
Primary structure: the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
... polypeptide chain; read from the N-terminal amino acid to the C-terminal amino acid • Secondary structure: conformations of amino acids in localized regions of a polypeptide chain; examples are -helix, b-pleated sheet, and random coil Tertiary structure: the overall conformation of a polypeptide ch ...
... polypeptide chain; read from the N-terminal amino acid to the C-terminal amino acid • Secondary structure: conformations of amino acids in localized regions of a polypeptide chain; examples are -helix, b-pleated sheet, and random coil Tertiary structure: the overall conformation of a polypeptide ch ...
Lecture 2 - Cell assembly
... these are responsible for making proteins • Vacuoles or vesicles – spaces in the cytoplasm that can store solids or gases • Mesosomes/Organelles –a membrane system internal to the cell which facilitates protein function; there are these structures specifically for ...
... these are responsible for making proteins • Vacuoles or vesicles – spaces in the cytoplasm that can store solids or gases • Mesosomes/Organelles –a membrane system internal to the cell which facilitates protein function; there are these structures specifically for ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.