DNA vs. RNA - WordPress.com
... RNA molecules are produced by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA required enzyme = RNA polymerase RNA polymerase binds to DNA (in nucleus) separates the DNA strands RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a ...
... RNA molecules are produced by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA required enzyme = RNA polymerase RNA polymerase binds to DNA (in nucleus) separates the DNA strands RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a ...
Chapter 3 The Same 20 Amino Acids Serve as Building Blocks for
... Serve as Building Blocks for All Proteins in Nature Homework 2 part 1: Ch. 5 problems 2, 9, 12, 16. ...
... Serve as Building Blocks for All Proteins in Nature Homework 2 part 1: Ch. 5 problems 2, 9, 12, 16. ...
Protein synthesis - Teachnet UK-home
... 1. An annotated flow chart showing the stages of protein synthesis. 2. Publish you work on your own website pages! (to go on school site ) Two sites below will help ...
... 1. An annotated flow chart showing the stages of protein synthesis. 2. Publish you work on your own website pages! (to go on school site ) Two sites below will help ...
citric acid cycle
... When a muscle contracts in an anaerobic medium, ie, one from which oxygen is excluded, glycogen disappears and lactate appears as the principal end product. When oxygen is admitted, aerobic recovery takes place and lactate disappears. However, if contraction occurs under aerobic conditions, lactate ...
... When a muscle contracts in an anaerobic medium, ie, one from which oxygen is excluded, glycogen disappears and lactate appears as the principal end product. When oxygen is admitted, aerobic recovery takes place and lactate disappears. However, if contraction occurs under aerobic conditions, lactate ...
13-2 PowerPoint
... Ribosomes use the sequence of codons in mRNA to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains. The decoding of an mRNA message into a protein is a process known as translation. ...
... Ribosomes use the sequence of codons in mRNA to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains. The decoding of an mRNA message into a protein is a process known as translation. ...
Chapter 3 Study Guide
... Honors Biology Study Guide Biochemistry – chapter 3 Know definition of organic and inorganic compounds Know organic molecules are found in living things Know the elements found in proteins, carbohydrates and lipids Know alcohols and hydroxyl groups Recognize and know examples of carbohydrates, prote ...
... Honors Biology Study Guide Biochemistry – chapter 3 Know definition of organic and inorganic compounds Know organic molecules are found in living things Know the elements found in proteins, carbohydrates and lipids Know alcohols and hydroxyl groups Recognize and know examples of carbohydrates, prote ...
DNA replication is molecular mechanism of
... Get in the habit of writing legibly, neatly, and in a NORMAL, MEDIUM-SIZED FONT. Please SCAN documents properly and upload them to Archie. Avoid taking photographs of or uploading dark, washed out, side ways, or upside down homework. Please use the scanner in the school’s media lab if one is not at ...
... Get in the habit of writing legibly, neatly, and in a NORMAL, MEDIUM-SIZED FONT. Please SCAN documents properly and upload them to Archie. Avoid taking photographs of or uploading dark, washed out, side ways, or upside down homework. Please use the scanner in the school’s media lab if one is not at ...
Review Packet CORRECT
... Acetyl CoA enters and is combined with other molecules to create ATP, NADH, FADH2 and CO2 a. What goes into the Krebs cycle? Acetyl CoA, NAD+, FADH+, ADP + P b. What comes out of the Krebs cycle? CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, ATP c. What is another name for the Krebs cycle? Citric Acid Cycle ...
... Acetyl CoA enters and is combined with other molecules to create ATP, NADH, FADH2 and CO2 a. What goes into the Krebs cycle? Acetyl CoA, NAD+, FADH+, ADP + P b. What comes out of the Krebs cycle? CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, ATP c. What is another name for the Krebs cycle? Citric Acid Cycle ...
