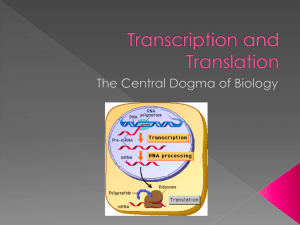
myosinActivity.pdf
... age of a living person or the age at which the person died. The R719W data is a combination of data from four unrelated families with the same mutation. ...
... age of a living person or the age at which the person died. The R719W data is a combination of data from four unrelated families with the same mutation. ...
Chapter 6 – How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Standard 1.g
... 1. The movement of electrons along an electron transport chain creates a proton gradient across the inner membrane. The protons diffuse back across the membrane through ATP synthase releasing energy that is used to make ATP by 2. ATP can also be made by transferring phosphate groups from organic mol ...
... 1. The movement of electrons along an electron transport chain creates a proton gradient across the inner membrane. The protons diffuse back across the membrane through ATP synthase releasing energy that is used to make ATP by 2. ATP can also be made by transferring phosphate groups from organic mol ...
Multiple Choice Review
... d. Sulfate because it produces the most NADH as an electron acceptor. 32. The process known as glycolysis is a catabolic pathway. Which of the following correctly lists the types of molecules that can be accepted into this pathway? a. Glucose only b. carbohydrates, proteins and fats c. nucleic acids ...
... d. Sulfate because it produces the most NADH as an electron acceptor. 32. The process known as glycolysis is a catabolic pathway. Which of the following correctly lists the types of molecules that can be accepted into this pathway? a. Glucose only b. carbohydrates, proteins and fats c. nucleic acids ...
Pyruvic acid is a valuable chemical intermediate in the production of
... Process development work was performed at the University of Iowa’s Center for Biocatalysis and Bioprocessing. High density, double recombinant, P. pastoris fermentation (100 g cells/L) was achieved at the 30 L scale. After fermentation, these cells were treated with a proprietary process (2) to enab ...
... Process development work was performed at the University of Iowa’s Center for Biocatalysis and Bioprocessing. High density, double recombinant, P. pastoris fermentation (100 g cells/L) was achieved at the 30 L scale. After fermentation, these cells were treated with a proprietary process (2) to enab ...
Amino acids
... – The most well-defined physicochemical properties – Easier to isolate and characterize than nucleic acids, polysaccharides, or lipids – Proteins had easily recognizable functions (enzymes) ...
... – The most well-defined physicochemical properties – Easier to isolate and characterize than nucleic acids, polysaccharides, or lipids – Proteins had easily recognizable functions (enzymes) ...
L5 Food proteins - e
... Proteins from animal sources (meat, poultry, milk, and fish) have a high quality because they contain all the essential amino acids in proportions similar to those required for synthesis of human tissue proteins [Note: Gelatin prepared from animal collagen is an exception; it has a low biological va ...
... Proteins from animal sources (meat, poultry, milk, and fish) have a high quality because they contain all the essential amino acids in proportions similar to those required for synthesis of human tissue proteins [Note: Gelatin prepared from animal collagen is an exception; it has a low biological va ...
Bacteria - Eubacteria
... How do Archaea tolerate the heat? • Proteins stabilized by more ionic bridges between amino acid r-groups and more-hydrophobic core amino acids • Heat shock protein (chaperonins) refold denatured proteins…Pyrococcus 121°C for 1 hour! • DNA depurination reduced by presence of 2,3diphosphoglycerate. • ...
... How do Archaea tolerate the heat? • Proteins stabilized by more ionic bridges between amino acid r-groups and more-hydrophobic core amino acids • Heat shock protein (chaperonins) refold denatured proteins…Pyrococcus 121°C for 1 hour! • DNA depurination reduced by presence of 2,3diphosphoglycerate. • ...
Honors Biology Unit 1 Objectives: The Chemistry of Life
... 1. Vocabulary: organism, molecule, element, atom, electron, proton, neutron, isotope, chemical bond, chemical reaction, law of conservation of matter, activation energy, ion, ionic bond, covalent bond, hydrogen bond, pH, acid, base, organic, macromolecule, monomer, polymer, carbohydrate, monosacchar ...
... 1. Vocabulary: organism, molecule, element, atom, electron, proton, neutron, isotope, chemical bond, chemical reaction, law of conservation of matter, activation energy, ion, ionic bond, covalent bond, hydrogen bond, pH, acid, base, organic, macromolecule, monomer, polymer, carbohydrate, monosacchar ...
