
cellular respiration
... – This step makes a LOT of ATP (overall total for 1 glucose molecule: ~34 ATP) ...
... – This step makes a LOT of ATP (overall total for 1 glucose molecule: ~34 ATP) ...
5.3 Presentation: Protein Synthesis
... • Cells respond to their environments by producing different types and amounts of proteins • The cell produces proteins that are structural (forms part of cell materials) or functional (enzymes and hormones). • All of an organisms cells have the same DNA, but the cells differ on the expression of th ...
... • Cells respond to their environments by producing different types and amounts of proteins • The cell produces proteins that are structural (forms part of cell materials) or functional (enzymes and hormones). • All of an organisms cells have the same DNA, but the cells differ on the expression of th ...
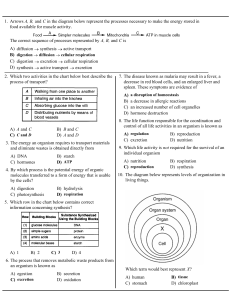
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. A solution of an enzyme normally found in the human body was added to a flask containing a solution of proteins in distilled water, and then the flask was stoppered. This mixture was then mainta ...
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. A solution of an enzyme normally found in the human body was added to a flask containing a solution of proteins in distilled water, and then the flask was stoppered. This mixture was then mainta ...
Lecture 2- protein structure
... extremely weak, they are significant because there are so many of them in large protein molecules. ...
... extremely weak, they are significant because there are so many of them in large protein molecules. ...
Microbiology(Hons)[Paper-IV] - Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira
... b) What are thermoduric microorganisms? c) How does TMAO reduces shelf life of modified atmosphere packaged fish? d) What are the antimicrobial barriers present in egg white? e) Write down the advantages and disadvantages of slow freezing in food preservation. ...
... b) What are thermoduric microorganisms? c) How does TMAO reduces shelf life of modified atmosphere packaged fish? d) What are the antimicrobial barriers present in egg white? e) Write down the advantages and disadvantages of slow freezing in food preservation. ...
04. Introduction to metabolism
... maintenance, growth and reproduction Catabolism is characterized by oxidation reactions and by release of free energy which is transformed to ATP. Anabolism is characterized by reduction reactions and by utilization of energy accumulated in ATP molecules. Catabolism and anabolism are tightly linked ...
... maintenance, growth and reproduction Catabolism is characterized by oxidation reactions and by release of free energy which is transformed to ATP. Anabolism is characterized by reduction reactions and by utilization of energy accumulated in ATP molecules. Catabolism and anabolism are tightly linked ...
Exam II Sample (1710).doc
... Genes which can contribute in a dominant fashion to a cell becoming ...
... Genes which can contribute in a dominant fashion to a cell becoming ...
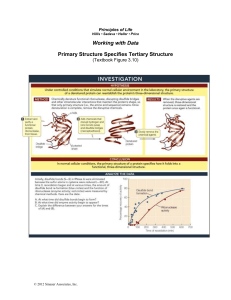
Principles of Life
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides
... • Parts of a large polypeptide chain will spontaneously organize into α-helices, βpleated sheets and sometimes other less common sub-structures. • These "sub-structures" will organize themselves into a specific 3D super-structure, which is mostly held together by non-covalent interactions like hydro ...
... • Parts of a large polypeptide chain will spontaneously organize into α-helices, βpleated sheets and sometimes other less common sub-structures. • These "sub-structures" will organize themselves into a specific 3D super-structure, which is mostly held together by non-covalent interactions like hydro ...
Polymer - Deans Community High School
... Condensation Polymers Polymers are very large molecules made by joining small molecules, monomers, in long chains or networks. Condensation polymers are made from monomers with two functional groups per molecule. Starch is made by polymerisation of about 300 glucose molecules ...
... Condensation Polymers Polymers are very large molecules made by joining small molecules, monomers, in long chains or networks. Condensation polymers are made from monomers with two functional groups per molecule. Starch is made by polymerisation of about 300 glucose molecules ...
CP Final Exam Study Guide 2015KEY
... Biology in the 21st Century 1. What is biology the study of? Life 2. What technology led to the discovery of cells? Microscope 3. What is the difference between an inference, hypothesis, and theory? 4. What are independent and dependent variables? (Explain) Independent variables include the factor t ...
... Biology in the 21st Century 1. What is biology the study of? Life 2. What technology led to the discovery of cells? Microscope 3. What is the difference between an inference, hypothesis, and theory? 4. What are independent and dependent variables? (Explain) Independent variables include the factor t ...
CHAPTER 20 - AMINO ACID METABOLISM Introduction Amino acid
... with them. They contain a variety of proteases for this purpose, known as cathepsins. The internal pH of a lysosome is acidic (-5), and lysosomal proteases have optimal activities in this pH range. Presumably, the cell is protected from damage associated with accidental lysosomal leakage because the ...