Functional and structural relationship of Cst-II sialyltransferases to synthesize mono- and di-sialylated lipo-oligosaccharides derivatives
... Sialyltransferases are enzymes responsible for the transfer of sialic acid to the terminal nascent oligosaccharides. The sialyltransferase in Campylobacter jejuni (Cst-II) is capable of transferring sialic acid moiety from cytidine-5monophospho-N-acetyl-neuraminic acid (CMP-NeuAc) to the terminal po ...
... Sialyltransferases are enzymes responsible for the transfer of sialic acid to the terminal nascent oligosaccharides. The sialyltransferase in Campylobacter jejuni (Cst-II) is capable of transferring sialic acid moiety from cytidine-5monophospho-N-acetyl-neuraminic acid (CMP-NeuAc) to the terminal po ...
Practice Test 11 - U of L Class Index
... argon (which is then removed using a vacuum, leaving only the phosphorus in the flask). A separate 750 mL flask contains 3.15 bar of fluorine gas (at 19.65 °C). The two flasks are connected so that the two compounds can react, producing phosphorus trifluoride (a gas that is colourless and odourless, ...
... argon (which is then removed using a vacuum, leaving only the phosphorus in the flask). A separate 750 mL flask contains 3.15 bar of fluorine gas (at 19.65 °C). The two flasks are connected so that the two compounds can react, producing phosphorus trifluoride (a gas that is colourless and odourless, ...
Protein Structure Prediction
... Definition of -turn A -turn is defined by four consecutive residues i, i+1, i+2 and i+3 that do not form a helix and have a C(i)-C(i+3) distance less than 7Å and the turn lead to reversal in the protein chain. (Richardson, ...
... Definition of -turn A -turn is defined by four consecutive residues i, i+1, i+2 and i+3 that do not form a helix and have a C(i)-C(i+3) distance less than 7Å and the turn lead to reversal in the protein chain. (Richardson, ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism
... A. More than 60% of our foods are carbohydrates. Starch, glycogen, sucrose, lactose and cellulose Dr.Saba ...
... A. More than 60% of our foods are carbohydrates. Starch, glycogen, sucrose, lactose and cellulose Dr.Saba ...
Cell Transport Worksheet
... prevent dehydration. Therefore the high concentration of water in feces needs to be moved into the surrounding cells. Is this osmosis? Explain your answer. 5. When you are exercising, your muscle cells use sugar to produce energy. To provide more sugar to these muscle cells, your body releases a hor ...
... prevent dehydration. Therefore the high concentration of water in feces needs to be moved into the surrounding cells. Is this osmosis? Explain your answer. 5. When you are exercising, your muscle cells use sugar to produce energy. To provide more sugar to these muscle cells, your body releases a hor ...
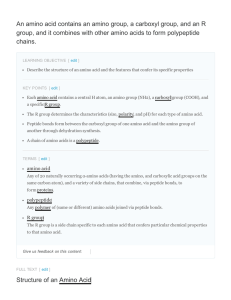
An amino acid contains an amino group, a carboxyl
... The resulting chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide chain. Each polypeptide has a free amino group at one end. This end is called the N terminal, or the amino terminal, and the other end has a free carboxyl group, also known as the C or carboxyl terminal. When reading or reporting the amino a ...
... The resulting chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide chain. Each polypeptide has a free amino group at one end. This end is called the N terminal, or the amino terminal, and the other end has a free carboxyl group, also known as the C or carboxyl terminal. When reading or reporting the amino a ...
Diseases of a Non-infectious Nature
... reduced or abnormal amino acid intake in fish/shrimp results in reduced biosynthesis of many vital substances: enzymes, hormones, certain pigments, and cofactors certain amino acids are necessary for oxidation and utilization of fats/carbo's amino acids also required for formation of purines, ...
... reduced or abnormal amino acid intake in fish/shrimp results in reduced biosynthesis of many vital substances: enzymes, hormones, certain pigments, and cofactors certain amino acids are necessary for oxidation and utilization of fats/carbo's amino acids also required for formation of purines, ...
