From DNA to Protein
... These chemical differences make it easy for the enzymes in the cell to tell DNA and RNA apart ...
... These chemical differences make it easy for the enzymes in the cell to tell DNA and RNA apart ...
What agents? What war?
... highly favorable reaction by pumping protons via three independent proton pumping pathways (aka proton wires!) H-bonding is always with us: net translocation of protons can occur over a “long distance” through a protein by hopping between pairs of hydrogen bonded donor and acceptor residues; a strin ...
... highly favorable reaction by pumping protons via three independent proton pumping pathways (aka proton wires!) H-bonding is always with us: net translocation of protons can occur over a “long distance” through a protein by hopping between pairs of hydrogen bonded donor and acceptor residues; a strin ...
Biochem lectures
... Hierarchical nature of hormonal control Hormonal regulation of some physiological activities involves a hierarchy of cell types acting on each other either to stimulate or to modulate the release and action of a particular hormone. The secretion of hormones from successive levels of endocrine cells ...
... Hierarchical nature of hormonal control Hormonal regulation of some physiological activities involves a hierarchy of cell types acting on each other either to stimulate or to modulate the release and action of a particular hormone. The secretion of hormones from successive levels of endocrine cells ...
Unit 1- Human Cells - Mrs Smith`s Biology
... membrane and this results in the synthesis of ATP. iii) ATP synthesis — high energy electrons are used to pump hydrogen ions across a membrane and flow of these ions back ...
... membrane and this results in the synthesis of ATP. iii) ATP synthesis — high energy electrons are used to pump hydrogen ions across a membrane and flow of these ions back ...
BIOL 202
... ¥ ¥ partly polar, partly non-polar ¥ ¥ components: 2 fatty acids, glycerol, alcohol, and ...
... ¥ ¥ partly polar, partly non-polar ¥ ¥ components: 2 fatty acids, glycerol, alcohol, and ...
chapter 11 - rci.rutgers.edu
... reactions to solve the problem. Know why the symptoms of Thiamine deficiency (beriberi) resemble the symptoms of poisoning with mercury or arsenite (494). Know the Glyoxylate Cycle, and why certain plants and bacteria need it (494-5). Remember that for humans, "sugar can make you fat, but fat can't ...
... reactions to solve the problem. Know why the symptoms of Thiamine deficiency (beriberi) resemble the symptoms of poisoning with mercury or arsenite (494). Know the Glyoxylate Cycle, and why certain plants and bacteria need it (494-5). Remember that for humans, "sugar can make you fat, but fat can't ...
Transport
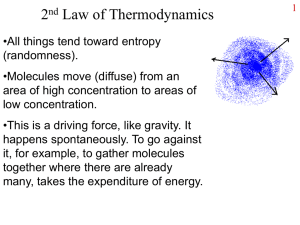
... •This is a driving force, like gravity. It happens spontaneously. To go against it, for example, to gather molecules together where there are already many, takes the expenditure of energy. ...
... •This is a driving force, like gravity. It happens spontaneously. To go against it, for example, to gather molecules together where there are already many, takes the expenditure of energy. ...
File
... disrupt them. In the first diagram, show how the processes work normally. Trace movement of an electron with an orange arrow, movement of H+ ions (active transport and chemiosmosis) with black arrows, and formation of ATP with a pink arrow. In the second diagram, draw arrows showing the movement of ...
... disrupt them. In the first diagram, show how the processes work normally. Trace movement of an electron with an orange arrow, movement of H+ ions (active transport and chemiosmosis) with black arrows, and formation of ATP with a pink arrow. In the second diagram, draw arrows showing the movement of ...
Document
... Very soon, my muscle cells started to run short of oxygen and acidic carbon dioxide started to build up in the blood. ...
... Very soon, my muscle cells started to run short of oxygen and acidic carbon dioxide started to build up in the blood. ...
Word - LangdonBiology.org
... and two nucleotides are linked together via their 3’ and 5’ carbons. DNA molecules are double helices composed of two strands of nucleotides across from each other with the nitrogenous bases inward (like rungs of a ladder) and the phosphate and deoxyribose on the outside. The two strands are antipar ...
... and two nucleotides are linked together via their 3’ and 5’ carbons. DNA molecules are double helices composed of two strands of nucleotides across from each other with the nitrogenous bases inward (like rungs of a ladder) and the phosphate and deoxyribose on the outside. The two strands are antipar ...
Chapter 4
... • Simple – composed only of amino acid residues • Conjugated – contain prosthetic groups (metal ions, co-factors, lipids, carbohydrates) Example: Hemoglobin – Heme ...
