1 CHAPTER 15. BIOCHEMISTRY: THE CHEMISTRY OF OUR
... bacteria that release enzymes which can break the linkages of the cellulose polymer, freeing the glucose units. Humans lack these bacteria. That is the reason why cows and sheep are able to eat grass, hay, and cornstalks, while humans cannot. Though cellulose is useless to us as food, it is importan ...
... bacteria that release enzymes which can break the linkages of the cellulose polymer, freeing the glucose units. Humans lack these bacteria. That is the reason why cows and sheep are able to eat grass, hay, and cornstalks, while humans cannot. Though cellulose is useless to us as food, it is importan ...
Lifeline Week 6 Follow-Along Sheet Cellular Respiration
... __________ and ____________ are coenzymes that are _______________ (have gained an electron and a proton). NAD+ and FADH are the _________________ form of the coenzymes (have lost an electron and a proton). These coenzymes are electron carriers that are required for cellular respiration to take ...
... __________ and ____________ are coenzymes that are _______________ (have gained an electron and a proton). NAD+ and FADH are the _________________ form of the coenzymes (have lost an electron and a proton). These coenzymes are electron carriers that are required for cellular respiration to take ...
Bio426Lecture25Apr3 - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... In aerobic conditions, pyruvate from glycolysis is converted to acetyl CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle where most of the NADH is produced. Fig. 11.6 ...
... In aerobic conditions, pyruvate from glycolysis is converted to acetyl CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle where most of the NADH is produced. Fig. 11.6 ...
Biomembranes and Membrane Transport
... o intracellular solutes e.g. negatively charged ions/organic molecules - water tends to flow in; can burst cell - Animal cells o Continuously pump out inorganic ions (e.g. Na+) o Primary purpose of Na+/K+ pump - Plants (and algae, fungi, bacteria) o cell wall keeps from bursting o cells become tur ...
... o intracellular solutes e.g. negatively charged ions/organic molecules - water tends to flow in; can burst cell - Animal cells o Continuously pump out inorganic ions (e.g. Na+) o Primary purpose of Na+/K+ pump - Plants (and algae, fungi, bacteria) o cell wall keeps from bursting o cells become tur ...
METABOLISM BACTERIAL METABOLISM
... – Light causes chlorophyll to give up electrons. Energy released from the transfer of electrons (oxidation) of chlorophyll through a system of carrier molecules is used to generate ATP. ...
... – Light causes chlorophyll to give up electrons. Energy released from the transfer of electrons (oxidation) of chlorophyll through a system of carrier molecules is used to generate ATP. ...
NUTRITION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
... Camels store fat in their humps since they have to go without food for several days. Plants store oils, mostly in their seeds e.g. mustard, groundnut, coconut. Animals and humans use only a part of the fats that they consume. They store the rest for future use in their body under their skin an ...
... Camels store fat in their humps since they have to go without food for several days. Plants store oils, mostly in their seeds e.g. mustard, groundnut, coconut. Animals and humans use only a part of the fats that they consume. They store the rest for future use in their body under their skin an ...
Semester Exam Review
... What is chemiosmosis? When does it occur? What is the Kreb’s cycle? What is the starting point? What is the end point? What recycles? What is the Calvin-Benson Cycle? What is the starting point? What is the end point? What recycles? What is the difference among C4, C3, and CAM plants? Why are plants ...
... What is chemiosmosis? When does it occur? What is the Kreb’s cycle? What is the starting point? What is the end point? What recycles? What is the Calvin-Benson Cycle? What is the starting point? What is the end point? What recycles? What is the difference among C4, C3, and CAM plants? Why are plants ...
FUNCTIONS OF CELL ORGANELLES
... nucleus. It is the repository of genetic information. Present as DNA- protein complex –Chromatin, which is organized into chromosomes. A typical human cell contains 46 chromosomes. To pack it effectively it requires interaction with a large number of proteins. These are called histones. They ...
... nucleus. It is the repository of genetic information. Present as DNA- protein complex –Chromatin, which is organized into chromosomes. A typical human cell contains 46 chromosomes. To pack it effectively it requires interaction with a large number of proteins. These are called histones. They ...
Multiple Choice: Choose the one best answer to each question
... NADH= _6_ FADH2= _2_ GTP= 2 CO2= _4 (2X2=4 CO2)_ Oxaloacetate= 2 Pyruvate= 0 31) 5 points: How do mitochondria produce ATP from ADP, Pi and the NADH and FADH2 generated in the question above? You will need to indicate/name all enzymes, proton gradients, and enzyme complexes. A sketch of the mitochon ...
... NADH= _6_ FADH2= _2_ GTP= 2 CO2= _4 (2X2=4 CO2)_ Oxaloacetate= 2 Pyruvate= 0 31) 5 points: How do mitochondria produce ATP from ADP, Pi and the NADH and FADH2 generated in the question above? You will need to indicate/name all enzymes, proton gradients, and enzyme complexes. A sketch of the mitochon ...
Y.B. Grechanina
... In the periods of acute crisis, the following is recommended: Discontinuing of the ordinary diet; Often introduction of drinking in a great amount. The frequency, amount, concentration of drinking depends on children age and the main disease. In urea cycle disorder it is necessary to increase m ...
... In the periods of acute crisis, the following is recommended: Discontinuing of the ordinary diet; Often introduction of drinking in a great amount. The frequency, amount, concentration of drinking depends on children age and the main disease. In urea cycle disorder it is necessary to increase m ...
File
... (4) The cell is composed only of DNA and protein. 3. Which of the following bases will not be present in a molecule of mRNA? (1) Adenine (2) Guanine (3) Uracil (4) Thymine (5) Cytosine 4. What is the role of DNA molecules in the synthesis of proteins? (1) They catalyze bond formation between amino a ...