Metabolomic Profiling of Dynamic and Basal Measures of Glucose
... Associate Professor, Department of Biochemistry Dr. Allred is a molecular biologist with a research focus on understanding the genetic architecture of complex diseases and underlying risk factors in minority populations. With an emphasis on metabolic disease, her research concentration is on diabete ...
... Associate Professor, Department of Biochemistry Dr. Allred is a molecular biologist with a research focus on understanding the genetic architecture of complex diseases and underlying risk factors in minority populations. With an emphasis on metabolic disease, her research concentration is on diabete ...
Level 2 Biology - No Brain Too Small
... Compare and contrast these two cell processes and their role in protein synthesis. In your answer: ...
... Compare and contrast these two cell processes and their role in protein synthesis. In your answer: ...
Layers of Strip Science
... electrons as current and calculates how much glucose it took to generate that much electricity. The meter displays that number on its screen. ...
... electrons as current and calculates how much glucose it took to generate that much electricity. The meter displays that number on its screen. ...
Protein Synthesis - No Brain Too Small
... Compare and contrast these two cell processes and their role in protein synthesis. In your answer: ...
... Compare and contrast these two cell processes and their role in protein synthesis. In your answer: ...
10. Keystone Assessment Anchor-
... Plastids A group of membrane‐bound organelles commonly found in photosynthetic organisms and mainly responsible for the synthesis and storage of food. Point Mutation A single‐base substitution causing the replacement of a single‐base nucleotide with another nucleotide (e.g., silent mutation, in whic ...
... Plastids A group of membrane‐bound organelles commonly found in photosynthetic organisms and mainly responsible for the synthesis and storage of food. Point Mutation A single‐base substitution causing the replacement of a single‐base nucleotide with another nucleotide (e.g., silent mutation, in whic ...
Cellular Respiration
... 1. Explain the interdependent relationship between autotrophs & heterotrophs in terms of chemical cycling and energy transfer (reactant, products, types of energy). -autotroph- organism that makes its own food; plant -heterotroph- organism that obtains food by eating other organisms; animal Autotrop ...
... 1. Explain the interdependent relationship between autotrophs & heterotrophs in terms of chemical cycling and energy transfer (reactant, products, types of energy). -autotroph- organism that makes its own food; plant -heterotroph- organism that obtains food by eating other organisms; animal Autotrop ...
Chapter 7
... Heterotrophs need food to live, they convert that food into usable energy (glucose) for the cell to make ATP ...
... Heterotrophs need food to live, they convert that food into usable energy (glucose) for the cell to make ATP ...
Biological vocabulary glossary, part 1
... A linear chain of amino acid residues is called polypeptide. A protein contains at least one polypeptide, but can contain more. The amino acids making up a polypeptide are bound together by covalent peptide bonds. Protein structure: Primary: The primary structure of a protein refers to the linear ...
... A linear chain of amino acid residues is called polypeptide. A protein contains at least one polypeptide, but can contain more. The amino acids making up a polypeptide are bound together by covalent peptide bonds. Protein structure: Primary: The primary structure of a protein refers to the linear ...
Vocabulary
... 2) oxygen is used and carbon dioxide is stored. 3) both oxygen and carbon dioxide are used. 4) oxygen is used and carbon dioxide is ...
... 2) oxygen is used and carbon dioxide is stored. 3) both oxygen and carbon dioxide are used. 4) oxygen is used and carbon dioxide is ...
(p. 522)
... 3. Disulfide bridges. These form between the side chains of two cysteine residues, and may hold distant parts of the chain close together. 4. Salt links. These form between oppositely-charged side chains, the charges being due to the COO¯ and -NH3+ groups. 5. Dispersion forces. Nonpolar side chains ...
... 3. Disulfide bridges. These form between the side chains of two cysteine residues, and may hold distant parts of the chain close together. 4. Salt links. These form between oppositely-charged side chains, the charges being due to the COO¯ and -NH3+ groups. 5. Dispersion forces. Nonpolar side chains ...
Document
... a frame shift mutation C. Transposable elements: DNA segments move spontaneously on chromosome which may inactivate the gene where it inserted itself ...
... a frame shift mutation C. Transposable elements: DNA segments move spontaneously on chromosome which may inactivate the gene where it inserted itself ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.