Chapter 8- An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism
... Cofactors: Supporting the Work of Enzymes Cofactors – metallic cofactors, such as iron, copper and zinc, they help to bring the active site and substrates together. Coenzymes – remove functional groups from one substrate molecule and add it to another substrate; i.e. they serve as transient carriers ...
... Cofactors: Supporting the Work of Enzymes Cofactors – metallic cofactors, such as iron, copper and zinc, they help to bring the active site and substrates together. Coenzymes – remove functional groups from one substrate molecule and add it to another substrate; i.e. they serve as transient carriers ...
Acid and Bases PPT
... Many reactions, such as the ones that occur in your body, work best at specific pH values. ...
... Many reactions, such as the ones that occur in your body, work best at specific pH values. ...
ENERGY FLOW WITHIN THE CELL (2) LEARNING OBJECTIVES
... CITRIC ACID CYCLE:- Also known as TCA cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle or Krebs cycle. It is a cyclic process. The cycle involves a sequence of compounds interrelated by oxidation – reduction and other reactions which finally produce CO2 and H2O. It is a final common pathway of breakdown or catabol ...
... CITRIC ACID CYCLE:- Also known as TCA cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle or Krebs cycle. It is a cyclic process. The cycle involves a sequence of compounds interrelated by oxidation – reduction and other reactions which finally produce CO2 and H2O. It is a final common pathway of breakdown or catabol ...
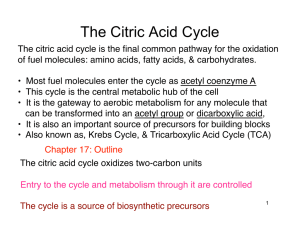
The Citric Acid Cycle
... The Citric Acid Cycle The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic ...
... The Citric Acid Cycle The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic ...
BIO 101: Transcription and Translation
... Theory: one gene codes for one polypeptide Some proteins are composed of a number of polypeptide chains. In this theory each chain has its own gene. However, eukaryotic genes are much more complex and this is not always the case! • Some genes control the expression of other genes • Some genes code f ...
... Theory: one gene codes for one polypeptide Some proteins are composed of a number of polypeptide chains. In this theory each chain has its own gene. However, eukaryotic genes are much more complex and this is not always the case! • Some genes control the expression of other genes • Some genes code f ...
BIO 101: Transcription and Translation
... Theory: one gene codes for one polypeptide Some proteins are composed of a number of polypeptide chains. In this theory each chain has its own gene. However, eukaryotic genes are much more complex and this is not always the case! • Some genes control the expression of other genes • Some genes code f ...
... Theory: one gene codes for one polypeptide Some proteins are composed of a number of polypeptide chains. In this theory each chain has its own gene. However, eukaryotic genes are much more complex and this is not always the case! • Some genes control the expression of other genes • Some genes code f ...
File
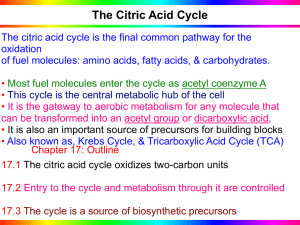
... The Citric Acid Cycle The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic meta ...
... The Citric Acid Cycle The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic meta ...
Metabolism of RBC
... (glucose transporter) facilitates transport of glucose in both directions • Glucose is metabolized mainly by glycolysis in erythrocytes. • Since erythrocytes lack mitochondria, the end product of glycolysis is lactic acid, which is released into the blood plasma. ...
... (glucose transporter) facilitates transport of glucose in both directions • Glucose is metabolized mainly by glycolysis in erythrocytes. • Since erythrocytes lack mitochondria, the end product of glycolysis is lactic acid, which is released into the blood plasma. ...
L2 Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Cells Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotes
... Backbone of the major macromolecules are made of carbon (valence of four), and offers many possibilities such as chains, branched chains, rings, double and triple bonds. ► These are the hydrocarbons, and various accessory groups can be attached. ...
... Backbone of the major macromolecules are made of carbon (valence of four), and offers many possibilities such as chains, branched chains, rings, double and triple bonds. ► These are the hydrocarbons, and various accessory groups can be attached. ...
Activity 6
... 6. If a person is sedentary after eating, so less ATP is used by their cells and it accumulates, how will that affect the equilibrium reaction described in Question 3 (Reaction 1). In that reaction, ...
... 6. If a person is sedentary after eating, so less ATP is used by their cells and it accumulates, how will that affect the equilibrium reaction described in Question 3 (Reaction 1). In that reaction, ...
Section 2
... The NITROGEN bases make up the rungs of the ladder and there are 4 (FOUR) of them; A always partners with T and C with G. The two nitrogen bases that make up each rung are often called BASE PAIRS. A section of three nitrogen bases represents a(n) AMINO ACID; there are 20 (TWENTY) of them possible. I ...
