The Red Blood Cells
... • RBCs must be able to squeeze through some tight spots in microcirculation. • For that RBCs must be easily & reversibly deformable, its membrane must be both fluid & flexible . • About 50% of membrane is protein, 40% is fat & up to 10% is carbohydrate. • RBCs membrane comprise a lipid bilayer( whic ...
... • RBCs must be able to squeeze through some tight spots in microcirculation. • For that RBCs must be easily & reversibly deformable, its membrane must be both fluid & flexible . • About 50% of membrane is protein, 40% is fat & up to 10% is carbohydrate. • RBCs membrane comprise a lipid bilayer( whic ...
(1) Identify the secondary structure described in each of the
... (b) If a Trp residue has = 60º , = -120º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (c) If a Val residue has = -150º , = 150, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (17) Pauling predicted the structures of both -helices and -sheets from modeling studies. What physiochemi ...
... (b) If a Trp residue has = 60º , = -120º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (c) If a Val residue has = -150º , = 150, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (17) Pauling predicted the structures of both -helices and -sheets from modeling studies. What physiochemi ...
metabolism and function of carbohydrates
... sulphate, dermatan sulphate, chondroitin sulphate), monomers, bonds, properties and significance. Glycosaminoglycans as component of proteoglycans, role of proteoglycans. 5. Oligosaccarides of glycoprotein complexes. Role of glycoproteins (give examples of representatives and their role). Structure ...
... sulphate, dermatan sulphate, chondroitin sulphate), monomers, bonds, properties and significance. Glycosaminoglycans as component of proteoglycans, role of proteoglycans. 5. Oligosaccarides of glycoprotein complexes. Role of glycoproteins (give examples of representatives and their role). Structure ...
Cells Unit Review Jeopardy power point
... Cell organelle made up of a phospholipid bilayer that regulates entry and exit into/out of the cell. (selective permeability) ...
... Cell organelle made up of a phospholipid bilayer that regulates entry and exit into/out of the cell. (selective permeability) ...
Biochemistry 2000 Sample Question Protein
... (b) If a Trp residue has = 60º , = 120º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (c) If a Gly residue has = 120º , = 60º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (5) Pauling predicted the structures of both -helices and -sheets from modeling studies. What physiochemic ...
... (b) If a Trp residue has = 60º , = 120º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (c) If a Gly residue has = 120º , = 60º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (5) Pauling predicted the structures of both -helices and -sheets from modeling studies. What physiochemic ...
III Bimester Questionnaire
... Describe two biotic and two abiotic factors in an ecosystem. Biotic: plants – they are living organisms that take in carbon dioxide and produce oxygen cleaning the air. They also serve as food for animals. Animals – they are living organisms that consume plants or other animals and serve as food for ...
... Describe two biotic and two abiotic factors in an ecosystem. Biotic: plants – they are living organisms that take in carbon dioxide and produce oxygen cleaning the air. They also serve as food for animals. Animals – they are living organisms that consume plants or other animals and serve as food for ...
Lipid Metabolizması - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Fat catabolism: generation of energy by fatty acid oxidation Fat (triacylglycerol) and Fatty Acids: 90% of dietary lipids are tryacylglycerol, a hydrophobic, neutral molecule made from reaction of OH group of glycerol and COO- group of fatty acids. Fatty acids are made up of a long hydrophobic hydro ...
... Fat catabolism: generation of energy by fatty acid oxidation Fat (triacylglycerol) and Fatty Acids: 90% of dietary lipids are tryacylglycerol, a hydrophobic, neutral molecule made from reaction of OH group of glycerol and COO- group of fatty acids. Fatty acids are made up of a long hydrophobic hydro ...
Slide
... • Protein Folding is the process by which a sequence of amino acids conforms to a three-dimensional shape. • Anfinsen’s hypothesis suggests that proteins fold to a minimum energy state. • So, our goal is to find a conformation with minimum energy. • We want to investigate algorithmic aspects of simu ...
... • Protein Folding is the process by which a sequence of amino acids conforms to a three-dimensional shape. • Anfinsen’s hypothesis suggests that proteins fold to a minimum energy state. • So, our goal is to find a conformation with minimum energy. • We want to investigate algorithmic aspects of simu ...
CHEM 220 Problem Set 3
... 4) What is the purpose of the sulfuric acid in these reactions? 5) What is the difference between “regular” glass and Pyrex or Kimax? 6) Describe (using sketches) Zone Purification of Si cylinders. 7) Write out the synthesis, including mechanism, of the amides of the following ...
... 4) What is the purpose of the sulfuric acid in these reactions? 5) What is the difference between “regular” glass and Pyrex or Kimax? 6) Describe (using sketches) Zone Purification of Si cylinders. 7) Write out the synthesis, including mechanism, of the amides of the following ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... Concept 5.3: Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, whi ...
... Concept 5.3: Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, whi ...
Third Lecture - LSU School of Medicine
... 4) serves as a cofactor for some enzymatic reactions and as an aid in the rearrangement of protein disulfide bonds. ...
... 4) serves as a cofactor for some enzymatic reactions and as an aid in the rearrangement of protein disulfide bonds. ...
Essential Knowledge
... secondary structure of the protein. Whether a region of the peptide chain produces α helices or β pleated sheet depends largely on the chemical nature of the amino acids which makes them up. ...
