The extracellular matrix (ECM)
... -sulfated glycoamino glycans and a protein core -cover huge areas of extracellular matrix - eg. Aggrecan in cartilage and other connective tissues -contains hyaluronic acid + link protein + core protein ...
... -sulfated glycoamino glycans and a protein core -cover huge areas of extracellular matrix - eg. Aggrecan in cartilage and other connective tissues -contains hyaluronic acid + link protein + core protein ...
DNA and protein synthesis
... With only a very few exception, every living cell contains DNA. (Red blood cells are one such exception.) In prokaryotic cells there may be just one DNA molecule. In eukaryotic cells there are usually several. For example, humans have 46 DNA molecules in their cells (when they are not dividing), bec ...
... With only a very few exception, every living cell contains DNA. (Red blood cells are one such exception.) In prokaryotic cells there may be just one DNA molecule. In eukaryotic cells there are usually several. For example, humans have 46 DNA molecules in their cells (when they are not dividing), bec ...
colon cleanse colon cleanse advanced
... and d-calcium pantothenate, pyridoxal 5’-phosphate, and magnesium for acetylation.[2-7] 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) is provided as Quatrefolic®, which has greater stability, solubility, and bioavailability than calcium salt forms. Using science and patented technology, the formula’s pharmaceut ...
... and d-calcium pantothenate, pyridoxal 5’-phosphate, and magnesium for acetylation.[2-7] 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) is provided as Quatrefolic®, which has greater stability, solubility, and bioavailability than calcium salt forms. Using science and patented technology, the formula’s pharmaceut ...
NOTES: Ch 9, part 4
... The Versatility of Catabolism ● Catabolic pathways funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration ● Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates ● Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the Krebs cycle ● Fats are digested t ...
... The Versatility of Catabolism ● Catabolic pathways funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration ● Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates ● Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed glycolysis or the Krebs cycle ● Fats are digested t ...
Chapter 9 - H-W Science Website
... difficulty explaining the relationship of breathing and digestion to cellular respiration. Students may be confused by terms that have familiar, everyday meanings distinct from their biological definitions. The term respiration is particularly confusing, because it is an everyday term with two biolo ...
... difficulty explaining the relationship of breathing and digestion to cellular respiration. Students may be confused by terms that have familiar, everyday meanings distinct from their biological definitions. The term respiration is particularly confusing, because it is an everyday term with two biolo ...
Basic Cell Chemistry :
... molecule may not be recognized by an enzyme that recognizes its d- isomer. Another important aspect of sugar chemistry is whether it is an aldose or a ketose, based on the type of carbonyl group it carries. This is easiest to understand looking at the position of the carbonyl group in the linear str ...
... molecule may not be recognized by an enzyme that recognizes its d- isomer. Another important aspect of sugar chemistry is whether it is an aldose or a ketose, based on the type of carbonyl group it carries. This is easiest to understand looking at the position of the carbonyl group in the linear str ...
Some words to think about
... • Remember that a nucleotide is made up of three parts: 1. Phosphate group 2. 5 carbon sugar 3. Nitrogenous base • The nitrogenous base differs • A, T, C or G in DNA • A, U, C or G in RNA ...
... • Remember that a nucleotide is made up of three parts: 1. Phosphate group 2. 5 carbon sugar 3. Nitrogenous base • The nitrogenous base differs • A, T, C or G in DNA • A, U, C or G in RNA ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... a) Draw and explain the double helical structure of DNA. b) Discuss any one method to determine N-terminal of an amino acid. ...
... a) Draw and explain the double helical structure of DNA. b) Discuss any one method to determine N-terminal of an amino acid. ...
Unit 1 Topic 2: Genes and Health
... 5. Describe how membrane structure can be investigated practically, eg by the effect of alcohol concentration or temperature on membrane permeability. 6. Describe the properties of gas exchange surfaces in living organisms (large surface area to volume ratio, thickness of surface, difference in conc ...