... The NITROGEN bases make up the rungs of the ladder and there are 4 (FOUR) of them; A always partners with T and C with G. The two nitrogen bases that make up each rung are often called BASE PAIRS. A section of three nitrogen bases represents a(n) AMINO ACID; there are 20 (TWENTY) of them possible. I ...
Peptide bonds, polypeptides and proteins printable pdf
... part of the polypeptide, is known as the primary structure of the polypeptide. We write the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide from its N- or amino terminus to its C- or carboxyl terminus, with the N-terminus to the left and the C-terminus to the right. A number of the amino acid R-groups are hydr ...
... part of the polypeptide, is known as the primary structure of the polypeptide. We write the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide from its N- or amino terminus to its C- or carboxyl terminus, with the N-terminus to the left and the C-terminus to the right. A number of the amino acid R-groups are hydr ...
glossary of terms - Personal Genome Diagnostics
... A chemical name for the molecule that carries genetic instructions in all living things. The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around one another to form a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to ...
... A chemical name for the molecule that carries genetic instructions in all living things. The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around one another to form a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to ...
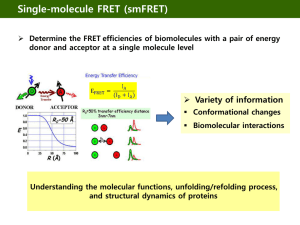
Single molecule analysis - Biomolecular Engineering Laboratory
... Large spectral separation between donor and acceptor emissions Similar quantum yields and detection efficiencies cf) Fluorescent proteins : low stability, photoinduced blinking Quantum dots : large size (>20 nm), lack of a monovalent ...
... Large spectral separation between donor and acceptor emissions Similar quantum yields and detection efficiencies cf) Fluorescent proteins : low stability, photoinduced blinking Quantum dots : large size (>20 nm), lack of a monovalent ...
ORGANIC ACIDS – Citric Acid Cycle (urine)
... or block. The metabolic block may be due to a nutrient deficiency, an inherited enzyme deficit, toxic build-up or drug effect. By evaluating organic acid levels and pinpointing the metabolic dysfunctions occurring at the cellular level, a comprehensive, customised treatment strategy can be tailor ma ...
... or block. The metabolic block may be due to a nutrient deficiency, an inherited enzyme deficit, toxic build-up or drug effect. By evaluating organic acid levels and pinpointing the metabolic dysfunctions occurring at the cellular level, a comprehensive, customised treatment strategy can be tailor ma ...
Amino Acids
... Negative nitrogen balance protein synthesis < protein degradation, as during illness, surgery. ...
... Negative nitrogen balance protein synthesis < protein degradation, as during illness, surgery. ...
File
... the lungs to pick up oxygen before pumping it through the heart and back round the body. Each side of the heart has an atrium and a ventricle. ◦ Blood enters the atria, they then contract pushing blood into the ventricles, which then contract pushing blood away from the heart. ...
... the lungs to pick up oxygen before pumping it through the heart and back round the body. Each side of the heart has an atrium and a ventricle. ◦ Blood enters the atria, they then contract pushing blood into the ventricles, which then contract pushing blood away from the heart. ...
B9AD
... The hypothesis in which the condition of Earth’s early atmosphere containing ammonia and water led to the formation of amino acids and eventually the development of life ...
... The hypothesis in which the condition of Earth’s early atmosphere containing ammonia and water led to the formation of amino acids and eventually the development of life ...
STUDY PROBLEMS AND CALCULATIONS: UV/VIS
... STUDY PROBLEMS AND CALCULATIONS: UV/VIS SPECTROSCOPY 1. Describe the general principle of colorimetric assays. 2. Which chemical groups are responsible for the absorption of ultra-violet radiation in proteins? Are proteins able to absorb visible light? 3. Which chemical groups absorb UV light in nuc ...
... STUDY PROBLEMS AND CALCULATIONS: UV/VIS SPECTROSCOPY 1. Describe the general principle of colorimetric assays. 2. Which chemical groups are responsible for the absorption of ultra-violet radiation in proteins? Are proteins able to absorb visible light? 3. Which chemical groups absorb UV light in nuc ...
STAAR Biology EOC Practice Test #1
... to produce different types of differentiated cells, such as liver cells, nerve cells, and heart muscle cells. Which of the following statements can best explain this result? A There are different genes in each of the individual stem cells that are cultured. B Environmental conditions influence which ...
... to produce different types of differentiated cells, such as liver cells, nerve cells, and heart muscle cells. Which of the following statements can best explain this result? A There are different genes in each of the individual stem cells that are cultured. B Environmental conditions influence which ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.