... secondary structure of the protein. Whether a region of the peptide chain produces α helices or β pleated sheet depends largely on the chemical nature of the amino acids which makes them up. ...
ppt10 - Plant Agriculture
... Therefore, the majority of the enzymes of the Calvin Cycle have nothing to do with removing C from CO2 to form C-C bonds, but rather, they are there to generate the 5C acceptor molecule!! Is there a more efficient way to do this? Evolution didn't create one, but can humans?!! ...
... Therefore, the majority of the enzymes of the Calvin Cycle have nothing to do with removing C from CO2 to form C-C bonds, but rather, they are there to generate the 5C acceptor molecule!! Is there a more efficient way to do this? Evolution didn't create one, but can humans?!! ...
Section 2-3 - Xavier High School
... Hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach to help digest food is a strong acid (pH 1.5) Base (Alkaline) – A compound that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution pH scale - a measurement system that indicates the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution; each step represents a factor of 10. Exam ...
... Hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach to help digest food is a strong acid (pH 1.5) Base (Alkaline) – A compound that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution pH scale - a measurement system that indicates the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution; each step represents a factor of 10. Exam ...
Section 2-3: Carbon Compounds (p. 44-48)
... proteins. – proteins are made of monomers, while polysaccharides are not. – polysaccharides are made of monosaccharides, while proteins are made of amino acids. – proteins carry genetic information, while ...
... proteins. – proteins are made of monomers, while polysaccharides are not. – polysaccharides are made of monosaccharides, while proteins are made of amino acids. – proteins carry genetic information, while ...
File - Mr. Holz`s Website
... 14. Know that enzymes are the catalysts in living cells. 15. Know the 4 main properties of enzymes: a. They are proteins b. They bind to specific substrates at the ACTIVE SITE like a lock and key c. Enzymes remain unchanged after a reaction, so they can continue doing their job (1 enzyme can bind to ...
... 14. Know that enzymes are the catalysts in living cells. 15. Know the 4 main properties of enzymes: a. They are proteins b. They bind to specific substrates at the ACTIVE SITE like a lock and key c. Enzymes remain unchanged after a reaction, so they can continue doing their job (1 enzyme can bind to ...
Chapter 7
... • nature of starch (amylose, amylopectin content) • interaction of starch with protein, fat. • presence of antinutrient such as phytate, tannin, saponins and enzyme inhibitors. ...
... • nature of starch (amylose, amylopectin content) • interaction of starch with protein, fat. • presence of antinutrient such as phytate, tannin, saponins and enzyme inhibitors. ...
The bridge between glycolysis and the citric acid (Krebs) cycle
... • They are indispensable to all life • They play specific roles in specific chemical processes in the metabolism of all cells • If certain organisms require the presence of these factors in their food while others can do without them, the reason is simply that the latter manufacture these compounds ...
... • They are indispensable to all life • They play specific roles in specific chemical processes in the metabolism of all cells • If certain organisms require the presence of these factors in their food while others can do without them, the reason is simply that the latter manufacture these compounds ...
Study Guide Cellular Respiration
... 1. Cellular Respiration: Liberation of Energy by Oxidation of Food 2. Respiration and Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis uses CO2 and H2O molecules to form C6H12O6 (glucose) and O2. Respiration is just the opposite, it uses O2 to breakdown glucose into CO2 and H2O. It results in chemical cycling in bios ...
... 1. Cellular Respiration: Liberation of Energy by Oxidation of Food 2. Respiration and Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis uses CO2 and H2O molecules to form C6H12O6 (glucose) and O2. Respiration is just the opposite, it uses O2 to breakdown glucose into CO2 and H2O. It results in chemical cycling in bios ...
Biochemistry I: Macromolecules
... the strength of the cell walls and also fibers such as wood. Biochemistry II: Proteins Proteins - have many functions in the cell - structural and functional roles - 105 different kinds of proteins made in eukaryotic cells Proteins are polymers of building blocks known as amino acids 20 different am ...
... the strength of the cell walls and also fibers such as wood. Biochemistry II: Proteins Proteins - have many functions in the cell - structural and functional roles - 105 different kinds of proteins made in eukaryotic cells Proteins are polymers of building blocks known as amino acids 20 different am ...
Document
... Addition polymerization – linking molecules incorporating double or triple chemical bonds. These extra bonds can break and serve as the links. Condensation polymerization – linking molecules containing functional groups (amines or carboxyls) which form a peptide bond and release water. ...
... Addition polymerization – linking molecules incorporating double or triple chemical bonds. These extra bonds can break and serve as the links. Condensation polymerization – linking molecules containing functional groups (amines or carboxyls) which form a peptide bond and release water. ...
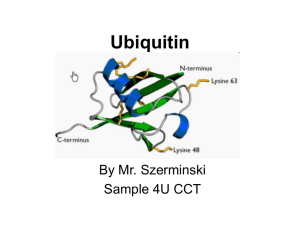
Ubiquitin
... Topics to be discussed • General info: - it is a regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotes - one of its functions: it directs protein recycling - can attach to proteins and label them for destruction. - discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004 ...
... Topics to be discussed • General info: - it is a regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotes - one of its functions: it directs protein recycling - can attach to proteins and label them for destruction. - discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004 ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.