Basic DNA
... • DNA carries the genetic information in the cell – i.e. it carries the instructions for making all the structures and materials the body needs to function. • DNA is capable of self-replication. • Most of the cell’s DNA is carried in the nucleus – a small amount is contained in the mitochondria. Wel ...
... • DNA carries the genetic information in the cell – i.e. it carries the instructions for making all the structures and materials the body needs to function. • DNA is capable of self-replication. • Most of the cell’s DNA is carried in the nucleus – a small amount is contained in the mitochondria. Wel ...
Ch. 25
... Because most biological oxidations involve the loss of hydrogen atoms, they are called dehydrogenation reactions. • When a substance is oxidized, the liberated hydrogen atoms do not remain free in the cell but are transferred immediately by coenzymes to another compound. • Reduction is the opposite ...
... Because most biological oxidations involve the loss of hydrogen atoms, they are called dehydrogenation reactions. • When a substance is oxidized, the liberated hydrogen atoms do not remain free in the cell but are transferred immediately by coenzymes to another compound. • Reduction is the opposite ...
Krebs Cycle
... Because most biological oxidations involve the loss of hydrogen atoms, they are called dehydrogenation reactions. • When a substance is oxidized, the liberated hydrogen atoms do not remain free in the cell but are transferred immediately by coenzymes to another compound. • Reduction is the opposite ...
... Because most biological oxidations involve the loss of hydrogen atoms, they are called dehydrogenation reactions. • When a substance is oxidized, the liberated hydrogen atoms do not remain free in the cell but are transferred immediately by coenzymes to another compound. • Reduction is the opposite ...
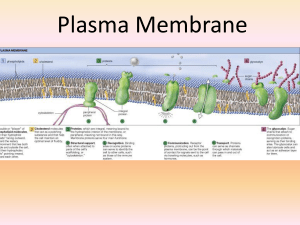
Plasma Membrane
... outside of cell; they provide an ID tag letting other cells know what type of cell they are 5. Channels for passive transport – integral proteins that have a channel in them to allow substances to move through; passive means substances move through from high to low concentration 6. Pumps for active ...
... outside of cell; they provide an ID tag letting other cells know what type of cell they are 5. Channels for passive transport – integral proteins that have a channel in them to allow substances to move through; passive means substances move through from high to low concentration 6. Pumps for active ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... NADH and ubiquinol from the Krebs cycle start a series of oxidation reduction reactions that move electrons through a series of carriers. The electron carriers together are called an “electron transport chain” ...
... NADH and ubiquinol from the Krebs cycle start a series of oxidation reduction reactions that move electrons through a series of carriers. The electron carriers together are called an “electron transport chain” ...
My-B-Tabs™ Myoden Spray - wm
... Both My-B-Tabs™ and Myoden Spray™ contains the ingredient, Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP) Adenosine Monophosphate is purine nucleotide that is an intermediate in cellular metabolism and nucleic acid metabolism. AMP is directly involved in many normal biochemical processes including protein synthesis ...
... Both My-B-Tabs™ and Myoden Spray™ contains the ingredient, Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP) Adenosine Monophosphate is purine nucleotide that is an intermediate in cellular metabolism and nucleic acid metabolism. AMP is directly involved in many normal biochemical processes including protein synthesis ...
Optional PowerPoint introduction to the case
... Natural amino acids form the basis for the structure of all proteins and enzymes in living organisms. The key to this is that each amino acid contains one stereocenter in its structure. All natural amino acids exist as a single enantiomer (the L isomer); this enantiomeric purity allows proteins (ami ...
... Natural amino acids form the basis for the structure of all proteins and enzymes in living organisms. The key to this is that each amino acid contains one stereocenter in its structure. All natural amino acids exist as a single enantiomer (the L isomer); this enantiomeric purity allows proteins (ami ...
Freeman 1e: How we got there
... • Chemolithotrophs use inorganic compounds as electron donors, whereas phototrophs use light to form a proton motive force. The proton motive force is involved in all forms of respiration and photosynthesis (Figure 5.23). ...