... (4) The cell is composed only of DNA and protein. 3. Which of the following bases will not be present in a molecule of mRNA? (1) Adenine (2) Guanine (3) Uracil (4) Thymine (5) Cytosine 4. What is the role of DNA molecules in the synthesis of proteins? (1) They catalyze bond formation between amino a ...
cell molecules
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
glycogen disappears
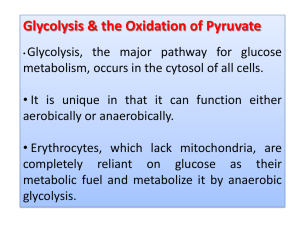
... Glycolysis & the Oxidation of Pyruvate Glycolysis, the major pathway for glucose metabolism, occurs in the cytosol of all cells. ...
... Glycolysis & the Oxidation of Pyruvate Glycolysis, the major pathway for glucose metabolism, occurs in the cytosol of all cells. ...
Biology model examination for grade 12
... C. Brassica carinata—Gomenzer B. Guizotia abyssinica—Niger seed(Nug) D. Carthamus tincture— Barely 42. The high species richness of plants & animals in Ethiopia is largely due to A. The presence of better ecological management B. The presence of national parks at different parts of the country. C. T ...
... C. Brassica carinata—Gomenzer B. Guizotia abyssinica—Niger seed(Nug) D. Carthamus tincture— Barely 42. The high species richness of plants & animals in Ethiopia is largely due to A. The presence of better ecological management B. The presence of national parks at different parts of the country. C. T ...
Brain Needs in Different Metabolic states
... Liver still synthesizes glucose to refill liver’s glycogen stores When liver has refilled glycogen stores + blood-glucose level still rises -> liver synthesizes fatty acids from excess glucose ...
... Liver still synthesizes glucose to refill liver’s glycogen stores When liver has refilled glycogen stores + blood-glucose level still rises -> liver synthesizes fatty acids from excess glucose ...
9 and 10 notes with blanks
... These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps ...
... These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps ...
From Gene to Protein
... • 1930 – Beadle and Ephrussi, eye color in flies is due to an enzyme for pigment production • Beadle and Tatum – minimal medium Neurospora crassa (bread mold), used x-rays to create mutations, complete media had 20 amino acids, looking for inability to metabolize amino acids from a limited source – ...
... • 1930 – Beadle and Ephrussi, eye color in flies is due to an enzyme for pigment production • Beadle and Tatum – minimal medium Neurospora crassa (bread mold), used x-rays to create mutations, complete media had 20 amino acids, looking for inability to metabolize amino acids from a limited source – ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Intermolecular
... Regardless, the dissolved Oxygen gas in water allows for life forms to live in the water. They mainly use gills or diffusion to get the Oxygen gas out of the water. 4. London Dispersion Forces (Non-polar molecules) (Please help students “see” the term.) a. These were discovered by Fritz London in ...
... Regardless, the dissolved Oxygen gas in water allows for life forms to live in the water. They mainly use gills or diffusion to get the Oxygen gas out of the water. 4. London Dispersion Forces (Non-polar molecules) (Please help students “see” the term.) a. These were discovered by Fritz London in ...
- CUNY Academic Works
... Active student engagement is likely to facilitate learning. Comprehension increases with the number of different learning methods employed, especially those involving kinesthetic learning (2, 5, 7, 10). The use of such low-cost demonstrations has been explored (11, 21) and found to be very successfu ...
... Active student engagement is likely to facilitate learning. Comprehension increases with the number of different learning methods employed, especially those involving kinesthetic learning (2, 5, 7, 10). The use of such low-cost demonstrations has been explored (11, 21) and found to be very successfu ...
Preparation and transformation of competent bacteria: Calcium
... 32. In addition to the general questions, answer the following PAH specific questions (use information from these databases or the Berg reading material, note that you may need to clink on links). Please indicate which source each answer comes from. a. What metabolic pathway does this protein belong ...
... 32. In addition to the general questions, answer the following PAH specific questions (use information from these databases or the Berg reading material, note that you may need to clink on links). Please indicate which source each answer comes from. a. What metabolic pathway does this protein belong ...
Lecture 3: Introduction to Proteins
... Draw the structure of a typical amino acid, indicating the following features: α-carbon, α-carboxyl group, α-amino group, side chain (“R group”), and ionic forms that predominate at acidic (say, pH 1), neutral (pH 7), and basic (pH 13) pH values. Classify each of the 20 common amino acids found in p ...
... Draw the structure of a typical amino acid, indicating the following features: α-carbon, α-carboxyl group, α-amino group, side chain (“R group”), and ionic forms that predominate at acidic (say, pH 1), neutral (pH 7), and basic (pH 13) pH values. Classify each of the 20 common amino acids found in p ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... Fermentation: Anaerobic Respiration Without O2 all that is left is NADH, Pyruvate, and Glucose with nowhere to go. ...
... Fermentation: Anaerobic Respiration Without O2 all that is left is NADH, Pyruvate, and Glucose with nowhere to go. ...
Updated Power Point
... lose access to oxygen and why this poses such a dire problem for your cells. b. How is it that some other organisms don’t suffocate in oxygen-free environments, and in fact thrive there? ...
... lose access to oxygen and why this poses such a dire problem for your cells. b. How is it that some other organisms don’t suffocate in oxygen-free environments, and in fact thrive there? ...
Chapter 3 (Protein structure and function)
... secondary structures – -helix and -sheet; hydrogen bonds tertiary structure – noncovalent bonds; folding of proteins into a conformation of lowest ...
... secondary structures – -helix and -sheet; hydrogen bonds tertiary structure – noncovalent bonds; folding of proteins into a conformation of lowest ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.