... with them. They contain a variety of proteases for this purpose, known as cathepsins. The internal pH of a lysosome is acidic (-5), and lysosomal proteases have optimal activities in this pH range. Presumably, the cell is protected from damage associated with accidental lysosomal leakage because the ...
Reproduction
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and bonucIeic acid (ANA) are two of the cell’s most Important molecules. These nucleic acids have a complex three-dimensional structure that enab les them to direct protein synthesis in the cell. • Study the structure of the DNA and RNA molecules shown below. Fill in the ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and bonucIeic acid (ANA) are two of the cell’s most Important molecules. These nucleic acids have a complex three-dimensional structure that enab les them to direct protein synthesis in the cell. • Study the structure of the DNA and RNA molecules shown below. Fill in the ...
Protein Purification
... • In Ultrafiltration, molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids are retained by the filter. • These filters can only separate very large proteins from very small proteins; they are mainly used for concentrating proteins and for exchanging buffers. 2. Protein Precipitation This step is used at an ...
... • In Ultrafiltration, molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids are retained by the filter. • These filters can only separate very large proteins from very small proteins; they are mainly used for concentrating proteins and for exchanging buffers. 2. Protein Precipitation This step is used at an ...
Amino acids [qualitative tests]
... Objectives: -general information about amino acids. -qualitative tests of amino acids. ...
... Objectives: -general information about amino acids. -qualitative tests of amino acids. ...
DNA Unit Test Corrections
... 6. What is it with the structure of DNA that allows it to store so much information?_______ ________________________________________________________________________ Part Two: DNA Replication 7. Where does DNA replication take place:__________________ 8. When does DNA replication take place:_________ ...
... 6. What is it with the structure of DNA that allows it to store so much information?_______ ________________________________________________________________________ Part Two: DNA Replication 7. Where does DNA replication take place:__________________ 8. When does DNA replication take place:_________ ...
ANSWER KEY Nucleic Acid and DNA Replication Outline Notes
... DNA Replication During MITOSIS- chromosomes (DNA) are copied (replicated) ...
... DNA Replication During MITOSIS- chromosomes (DNA) are copied (replicated) ...
Concepts in Biochemistry 3/e
... NAD+ is an oxidizing agent, typically to oxidize alcohols NADH is a reducing agent, typically to reduce ketones and aldehydes ...
... NAD+ is an oxidizing agent, typically to oxidize alcohols NADH is a reducing agent, typically to reduce ketones and aldehydes ...
genetic et.al - UniMAP Portal
... organisms that grow only in the absence of oxygen, avoid the gas by living in highly reduced environments such as soil. They use fermentative processes to satisfy their energy requirements. ...
... organisms that grow only in the absence of oxygen, avoid the gas by living in highly reduced environments such as soil. They use fermentative processes to satisfy their energy requirements. ...
Biology II Chapter 5 The Working Cell Notes Outline MEMBRANE
... – _________________________ are organic molecules and are often vitamins ______________________________ are chemicals that inhibit an enzyme’s activity – One group inhibits because they ____________________ for the enzyme’s active site and thus ______________________ substrates from entering the act ...
... – _________________________ are organic molecules and are often vitamins ______________________________ are chemicals that inhibit an enzyme’s activity – One group inhibits because they ____________________ for the enzyme’s active site and thus ______________________ substrates from entering the act ...
Dr Azis Ariffin and Dr Nora. UPM.
... The omega-6 (C18:2, linoleic) and omega-3 (C18:3, linolenic acid) fatty acids which are necessary but cannot be synthesized by the body. Some plants have oils with exceptionally high content of essential fatty acids. Plant oil rich in essential acids may not have the aromatic compound or “essence” t ...
... The omega-6 (C18:2, linoleic) and omega-3 (C18:3, linolenic acid) fatty acids which are necessary but cannot be synthesized by the body. Some plants have oils with exceptionally high content of essential fatty acids. Plant oil rich in essential acids may not have the aromatic compound or “essence” t ...
Cellular Respiration Guided Reading Notes Section 7
... 18. Table _____________________________ and ____________________ are made by yeast during alcoholic fermentation. 19. One molecule of sugar produces _________________ kilocalories of energy. 20. ________________________ respiration, like glycolysis, produces less energy than ________________________ ...
... 18. Table _____________________________ and ____________________ are made by yeast during alcoholic fermentation. 19. One molecule of sugar produces _________________ kilocalories of energy. 20. ________________________ respiration, like glycolysis, produces less energy than ________________________ ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.



![Microbiology(Hons)[Paper-IV] - Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017635075_1-cacd0a5e5aa4de554a7e55477a5947cd-300x300.png)










![Amino acids [qualitative tests]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008282328_1-c8bb4ef27caebe478c13494a7af59cc2-300x300.png)