... • Chemolithotrophs use inorganic compounds as electron donors, whereas phototrophs use light to form a proton motive force. The proton motive force is involved in all forms of respiration and photosynthesis (Figure 5.23). ...
Take Home Part 1 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... D) NAD+ has more chemical energy than NADH. E) NAD+ can donate electrons for use in oxidative phosphorylation. ...
... D) NAD+ has more chemical energy than NADH. E) NAD+ can donate electrons for use in oxidative phosphorylation. ...
Respiration
... In the absence of oxygen, the cell resorts to anaerobic metabolism. In animal cells, pyruvate is converted to lactic acid. In yeast and bacteria, the pyruvate is often converted to ethanol. In both cases, no new ATP is produced, so the net production of the energy-carrying molecule is only the two m ...
... In the absence of oxygen, the cell resorts to anaerobic metabolism. In animal cells, pyruvate is converted to lactic acid. In yeast and bacteria, the pyruvate is often converted to ethanol. In both cases, no new ATP is produced, so the net production of the energy-carrying molecule is only the two m ...
Name: Date: Concept Check Questions Chapter 8 (orange) or 6
... 2. A key process in metabolism is the transfer of H+ ions across a membrane to create a concentration gradient. In some conditions, H+ ions flow back across the membrane and come to equal concentrations on each side. In which conditions can the H+ ions perform work in this system? 8.3 ATP powers cel ...
... 2. A key process in metabolism is the transfer of H+ ions across a membrane to create a concentration gradient. In some conditions, H+ ions flow back across the membrane and come to equal concentrations on each side. In which conditions can the H+ ions perform work in this system? 8.3 ATP powers cel ...
anaerobic and aerobic respiration
... Albert von Szent-Gyorgyi, a Hungarian (who later moved to the USA in 1947), extended these studies by describing a sequence of reactions for succinate oxidation, specifically from succinate to fumarate to malate to oxaloacetate. Von Szent-Gyorgyi further discovered that adding a small amount of mala ...
... Albert von Szent-Gyorgyi, a Hungarian (who later moved to the USA in 1947), extended these studies by describing a sequence of reactions for succinate oxidation, specifically from succinate to fumarate to malate to oxaloacetate. Von Szent-Gyorgyi further discovered that adding a small amount of mala ...
gr11chemreview
... 12. Explain why polar molecules have higher boiling and melting points than non polar molecules. ...
... 12. Explain why polar molecules have higher boiling and melting points than non polar molecules. ...
TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE
... oxidation of carbohydrate, fat and amino acids via acetyl coenzyme A. • Pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. • The reactions of the TCA cycle generate carbon dioxide, reduced NAD, reduced FAD and GTP • There are negative and positive controls for the TCA ...
... oxidation of carbohydrate, fat and amino acids via acetyl coenzyme A. • Pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. • The reactions of the TCA cycle generate carbon dioxide, reduced NAD, reduced FAD and GTP • There are negative and positive controls for the TCA ...
Chapter 17. Amino Acid Oxidation and the Production of Urea
... • NH4+ in hepatocytes is converted into urea through ...
... • NH4+ in hepatocytes is converted into urea through ...
Ecology Pre
... transmission and conservation of the genetic information. SC.912.L.16.10 Evaluate the impact of biotechnology on the individual, society and the environment, including medical and ethical issues. SC.912.L.16.4 Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence may or may not result in phenotypic change. Expl ...
... transmission and conservation of the genetic information. SC.912.L.16.10 Evaluate the impact of biotechnology on the individual, society and the environment, including medical and ethical issues. SC.912.L.16.4 Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence may or may not result in phenotypic change. Expl ...
Biochemistry 2007
... The aspartate aminotransferase enzyme (AST) catalyzes: (a) The transfer of the amino group of glutamate to oxaloacetate, generating aspartate and alpha-ketoglutarate. (b) The transfer of the amino group from glutamate to pyruvate, generating aspartate and alpha-ketoglutarate. (c) The transfer of the ...