NAME: : :______ Honors Biology Reading Guide – Chapter 6
... 45. Will enzymatic activity continue to increase with an increase in temperature? Explain. ...
... 45. Will enzymatic activity continue to increase with an increase in temperature? Explain. ...
Dear Notetaker:
... a. The mitochondria when citrate builds up i. If Krebs cycle has enough energy, it slows down, citrate builds up, and acetyl CoA can leave then. Regulatory step that is important..need to understand!! 7. How many moles of ATP are produced when one mole of glucose is completely oxidized to carbon dio ...
... a. The mitochondria when citrate builds up i. If Krebs cycle has enough energy, it slows down, citrate builds up, and acetyl CoA can leave then. Regulatory step that is important..need to understand!! 7. How many moles of ATP are produced when one mole of glucose is completely oxidized to carbon dio ...
BIOL 101 Rev Oct 2015 - Glendale Community College
... explain the basic mechanisms of gene regulation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. demonstrate proper use of laboratory equipment including the microscope, spectrophotometer, and micropipettes; demonstrate proficiency with data collection, analysis, and graphical representation. ...
... explain the basic mechanisms of gene regulation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. demonstrate proper use of laboratory equipment including the microscope, spectrophotometer, and micropipettes; demonstrate proficiency with data collection, analysis, and graphical representation. ...
Polymers and Amino Acids
... A peptide bond can be split by refluxing with hydrochloric acid. During hydrolysis, the water molecule adds across the peptide bond, forming a mixture of the two amino acids. ...
... A peptide bond can be split by refluxing with hydrochloric acid. During hydrolysis, the water molecule adds across the peptide bond, forming a mixture of the two amino acids. ...
Biology 123 SI-Dr. Raut`s Class Session 10
... that particular molecule is reduced. When the electrons move on to the next molecule, the first molecule is oxidized. Therefore the electron transport chain is a series of redox reaction, with oxygen getting oxidized at the end. When the electrons combine with ½ O2, two hydrogen atoms join ½ O2 to m ...
... that particular molecule is reduced. When the electrons move on to the next molecule, the first molecule is oxidized. Therefore the electron transport chain is a series of redox reaction, with oxygen getting oxidized at the end. When the electrons combine with ½ O2, two hydrogen atoms join ½ O2 to m ...
Flower`n`Fruit
... Aspartic acid: This is a source of nitrogen for plants as it is involved in numerous metabolic processes. Alanine: This facilitates the synthesis of chlorophyll, leading to greater photosynthetic working potential. It is involved in plant hormone metabolism. Arginine: This stimulates photosynthesis ...
... Aspartic acid: This is a source of nitrogen for plants as it is involved in numerous metabolic processes. Alanine: This facilitates the synthesis of chlorophyll, leading to greater photosynthetic working potential. It is involved in plant hormone metabolism. Arginine: This stimulates photosynthesis ...
Chem 150 - Fall 2015 Exam I
... d. Water (H2O) has a very high melting point compared to other molecules of similar size and composition, e.g., H2S, CH4, NH3, HF, which unlike water are all gases at room temperature. Explain why water stands out among this group ...
... d. Water (H2O) has a very high melting point compared to other molecules of similar size and composition, e.g., H2S, CH4, NH3, HF, which unlike water are all gases at room temperature. Explain why water stands out among this group ...
22. Think of two different proteins: both are enzymes. a) What
... Phosphorylation/Dephosphorylation: requires donor of phosphate group (ATP=P1+energy) d) What is the main difference between the mechanism in c) and allosteric control? Two enzymes are needed to regulate for covalent binding in phosphorylation/de. and no enzymes are used for non covalent allosteric b ...
... Phosphorylation/Dephosphorylation: requires donor of phosphate group (ATP=P1+energy) d) What is the main difference between the mechanism in c) and allosteric control? Two enzymes are needed to regulate for covalent binding in phosphorylation/de. and no enzymes are used for non covalent allosteric b ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.