... • Simple – composed only of amino acid residues • Conjugated – contain prosthetic groups (metal ions, co-factors, lipids, carbohydrates) Example: Hemoglobin – Heme ...
doc NUR1 200 Midterm 2006
... B) usually catalyze several different reactions within a metabolic pathway. C) usually have more than one polypeptide chain. D) usually have only one active site. E) usually show strict Michaelis-Menten kinetics. 40. Which of the following is true about the Edman degradation system of sequencing pol ...
... B) usually catalyze several different reactions within a metabolic pathway. C) usually have more than one polypeptide chain. D) usually have only one active site. E) usually show strict Michaelis-Menten kinetics. 40. Which of the following is true about the Edman degradation system of sequencing pol ...
The spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to
... Whichever one of the conditions required for photosynthesis is in the shortest supply. ...
... Whichever one of the conditions required for photosynthesis is in the shortest supply. ...
Biology\Ch 2 Chemistry
... shares (covalently bonds) easily with other atoms, sometimes sharing 1, 2, or 3 electrons with another atom. (In other words, forming single, double, or triple bonds.) Carbons can bond together to form chains, branched chains, or rings. Carbon can form large molecules, called macromolecules, that ar ...
... shares (covalently bonds) easily with other atoms, sometimes sharing 1, 2, or 3 electrons with another atom. (In other words, forming single, double, or triple bonds.) Carbons can bond together to form chains, branched chains, or rings. Carbon can form large molecules, called macromolecules, that ar ...
Biology 1406 Quiz 2 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) When biologists
... D) transferring electrons from organic molecules to pyruvate. E) generating carbon dioxide and oxygen in the electron transport chain. 46) During aerobic respiration, H2O is formed. Where does the oxygen atom for the formation of the water come from? A) carbon dioxide (CO2) B) glucose (C6H12O6) C) m ...
... D) transferring electrons from organic molecules to pyruvate. E) generating carbon dioxide and oxygen in the electron transport chain. 46) During aerobic respiration, H2O is formed. Where does the oxygen atom for the formation of the water come from? A) carbon dioxide (CO2) B) glucose (C6H12O6) C) m ...
Aerobic Metabolism: The Citric Acid Cycle
... In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water to generate a form of usable energy. The citric acid cycle also provides precursors for many compounds such as certain amin ...
... In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water to generate a form of usable energy. The citric acid cycle also provides precursors for many compounds such as certain amin ...
L2 Protein structure - e
... Different domains can possess different functions. Proteins can have one to many domains depending on protein size. A polypeptide with 200 amino acids consists of two or more domains. Domains are usually connected with relatively flexible areas of protein. ...
... Different domains can possess different functions. Proteins can have one to many domains depending on protein size. A polypeptide with 200 amino acids consists of two or more domains. Domains are usually connected with relatively flexible areas of protein. ...
lo_ppt20
... • Starch digestible by humans, Cellulose not – The enzymes in humans can only work on the glycosidic linkage found in starch ...
... • Starch digestible by humans, Cellulose not – The enzymes in humans can only work on the glycosidic linkage found in starch ...
Chapter 27 Protein Metabolism
... • mRNAs carry the genetic information copied from DNA in the form of genetic codons. • tRNAs mediate the incorporation of specific amino acids according to genetic codons present on the mRNA molecules via their specific anticodon triplets. • rRNAs associate with a set of proteins to form the protein ...
... • mRNAs carry the genetic information copied from DNA in the form of genetic codons. • tRNAs mediate the incorporation of specific amino acids according to genetic codons present on the mRNA molecules via their specific anticodon triplets. • rRNAs associate with a set of proteins to form the protein ...
Chapter 10. Photosynthesis: The Calvin Cycle Life
... Remember what it means to be a plant… Need to produce all organic molecules necessary for growth carbohydrates, lipids proteins, nucleic acids ...
... Remember what it means to be a plant… Need to produce all organic molecules necessary for growth carbohydrates, lipids proteins, nucleic acids ...
Excretory system
... – Loop of Henle reabsorbs any glucose and salt it needs . The water follows the salt by osmosis. ...
... – Loop of Henle reabsorbs any glucose and salt it needs . The water follows the salt by osmosis. ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... 1. The synthesis of urea requires four high-energy phosphate groups. - Two ATP molecules are required to make carbamoyl phosphate - Two for making arginosuccinate 2. The urea cycle also causes a net conversion of oxaloacetate to fumarate (via aspartate), and the regeration of axaloacetate produces N ...
... 1. The synthesis of urea requires four high-energy phosphate groups. - Two ATP molecules are required to make carbamoyl phosphate - Two for making arginosuccinate 2. The urea cycle also causes a net conversion of oxaloacetate to fumarate (via aspartate), and the regeration of axaloacetate produces N ...
Chapter 9: The Need for Energy
... 1d. Photolysis: Water is broken down into oxygen (given off by plant) and ...
... 1d. Photolysis: Water is broken down into oxygen (given off by plant) and ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.