... The aspartate aminotransferase enzyme (AST) catalyzes: (a) The transfer of the amino group of glutamate to oxaloacetate, generating aspartate and alpha-ketoglutarate. (b) The transfer of the amino group from glutamate to pyruvate, generating aspartate and alpha-ketoglutarate. (c) The transfer of the ...
Handout
... the same as weight since weight varies with gravity. Your amount of matter, how much stuff comprises you right now, remains constant regardless of where you are standing, but you weigh more here on earth and far less on the moon. This is because the gravity of the moon pulls less strongly on your ma ...
... the same as weight since weight varies with gravity. Your amount of matter, how much stuff comprises you right now, remains constant regardless of where you are standing, but you weigh more here on earth and far less on the moon. This is because the gravity of the moon pulls less strongly on your ma ...
Respiration - Goffs School
... In the first stage of respiration which occurs in the .............. of the cell, glucose is .............. to pyruvic acid. Glycolysis yields .............. and reduced coenzyme. The pyruvic acid then combines with coenzyme A to form ................ which enters the Kreb's cycle which occurs in th ...
... In the first stage of respiration which occurs in the .............. of the cell, glucose is .............. to pyruvic acid. Glycolysis yields .............. and reduced coenzyme. The pyruvic acid then combines with coenzyme A to form ................ which enters the Kreb's cycle which occurs in th ...
ENZYMES
... • Some reactions RELEASE energy ie: 2H2+O2---> 2H2O + heat • Some reactions ABSORB energy ie: 2H2O----> 2H2+O2 (energy is needed - light reactions of photosynthesis) • Energy is stored in the bonds between molecules • Matter and energy must be conserved - some reactions happen slowly, others happen ...
... • Some reactions RELEASE energy ie: 2H2+O2---> 2H2O + heat • Some reactions ABSORB energy ie: 2H2O----> 2H2+O2 (energy is needed - light reactions of photosynthesis) • Energy is stored in the bonds between molecules • Matter and energy must be conserved - some reactions happen slowly, others happen ...
Document
... Primary structure: Polypeptide sequence composed of 20 amino acids by peptide bond Secondary structure: Polypeptide chain forms the α-helix and β-pleated sheet by hydrogen bonds Tertiary structure: The conformation of the entire protein. Tertiary structure is unlimitedly stabilized by an array of n ...
... Primary structure: Polypeptide sequence composed of 20 amino acids by peptide bond Secondary structure: Polypeptide chain forms the α-helix and β-pleated sheet by hydrogen bonds Tertiary structure: The conformation of the entire protein. Tertiary structure is unlimitedly stabilized by an array of n ...
A1984SR69800002
... work i n several directions. Enzymes and enzyme inhibitors were immobilized onto a variety of hydroxylic supports. Not much later, our work on activation of agarose for enzyme immobilization was described, and this work initiated an almost explosive development i n (bio-)affinity chromatography. "We ...
... work i n several directions. Enzymes and enzyme inhibitors were immobilized onto a variety of hydroxylic supports. Not much later, our work on activation of agarose for enzyme immobilization was described, and this work initiated an almost explosive development i n (bio-)affinity chromatography. "We ...
Cellular Respiration Review
... Respiration= obtaining O2 and releasing CO2; aerobic break down of food molecules to yield ATP. Releasing ATP= main function of cellular respiration. Equation for cellular respiration: 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2+ 6H20 +36ATP Glucose= most commonly shown as the representative food molecule for cell ...
... Respiration= obtaining O2 and releasing CO2; aerobic break down of food molecules to yield ATP. Releasing ATP= main function of cellular respiration. Equation for cellular respiration: 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2+ 6H20 +36ATP Glucose= most commonly shown as the representative food molecule for cell ...
Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy
... Mitochondria are everywhere!! animal cells plant cells ...
... Mitochondria are everywhere!! animal cells plant cells ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.