... 5. Describe how membrane structure can be investigated practically, eg by the effect of alcohol concentration or temperature on membrane permeability. 6. Describe the properties of gas exchange surfaces in living organisms (large surface area to volume ratio, thickness of surface, difference in conc ...
Chapter 12
... Branched-chain alkanes are chains of carbon atoms with attached side chains or branches. These occur when the number of carbon atoms exceeds three (3), or for C4 compounds and above, and allow the formation of isomers, molecules with the same molecular formulas but different molecular structures. Al ...
... Branched-chain alkanes are chains of carbon atoms with attached side chains or branches. These occur when the number of carbon atoms exceeds three (3), or for C4 compounds and above, and allow the formation of isomers, molecules with the same molecular formulas but different molecular structures. Al ...
Fab Four – The Muscle-Building Supplements
... performance and enhancement through many different studies. Approximately 30 – 40 grams after a workout is the whey to go. ...
... performance and enhancement through many different studies. Approximately 30 – 40 grams after a workout is the whey to go. ...
ch3b FA11 - Cal State LA
... • Collection of biochemical rxns within a cell • Metabolic pathways – Sequence of rxns – Each step catalyzed by a different enzyme • Enzymes of a pathway often physically interact to form large complexes – Limits amount of diffusion needed at each step of the pathway – The product of the preceding s ...
... • Collection of biochemical rxns within a cell • Metabolic pathways – Sequence of rxns – Each step catalyzed by a different enzyme • Enzymes of a pathway often physically interact to form large complexes – Limits amount of diffusion needed at each step of the pathway – The product of the preceding s ...
7 - Coastalzone
... DNA is organized into chromosomes and is wound around a protein called histones. Read about how DNA is organized on page249. Chapter 14 RNA and protein synthesis Proteins you will remember are one of the important groups of organic compounds. Proteins are critical to cell life at various times, serv ...
... DNA is organized into chromosomes and is wound around a protein called histones. Read about how DNA is organized on page249. Chapter 14 RNA and protein synthesis Proteins you will remember are one of the important groups of organic compounds. Proteins are critical to cell life at various times, serv ...
Name: Protein Synthesis PRICE DNA DNA contains ______
... What are the 4 nitrogenous bases in RNA? ________________ DNA has __ strand(s), RNA has ____ strand(s). The type of RNA that transfers amino acids to ribosomes is _________________. The type of RNA that makes up the ribosome. __________________ The type of RNA that copies DNA’s code. _______________ ...
... What are the 4 nitrogenous bases in RNA? ________________ DNA has __ strand(s), RNA has ____ strand(s). The type of RNA that transfers amino acids to ribosomes is _________________. The type of RNA that makes up the ribosome. __________________ The type of RNA that copies DNA’s code. _______________ ...
Document
... • Describe the structure of DNA and RNA, including the importance of base pairing and hydrogen bonding • Explain how DNA replicates semi-conservatively during interphase • State that a polypeptide is coded for by a gene, and that a gene is a sequence of nucleotides that forms part of a DNA molecule ...
... • Describe the structure of DNA and RNA, including the importance of base pairing and hydrogen bonding • Explain how DNA replicates semi-conservatively during interphase • State that a polypeptide is coded for by a gene, and that a gene is a sequence of nucleotides that forms part of a DNA molecule ...
Transfer RNA and Protein Building Name_________________
... Rarely does the DNA code of instructions make an error in directing cells to form a protein. When it does, however, the error is called a ______________________. A mutation may result in a different type of protein. Hemoglobin is a large protein found in red blood cells. Hemoglobin carries _________ ...
... Rarely does the DNA code of instructions make an error in directing cells to form a protein. When it does, however, the error is called a ______________________. A mutation may result in a different type of protein. Hemoglobin is a large protein found in red blood cells. Hemoglobin carries _________ ...
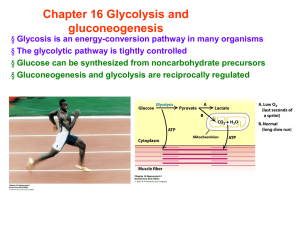
Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... inhibited by citrate [TCA cycle] and enhancing the inhibitory effect of ATP (not by pH of lactate) activated by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (F 2,6-BP) [Glc] [F 2,6-BP] glycolysis [feedforward stimulation] ...
... inhibited by citrate [TCA cycle] and enhancing the inhibitory effect of ATP (not by pH of lactate) activated by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (F 2,6-BP) [Glc] [F 2,6-BP] glycolysis [feedforward stimulation] ...
Nutritional Control of Cell Division in a Species of Erwinia
... were optimal for the elongation being obtained. Because these studies revealed that the. inorganic ammonium salt (NH4 CI) was not needed in the medium when organic nitrogen (DL aspartic acid) was present, the NH4CI was left out of the medium in future studies. Although inorganic nitrogen was not nee ...
... were optimal for the elongation being obtained. Because these studies revealed that the. inorganic ammonium salt (NH4 CI) was not needed in the medium when organic nitrogen (DL aspartic acid) was present, the NH4CI was left out of the medium in future studies. Although inorganic nitrogen was not nee ...
In the nucleus
... for Amino Acids. Codon- three base sequence of mRNA that codes for an amino acid. Anticodon- three base sequence of tRNA that is complimentary to a mRNA codon. Directs the sequence of Amino Acids. Types of Proteins made during Protein ...
... for Amino Acids. Codon- three base sequence of mRNA that codes for an amino acid. Anticodon- three base sequence of tRNA that is complimentary to a mRNA codon. Directs the sequence of Amino Acids. Types of Proteins made during Protein ...
Most molecules of human vasopressin have a net charge of _____
... 3. After taking this class, you decide you love biochemistry so much that you want to study it more in graduate school. So you end up being a TA for a class like 153A. On the first exam you grade a titration curve problem. The question asks the students to draw a pH titration curve for the following ...
... 3. After taking this class, you decide you love biochemistry so much that you want to study it more in graduate school. So you end up being a TA for a class like 153A. On the first exam you grade a titration curve problem. The question asks the students to draw a pH titration curve for the following ...
Cell Size and Shape
... In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is a metabolic pathway that forms part of the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water in order to generate energy. It is one of three metabolic pathways that are involved in fuel molecule catabolism and ATP production th ...
... In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is a metabolic pathway that forms part of the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water in order to generate energy. It is one of three metabolic pathways that are involved in fuel molecule catabolism and ATP production th ...
SUPPLEMENTARY DISCUSSION The applied Hi3 approach relies
... of the three most abundant peptides correlates with the abundance of the corresponding protein [1]. However, the ionization properties of specific peptides may influence the corresponding signal intensity during the mass spectrometric measurement. This may interfere with subsequent calculations of t ...
... of the three most abundant peptides correlates with the abundance of the corresponding protein [1]. However, the ionization properties of specific peptides may influence the corresponding signal intensity during the mass spectrometric measurement. This may interfere with subsequent calculations of t ...
ws bubbles new 1213 with answers
... 2. Transcribe the complementary strand into mRNA 3. Translate the mRNA into tRNA 4. Use Table A to identify the amino acid that corresponds to each anticodon 5. Use Table B to identify the protein coded for by that strand of DNA 6. Identify the kind of mutation that makes each pair of proteins diffe ...
... 2. Transcribe the complementary strand into mRNA 3. Translate the mRNA into tRNA 4. Use Table A to identify the amino acid that corresponds to each anticodon 5. Use Table B to identify the protein coded for by that strand of DNA 6. Identify the kind of mutation that makes each pair of proteins diffe ...
RESPIRATION: SYNTHESIS OF ATP
... moves from inside to outside of membrane as electrons move from NADH to O2. ! H+ moves back to the inside through an enzyme --ATP synthetase--that forms ATP + H2O from ...
... moves from inside to outside of membrane as electrons move from NADH to O2. ! H+ moves back to the inside through an enzyme --ATP synthetase--that forms ATP + H2O from ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.